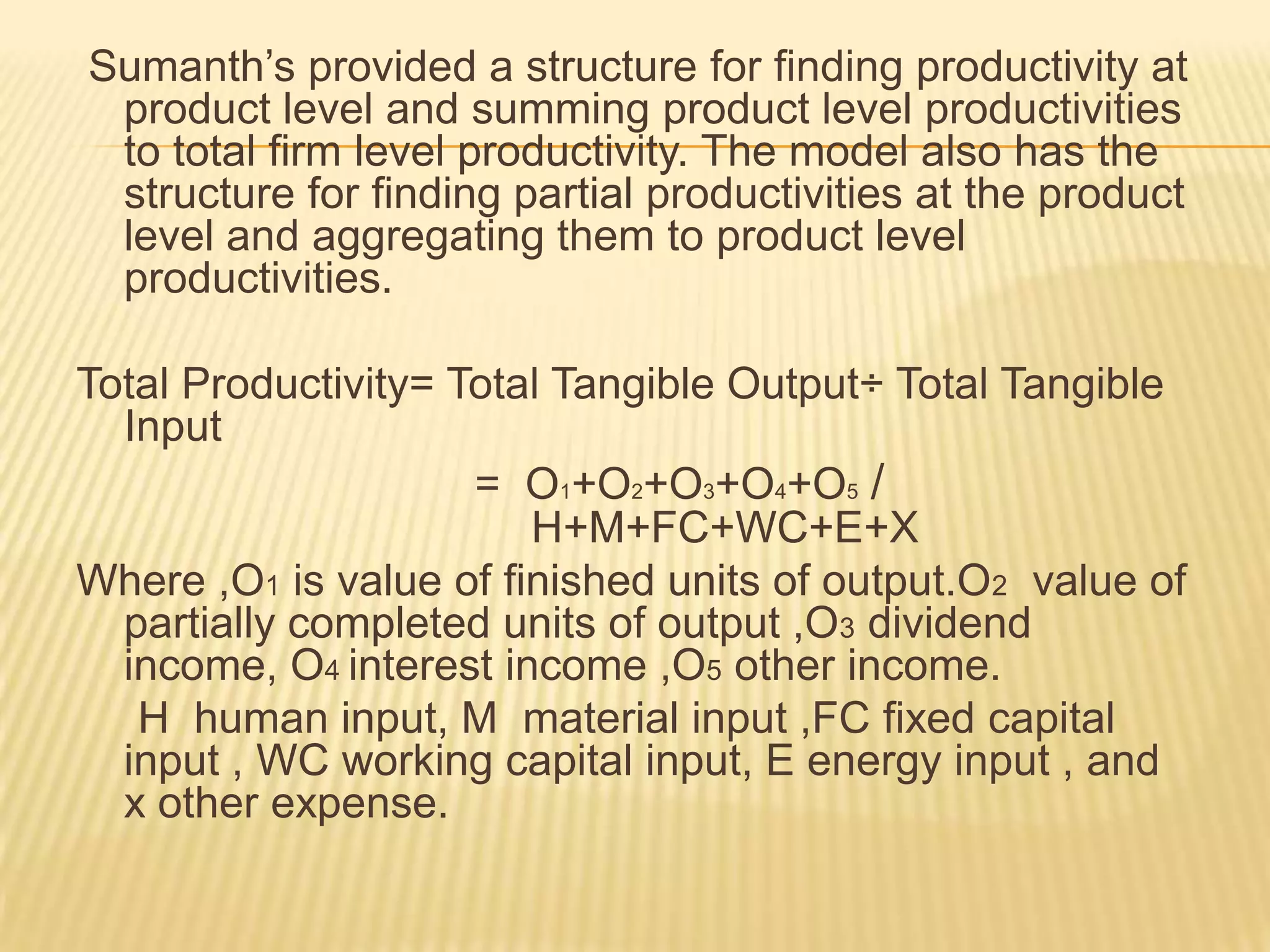
Dr. David J. Sumanth developed a Total Productivity Model in 1979 that considers five key inputs: human, material, capital, energy, and other expenses. The model defines Total Productivity as Total Tangible Output divided by Total Tangible Input. Total tangible output includes the value of finished units produced, partial units produced, dividends, interests, and other incomes. Total tangible inputs include human, capital, materials, energy, and other expenses. Sumanth's model provides a structure for calculating productivity at the product level and aggregating to the firm level, as well as partial productivities at the product level. It defines productivity ratios that consider both outputs and inputs.