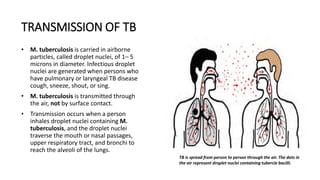
Tuberculosis (TB) is an airborne disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, primarily affecting the lungs but potentially impacting other organs. Transmission occurs through inhalation of droplet nuclei, and symptoms can include a persistent cough, fever, and weight loss. Treatment involves a lengthy course of multiple antibiotics, and prevention relies on vaccination, early detection, and treatment of active cases.