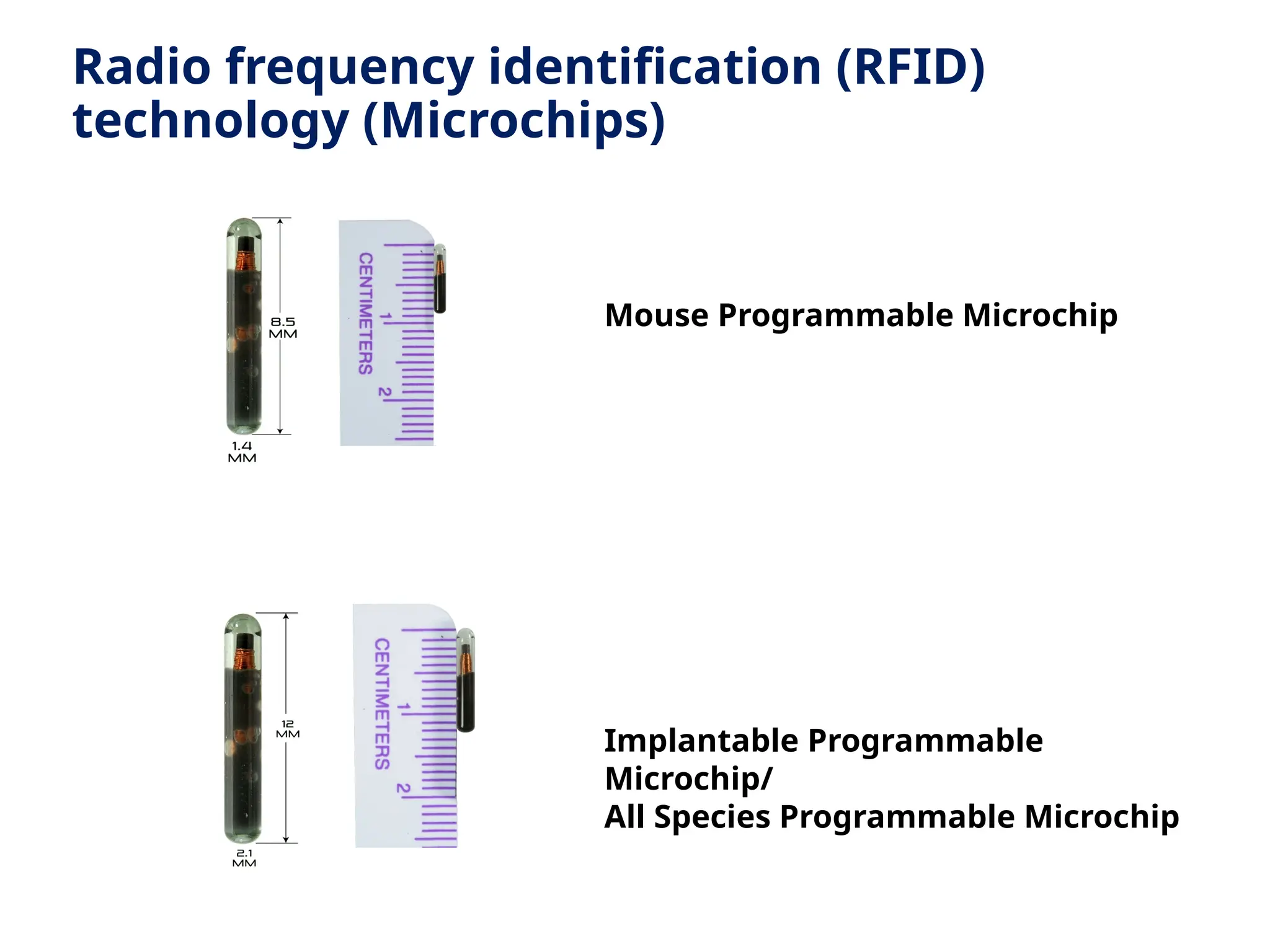
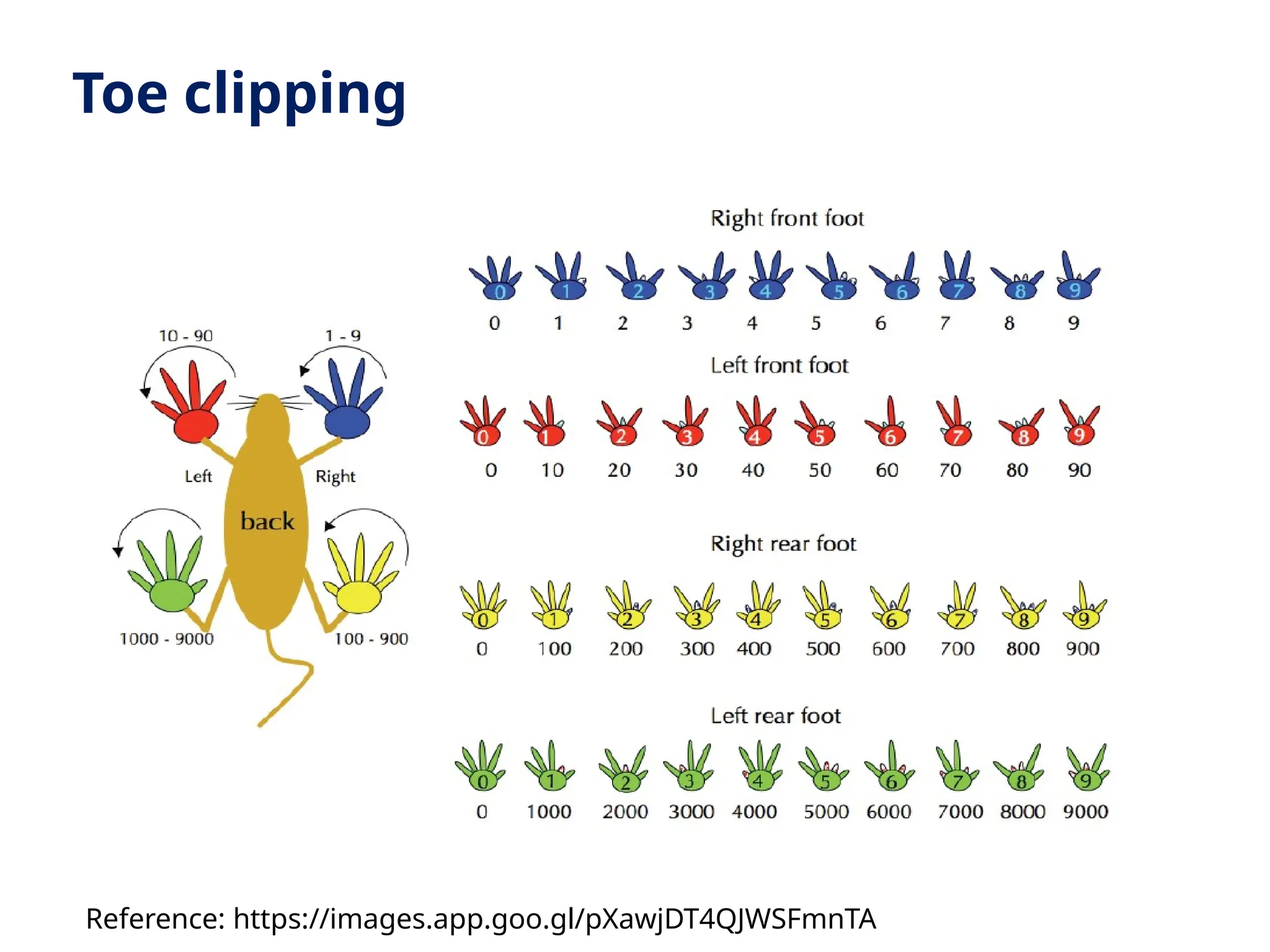
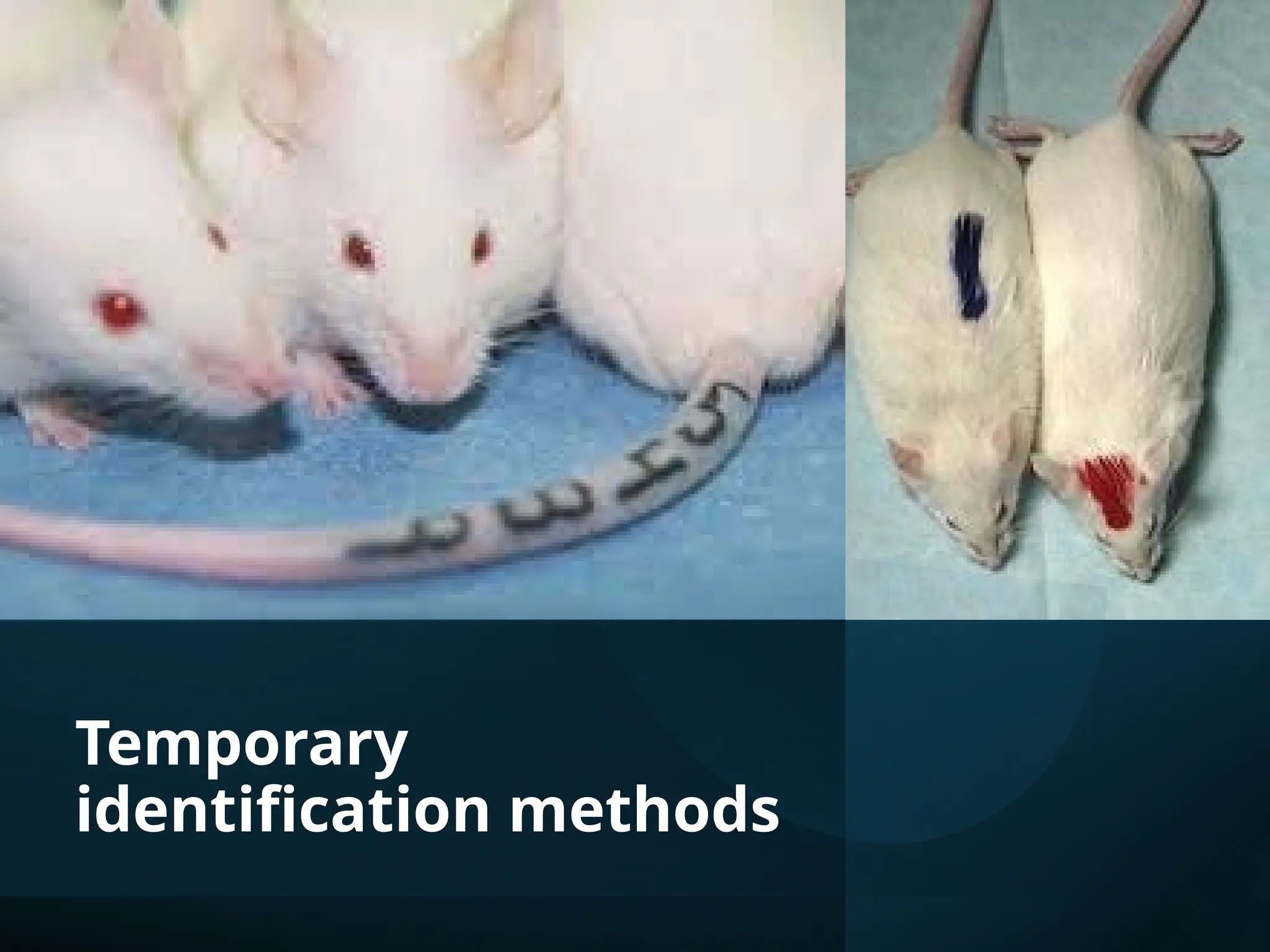
The document discusses the importance of laboratory animal identification for research purposes, focusing on various methods of identification including permanent and temporary techniques. It outlines the benefits of identification for tracking, compliance with regulations, health monitoring, and inventory management. Additionally, it examines specific methods such as ear notching, branding, microchipping, and the ethical considerations associated with animal welfare.