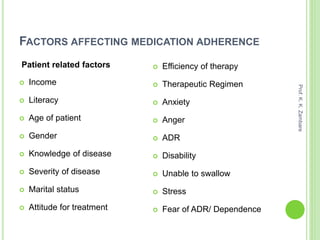
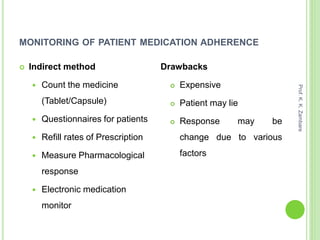
The document discusses medication adherence, defining it as the extent to which patients follow prescribed treatments. It highlights causes and consequences of non-adherence, including patient-related, social, disease-related, and healthcare provider-related factors. Additionally, it outlines the pharmacist's role in enhancing adherence and monitors methods while noting their benefits and drawbacks.