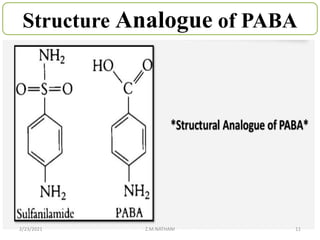
- Sulfonamide is a class of antibacterial medications derived from p-aminobenzene sulfonamide. They act as competitive inhibitors of p-amino benzoic acid in the bacterial folic acid synthesis pathway.
- Sulfonamide was the first antibacterial discovered in the 1930s and ushered in the "sulfur drug era". It works by interfering with the production of folic acid which is essential for bacterial cell division and growth.
- Cotrimoxazole is a fixed-dose combination of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim that provides broad-spectrum antibacterial activity. It is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and Pneumoc