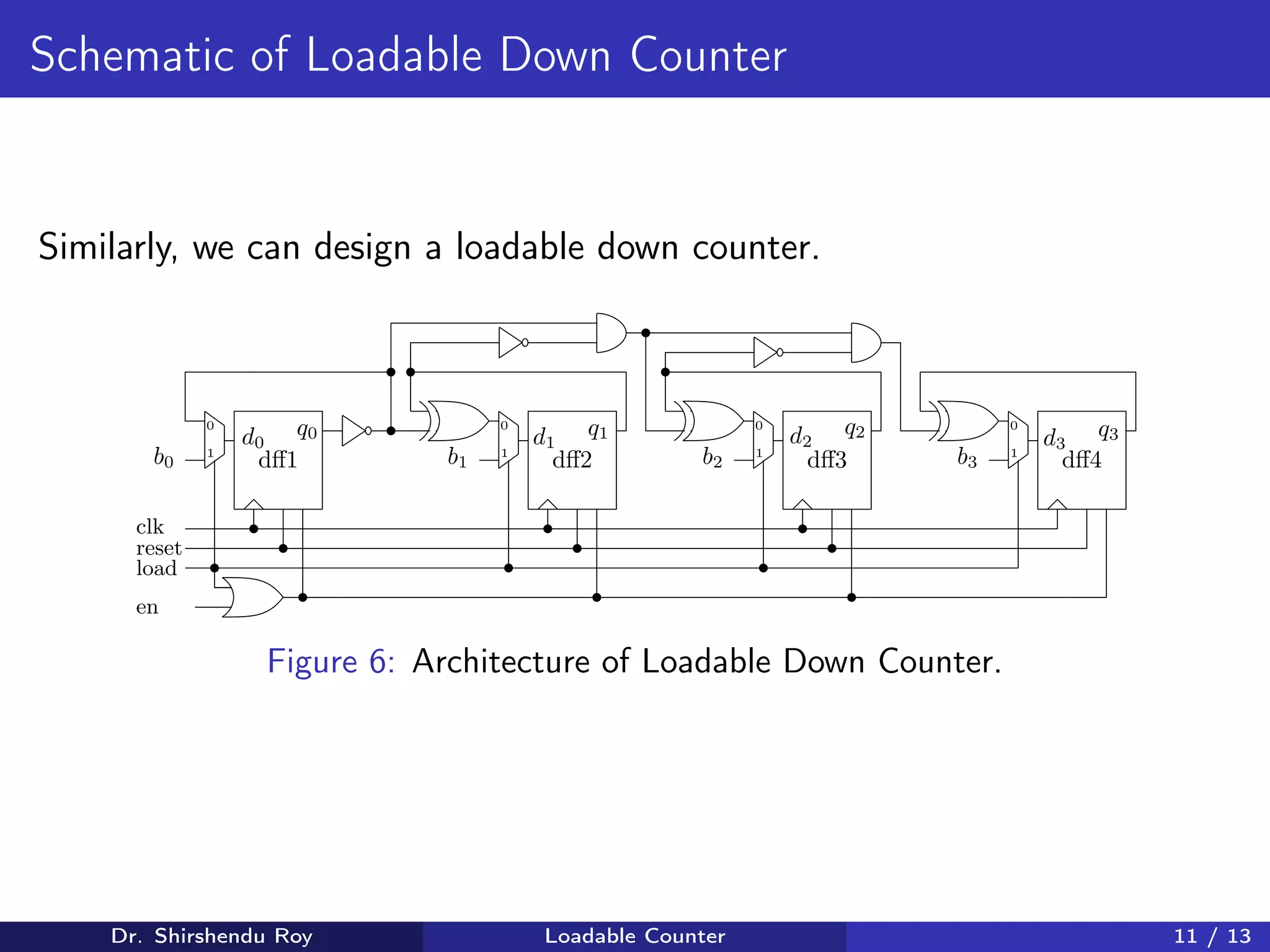
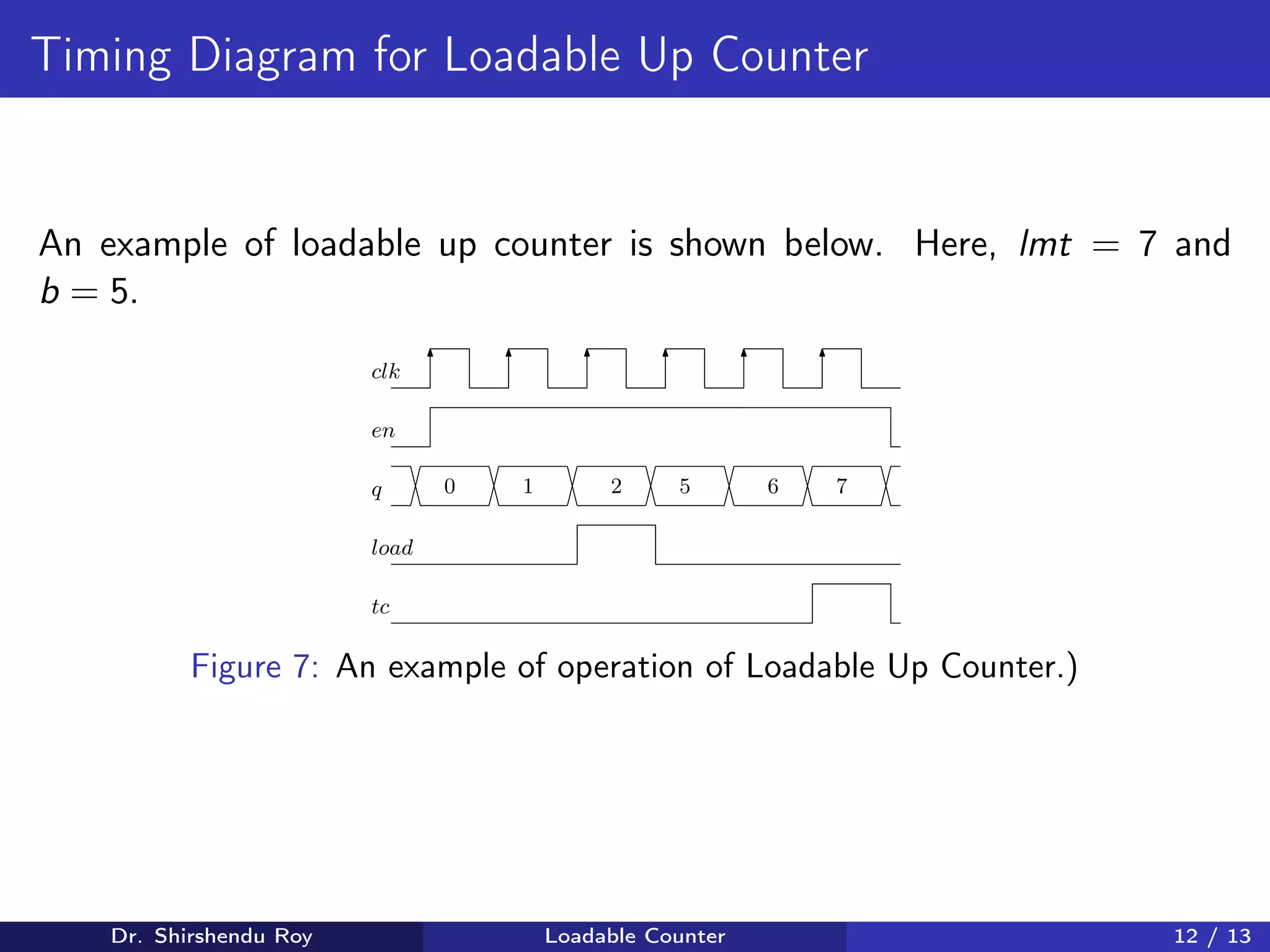
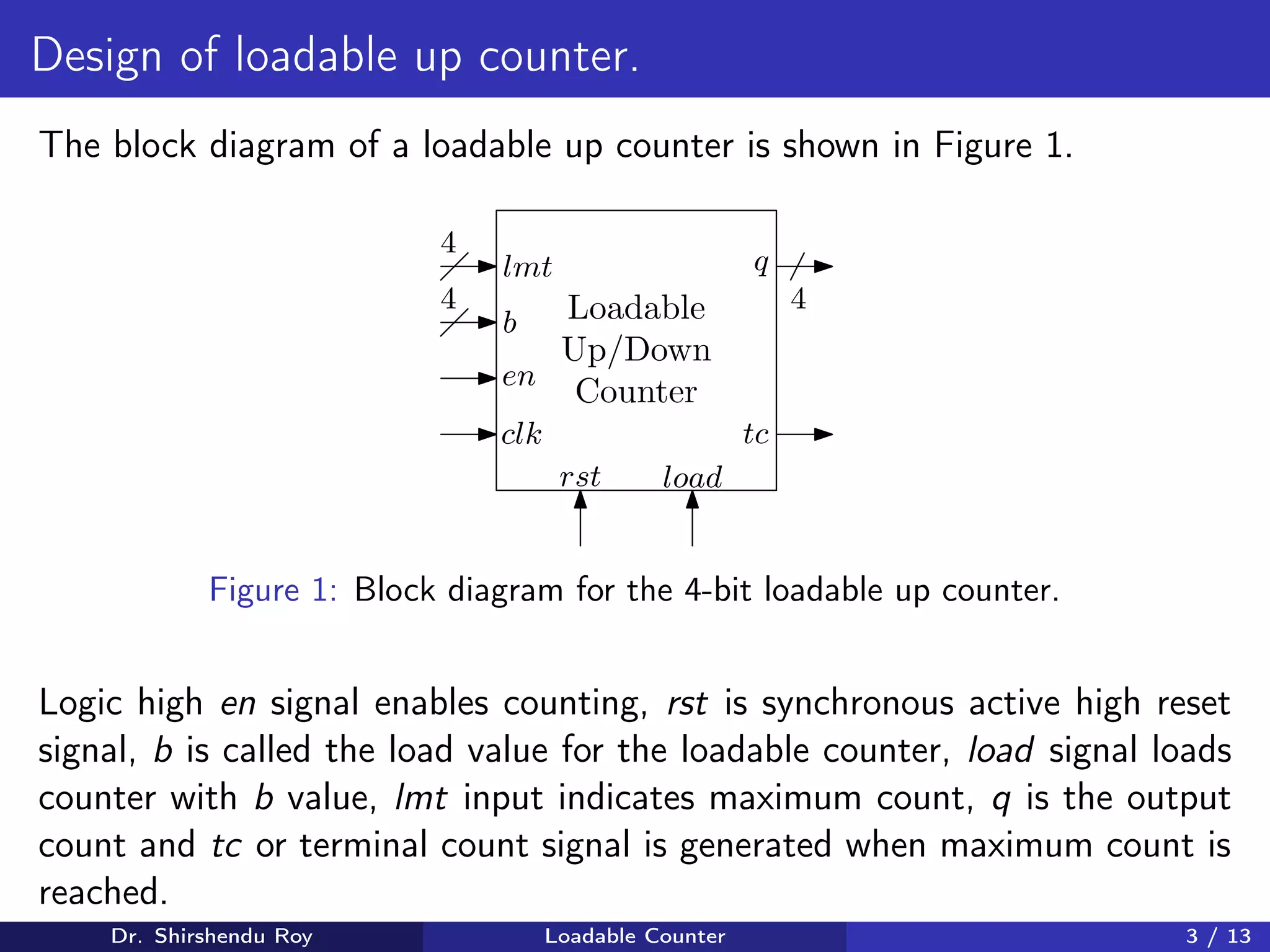
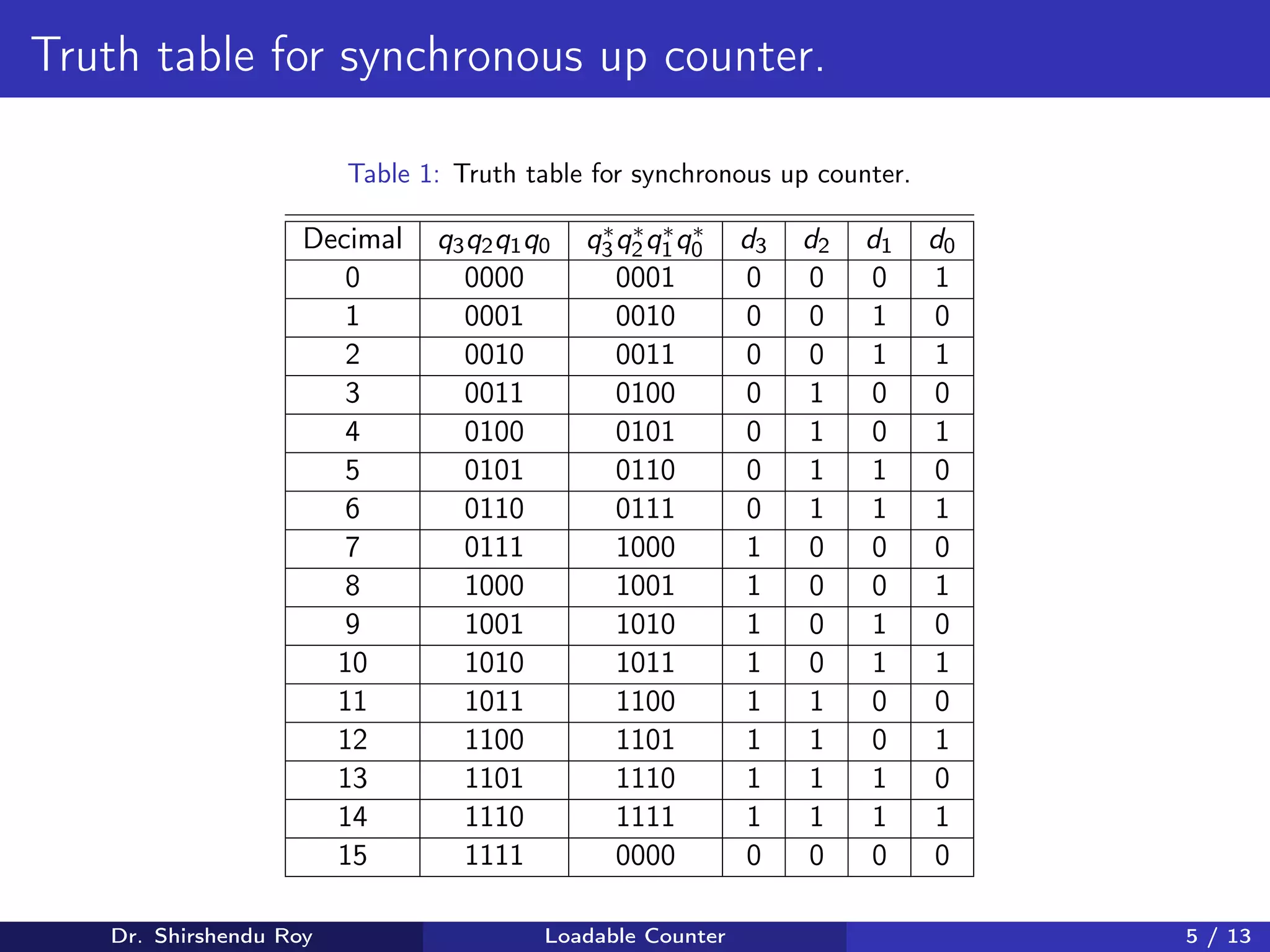
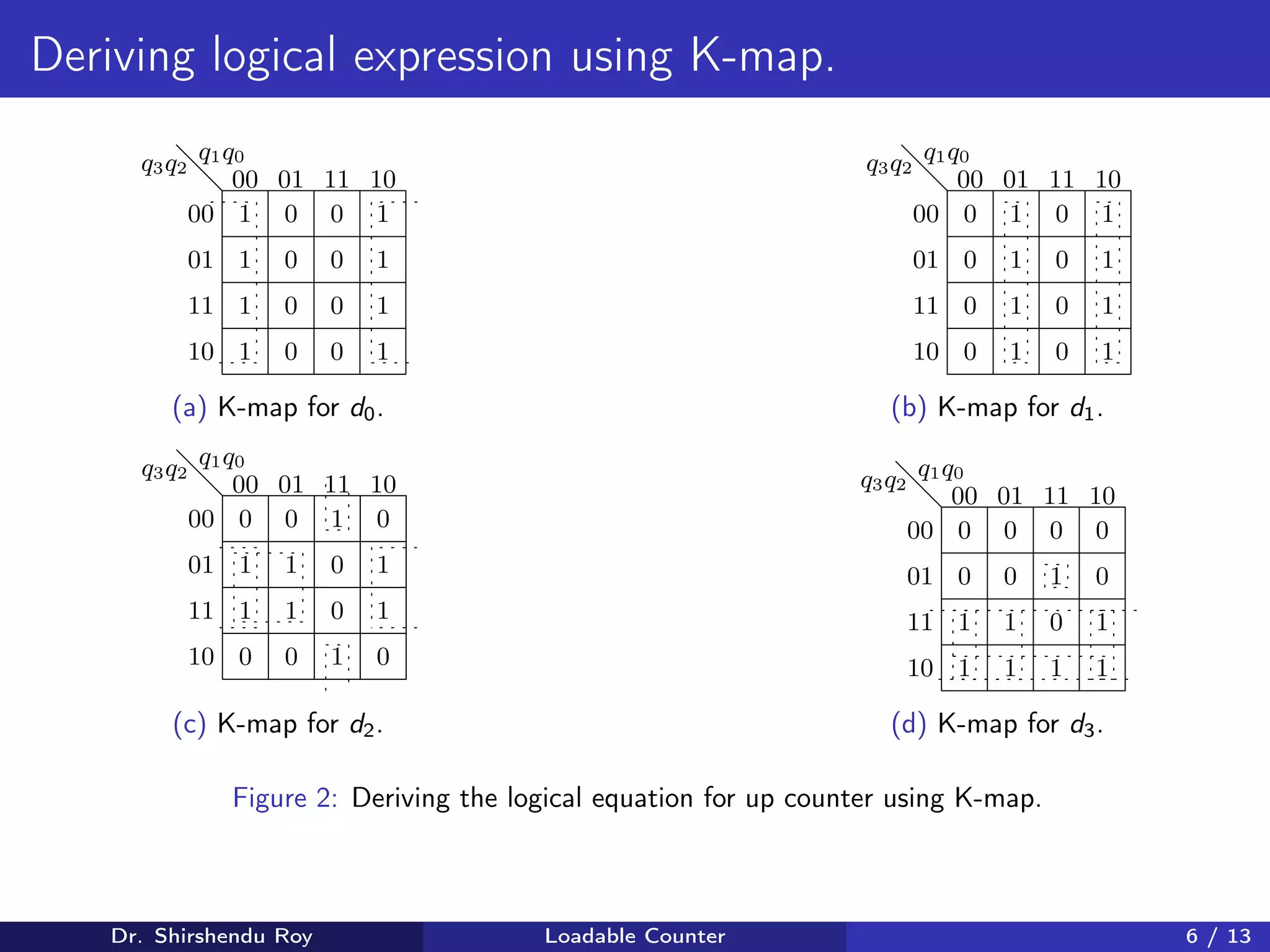
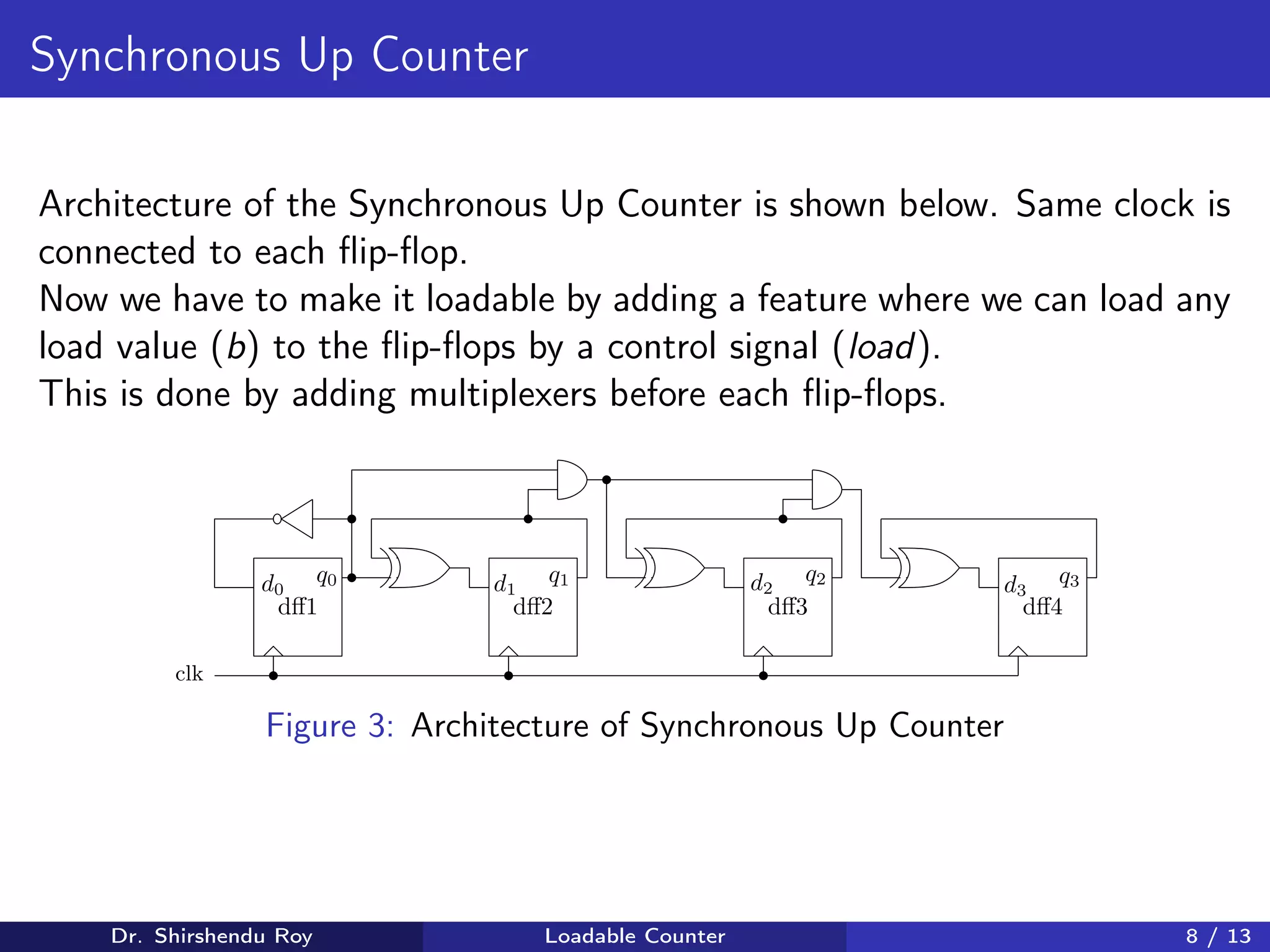
The document presents the design of a synchronous loadable up and down counter, detailing its applications in counting and memory block activation. It includes the design procedure, truth tables, Karnaugh maps, and Boolean expressions for both up and down counting. Additionally, it provides schematics and examples to demonstrate how the loadable counter functions with control signals and architectural features.

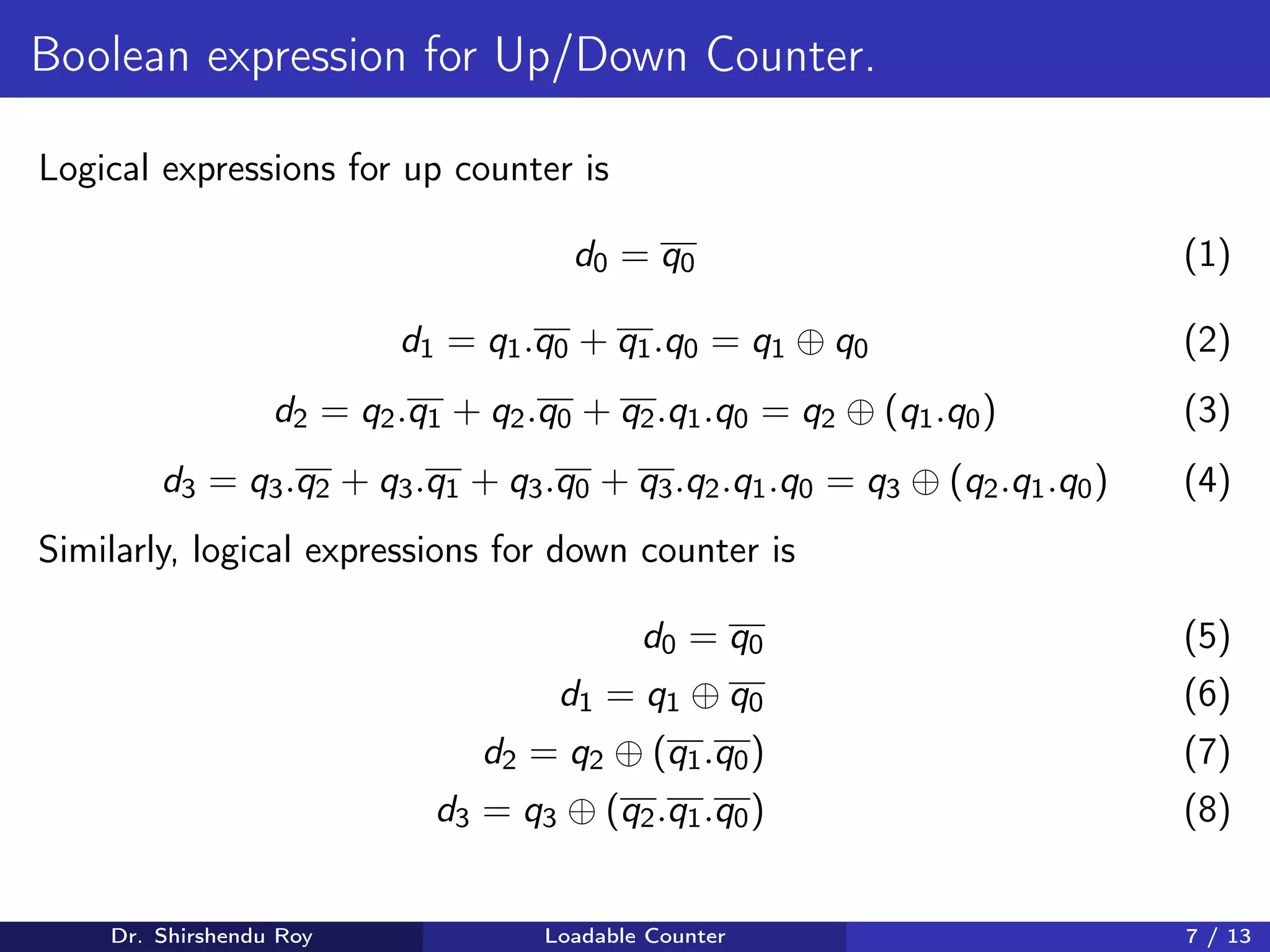
![Schematic of Loadable Up Counter
0
1
d0
0
1
0
1
0
1
dff1 dff2 dff3 dff4
q0 d1
q1 d2
q2 d3
q3
b0 b1 b2 b3
clk
reset
load
en
Equality
Comparator
q[3 : 0]
lmt[3 : 0]
tc
Figure 4: Schematic of Loadable Up Counter
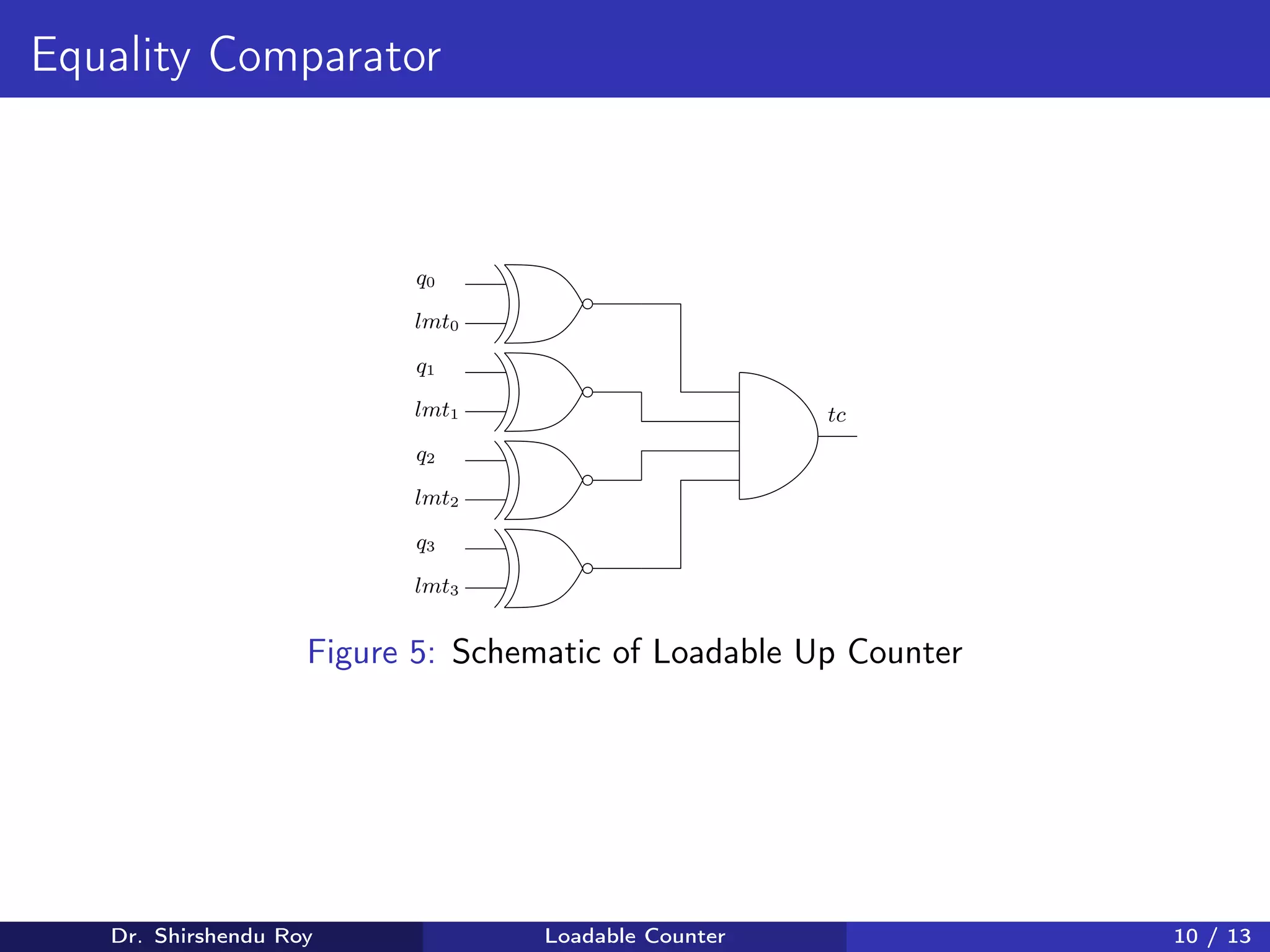
Whenever the load signal is high input b is passed to the flip-flops and
whenever the counter reaches lmt value a tc signal is generated by a equality
comparator.
Dr. Shirshendu Roy Loadable Counter 9 / 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/loadablecounter-211207175529/75/Synchronous-Loadable-Up-and-Down-Counter-9-2048.jpg)