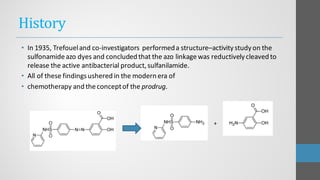
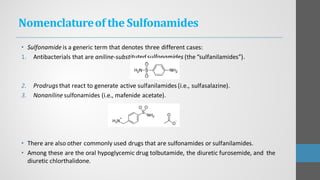
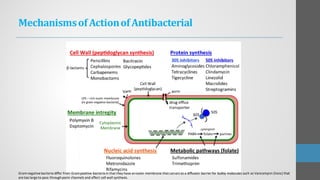
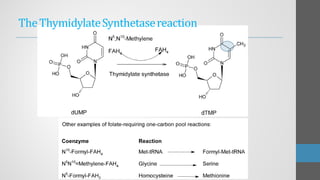
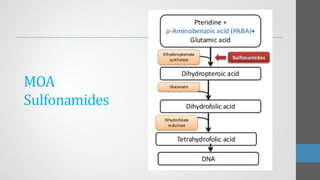
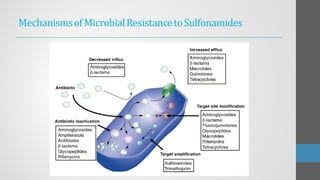
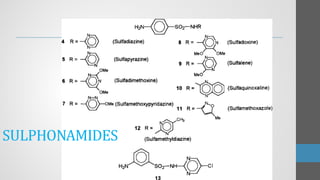
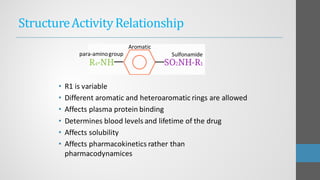
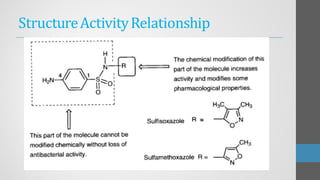
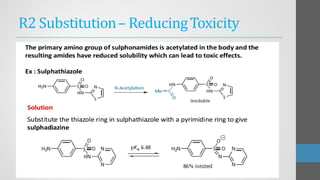
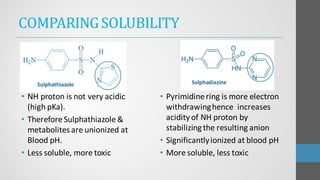
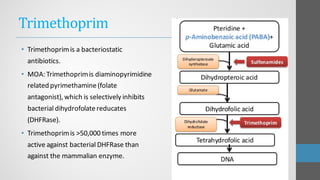
Sulfonamides are synthetic antibacterial agents that were the first effective treatments for bacterial infections, although their use has decreased due to resistance and the rise of broader-spectrum antibiotics. Despite this, the combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole has led to a resurgence in their application, particularly against opportunistic infections. They act as competitive inhibitors of bacterial folate biosynthesis, ultimately blocking bacterial growth and cell division without directly killing the bacteria.