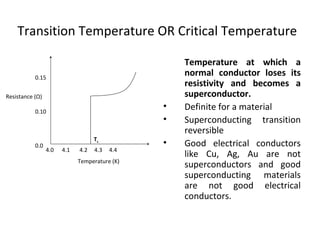
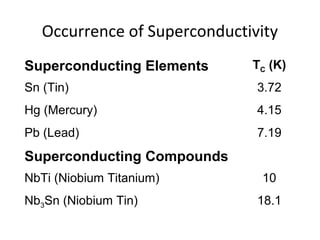
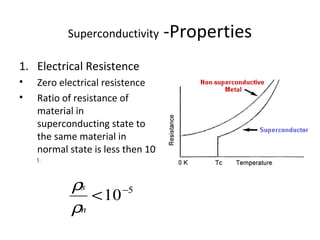
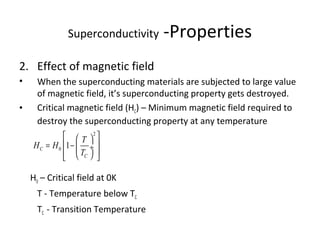
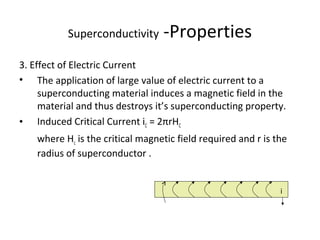
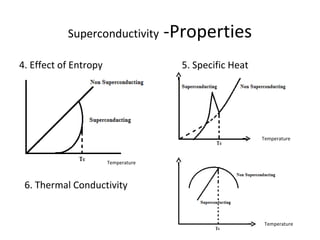
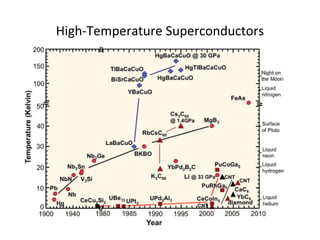
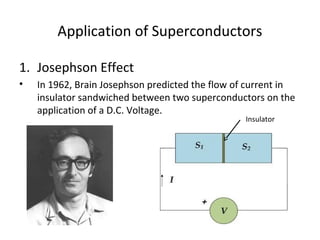
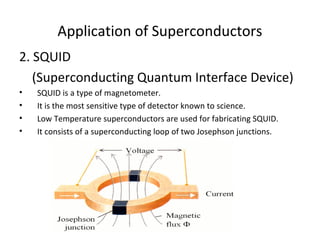
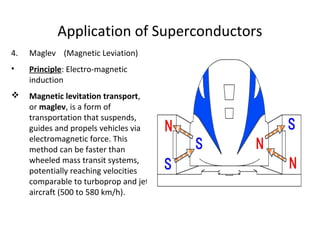
The document discusses superconductivity, starting with its discovery by Kamerlingh Onnes and explaining key concepts such as transition temperature, electrical resistance, and the effects of magnetic fields and electric currents on superconductors. It details types of superconductors, including Type I and Type II, along with high-temperature superconductors and their applications like the Josephson effect, SQUID devices, cryotron switches, and maglev transportation systems. The document emphasizes the unique properties and advantages of superconductors in technological applications.