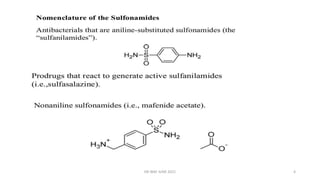
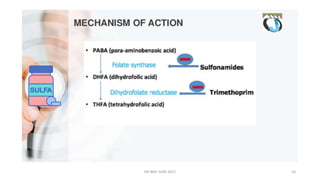
This document summarizes information about sulphonamides, a class of antibiotic drugs. It discusses the history of sulphonamides dating back to their discovery in 1935. It also covers the chemistry, mechanisms of action, spectrum of activity, resistance, interactions, uses and adverse effects of various sulphonamide drugs including co-trimoxazole, silver sulphadiazine, and dapsone. The document is intended to provide an overview of sulphonamides for educational purposes.