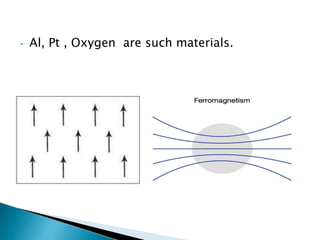
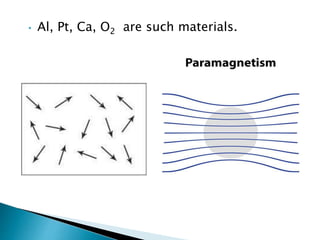
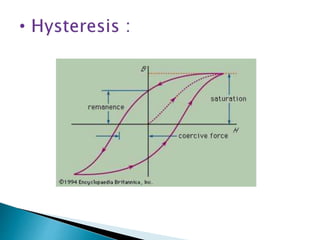
This document defines and classifies different types of magnetic materials. It discusses ferromagnetic, paramagnetic, and diamagnetic materials, and how their properties including permeability and susceptibility differ. It also defines magnetically soft and hard materials, providing examples and characteristics of each. Finally, it outlines some applications of these magnetic materials, such as their use in recording devices, magnetic levitation, electromagnets, and permanent magnets.