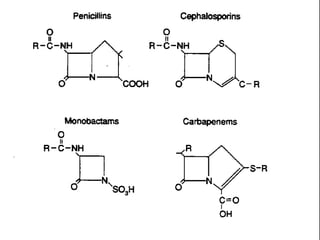
Carbapenems are a class of beta-lactam antibiotics with a fused beta-lactam ring. They include imipenem, meropenem, ertapenem, and aztreonam (a monobactam). Carbapenems have broad spectra of activity against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Imipenem is inactivated by renal dipeptidases but combined with cilastatin. Meropenem and ertapenem are more stable. Aztreonam only covers gram-negatives but is useful in penicillin allergic patients. Carbapenems are used to treat various infections including respiratory, abdominal, skin and bone infections.