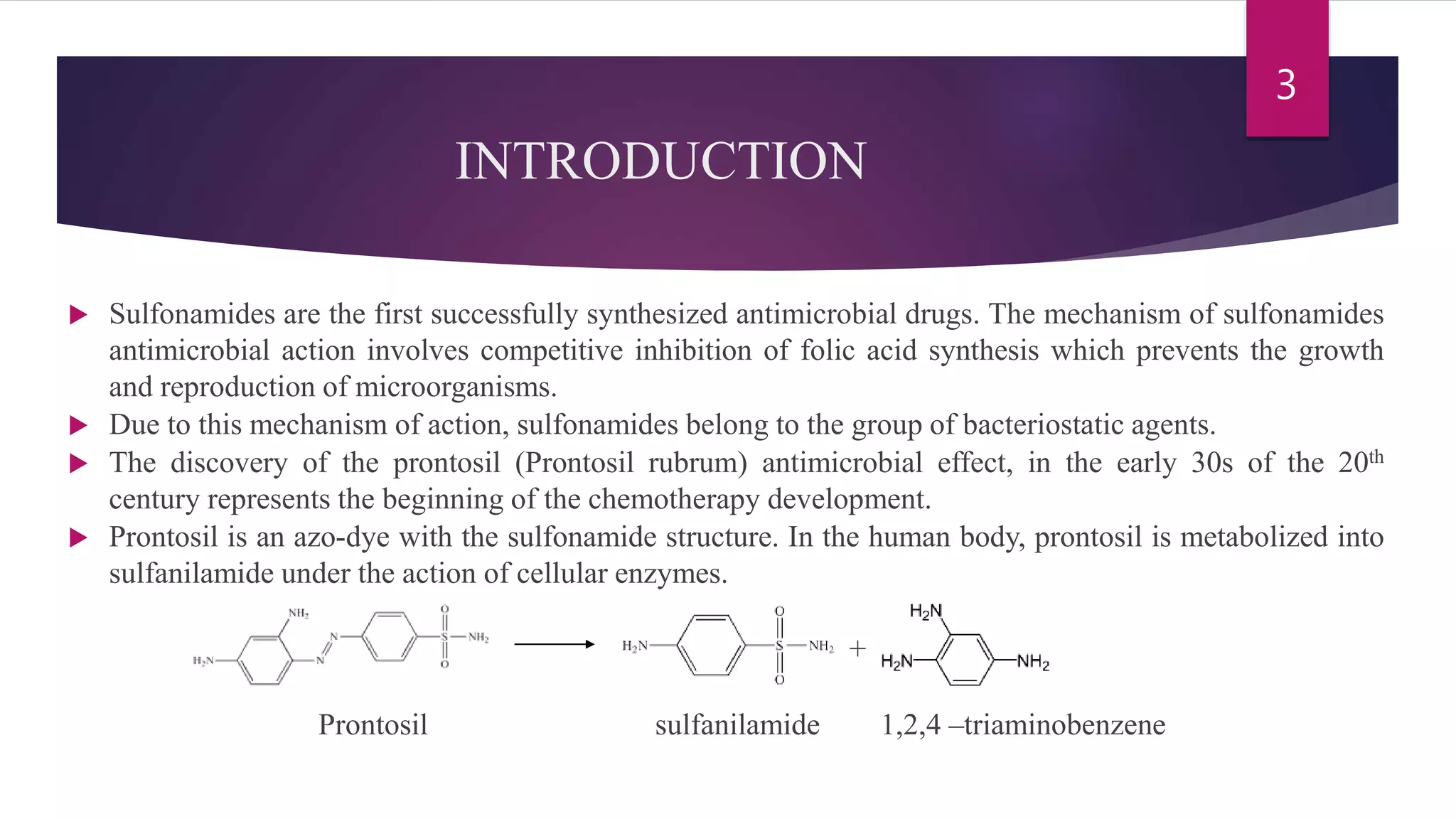
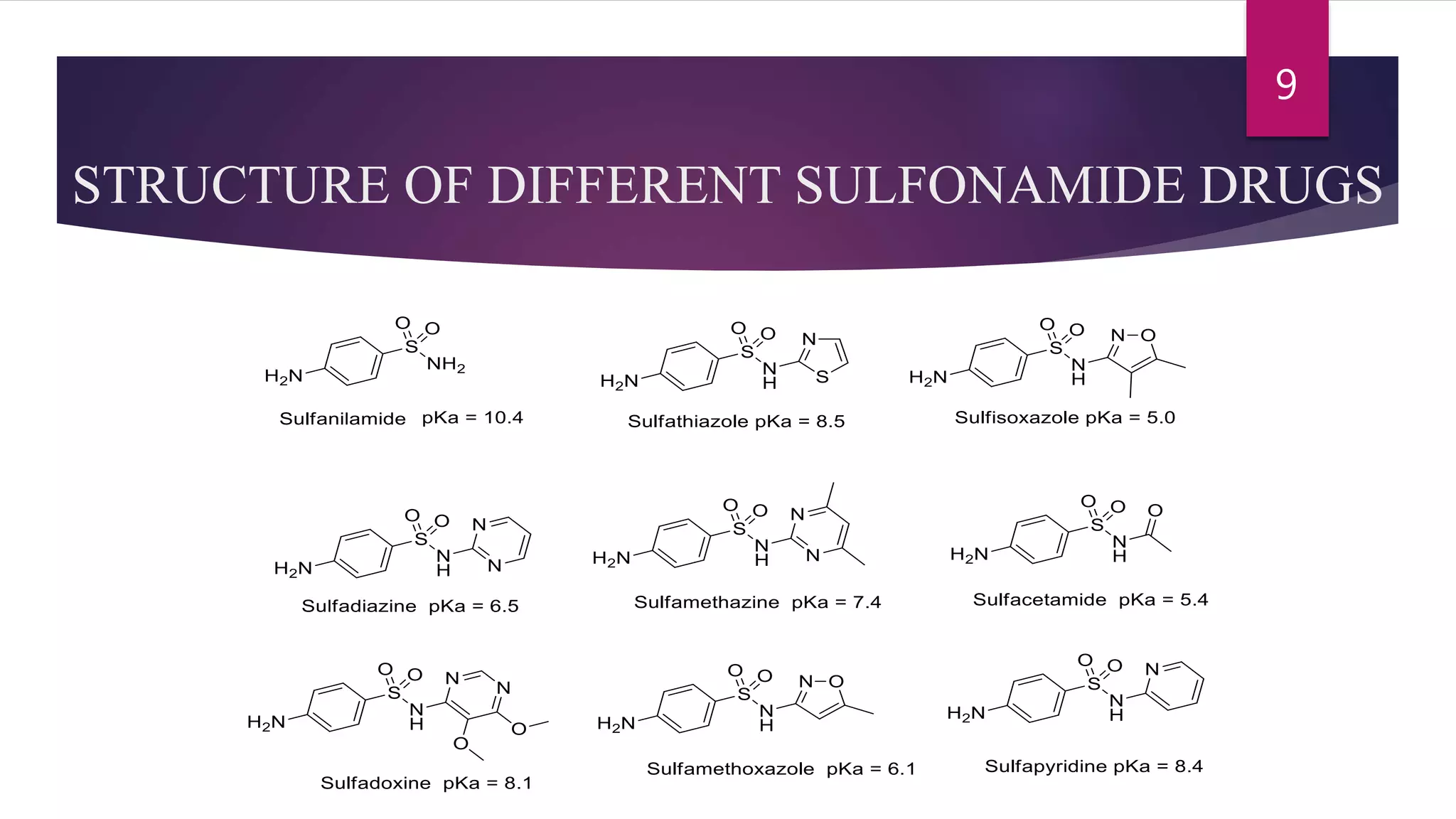
Sulfonamides are the first synthesized antimicrobial drugs that work by inhibiting folic acid synthesis in bacteria, leading to their bacteriostatic effects. They can be classified into absorbable, non-absorbable, and topical forms, with specific applications for various infections. While effective in treating several conditions, sulfonamides are limited by potential adverse effects and bacterial resistance, prompting ongoing research for new compounds and formulations.