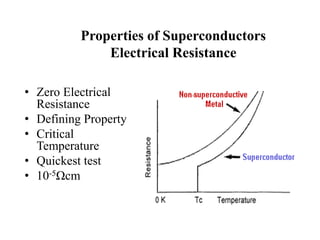
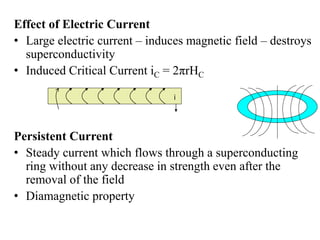
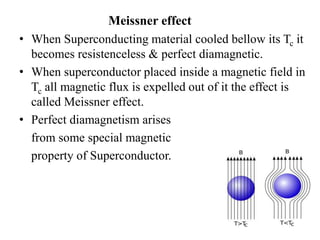
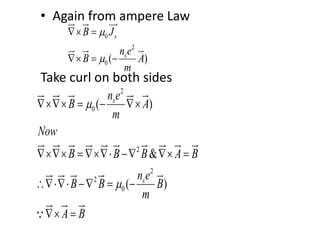
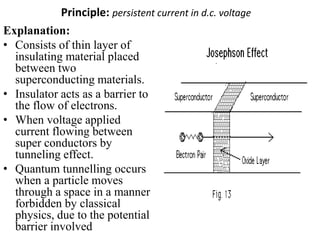
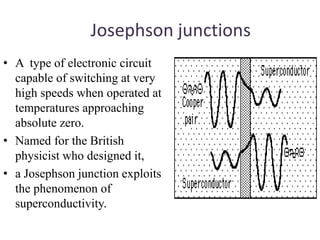
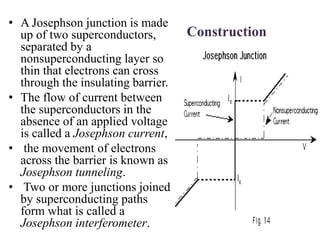
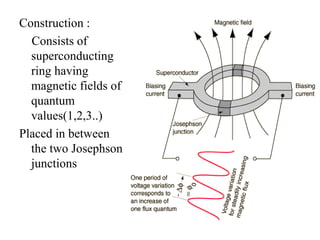
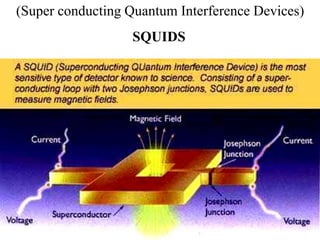
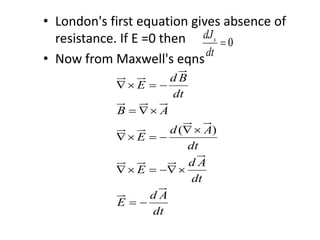1. Superconductivity occurs when the electrical resistance of a material drops to zero below a certain critical temperature. In certain metals such as lead, the electrical resistance becomes zero at temperatures below 7.2K.
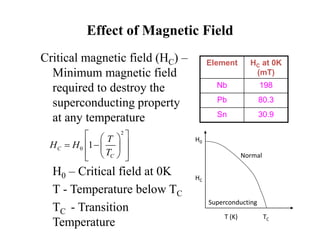
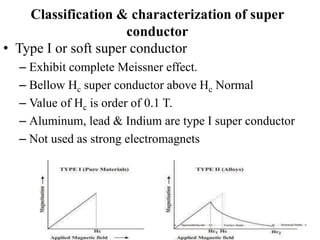
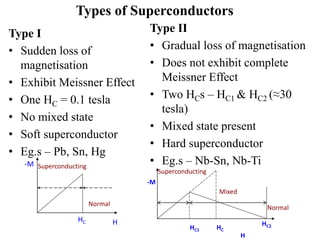
2. There are two types of superconductors - Type I superconductors exhibit an abrupt loss of magnetization above a critical field strength, while Type II superconductors show a more gradual loss of magnetization above two critical field strengths.
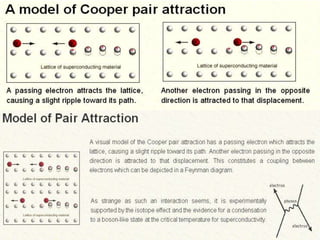
3. The BCS theory developed by Bardeen, Cooper, and Schrieffer in 1957 explains superconductivity as arising from electrons forming pairs (Cooper pairs) that condense into the same quantum state. This pairing is mediated by lattice vibrations