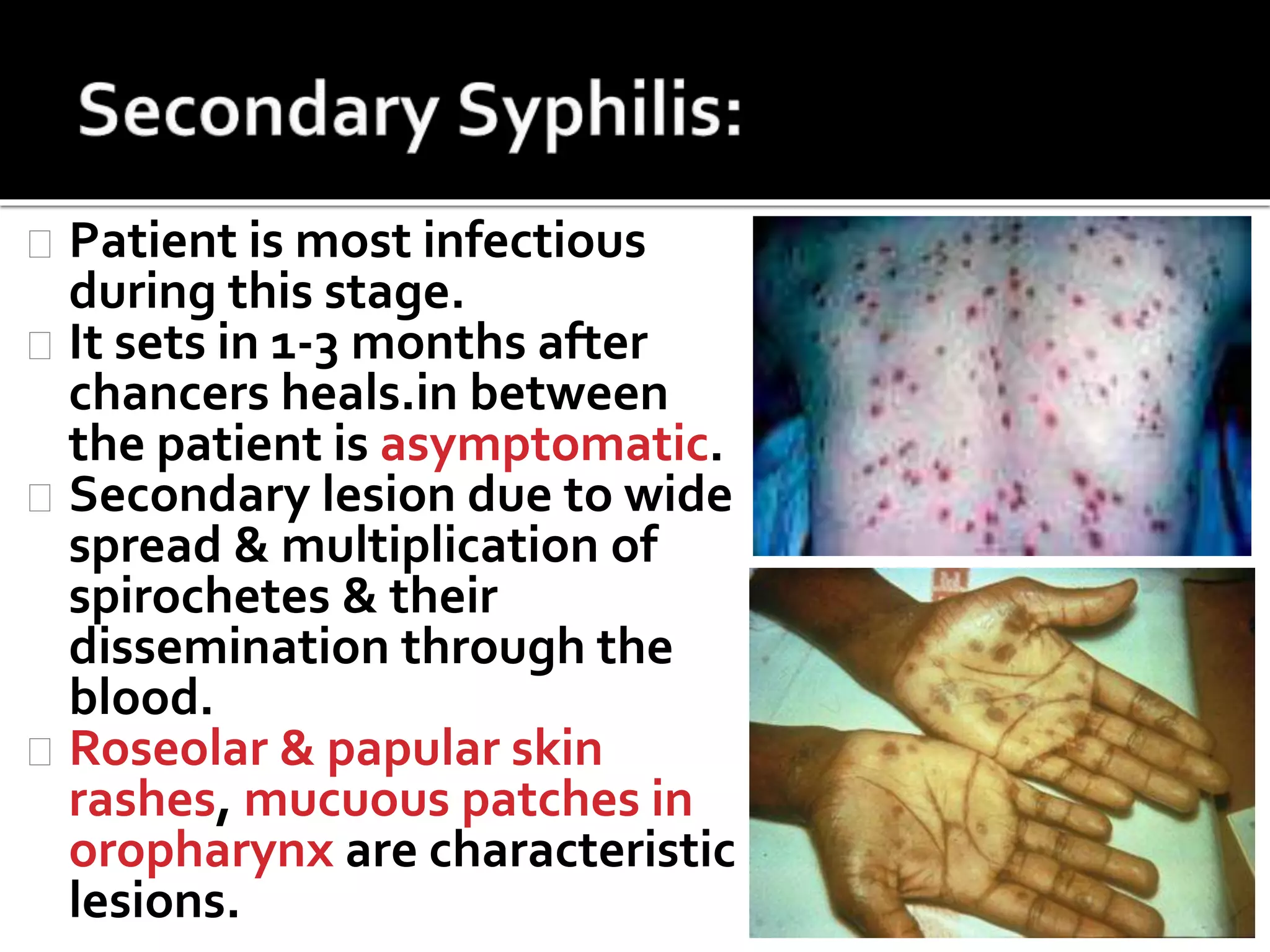
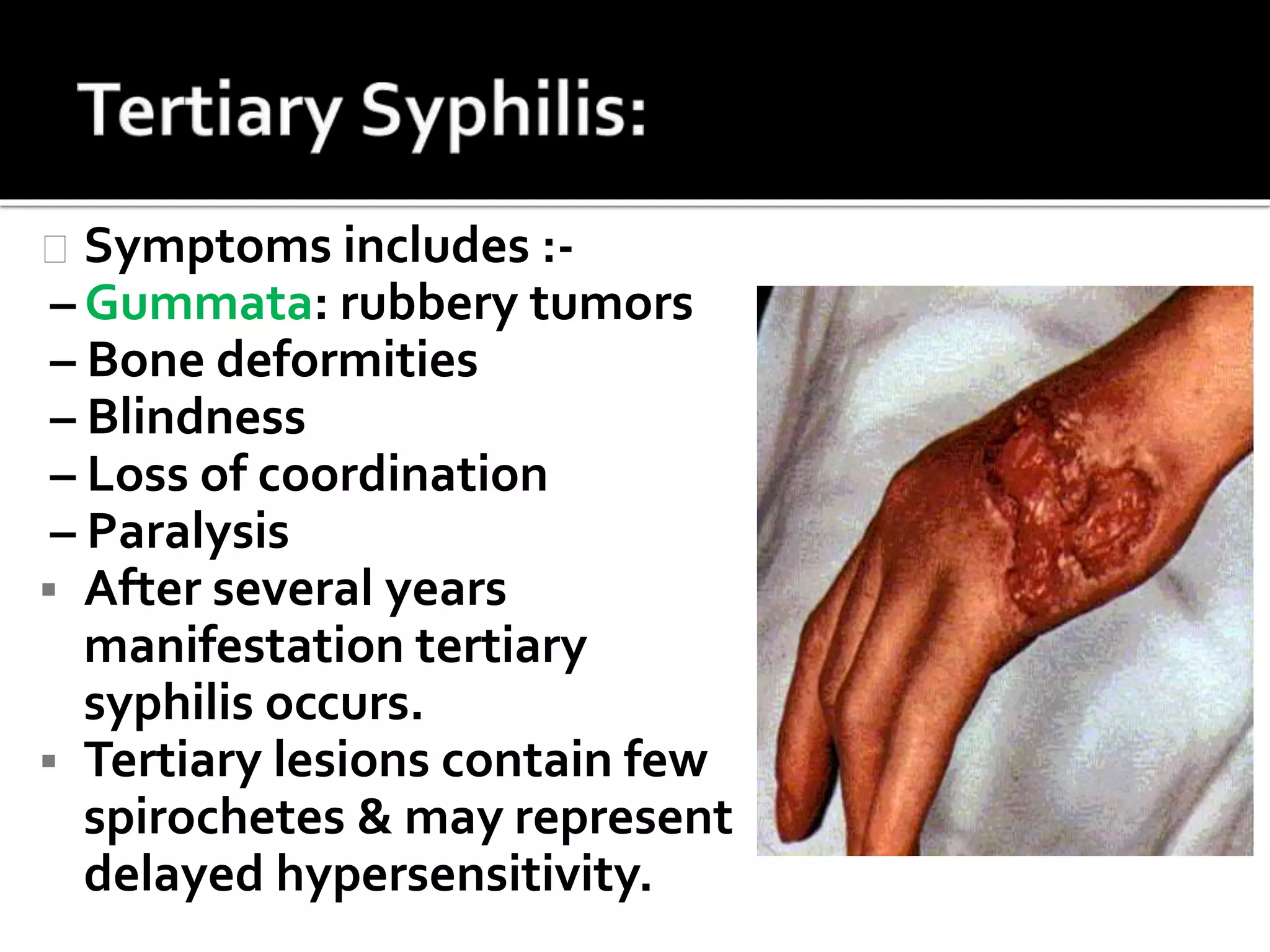
Treponema pallidum is a spirochete bacterium that causes syphilis. It is thin and motile, seen under darkfield microscopy. Syphilis is transmitted sexually or from mother to fetus. It has three stages - primary, secondary, and tertiary - with characteristic lesions developing at each stage like chancres. Diagnosis involves serological tests detecting antibodies like VDRL and RPR. Penicillin is the treatment of choice.