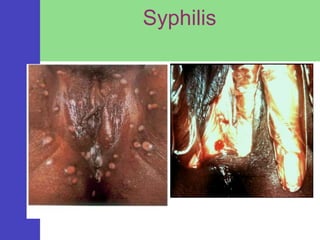
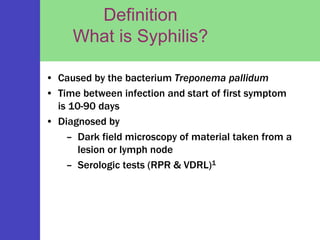
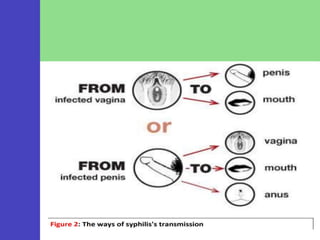
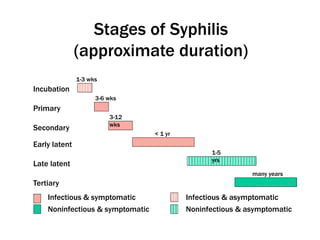
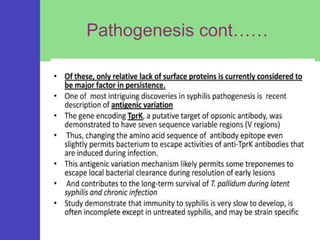
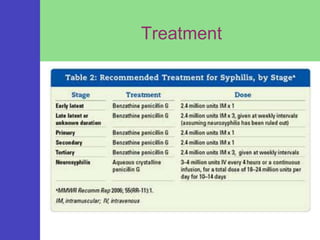
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, which can be transmitted through sexual contact or from mother to child during pregnancy. The disease progresses through four stages with varying symptoms, including painless sores, rashes, and potential serious complications if untreated. Although it is a preventable and treatable disease, prompt diagnosis and intervention are crucial to avoid severe health outcomes.