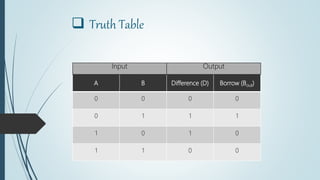
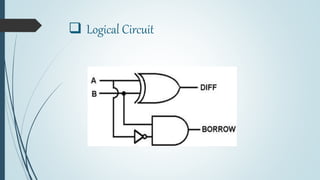
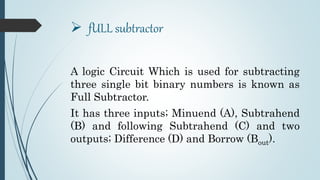
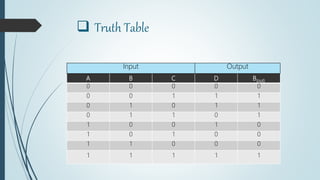
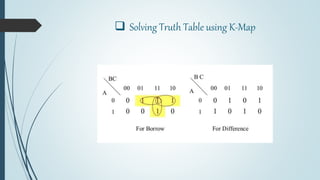
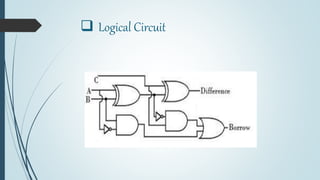
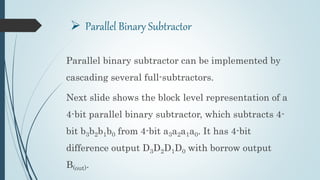
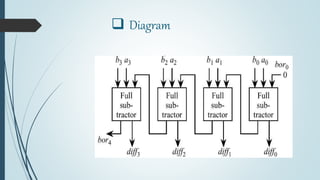
This document discusses digital subtractors. It defines a subtractor as an electronic logic circuit that calculates the difference between two binary numbers. There are two main types: half subtractors and full subtractors. A half subtractor is used for single bit subtraction and has two inputs, two outputs, and a truth table. A full subtractor can subtract three single bit numbers, with three inputs and two outputs defined by its truth table. Parallel binary subtractors are built by cascading multiple full subtractors to subtract larger binary numbers. Subtractors have applications in signal processing, arithmetic logic units, address calculation, and more.