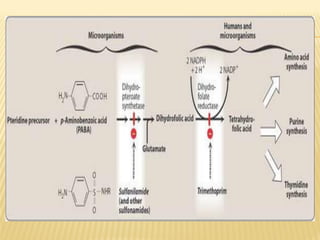
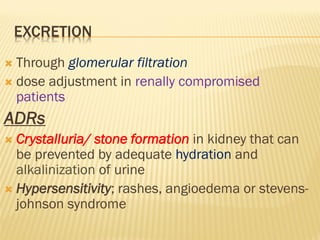
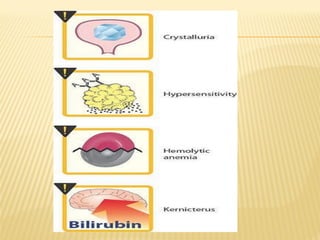
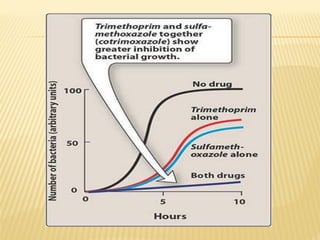
This document discusses the classification, mechanisms of action, antimicrobial spectrum, pharmacokinetics, and adverse effects of several classes of antifolate drugs including sulfonamides, trimethoprim, and cotrimoxazole. Sulfonamides are bacteriostatic inhibitors of bacterial folate synthesis that compete with PABA. Trimethoprim inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Cotrimoxazole combines trimethoprim and a sulfonamide for broad-spectrum antibacterial activity through dual inhibition of folate synthesis. These drugs are absorbed orally, distributed widely, and excreted renally. Common adverse effects include hematologic and gastrointestinal issues.