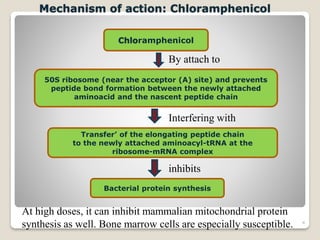
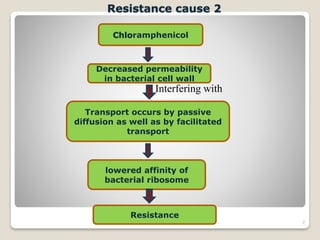
Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic produced by Streptomyces venezuelae bacteria. It works by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis at the ribosome. It has activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria as well as some protozoa. Chloramphenicol can cause serious and potentially fatal bone marrow suppression. As a result, it is now rarely used except for certain severe infections like meningitis and anaerobic infections. It is also used topically for eye and ear infections.