1) The document discusses binary adders and subtractors, including half adders, full adders, and full subtractors. It provides truth tables and logic diagrams for each circuit.
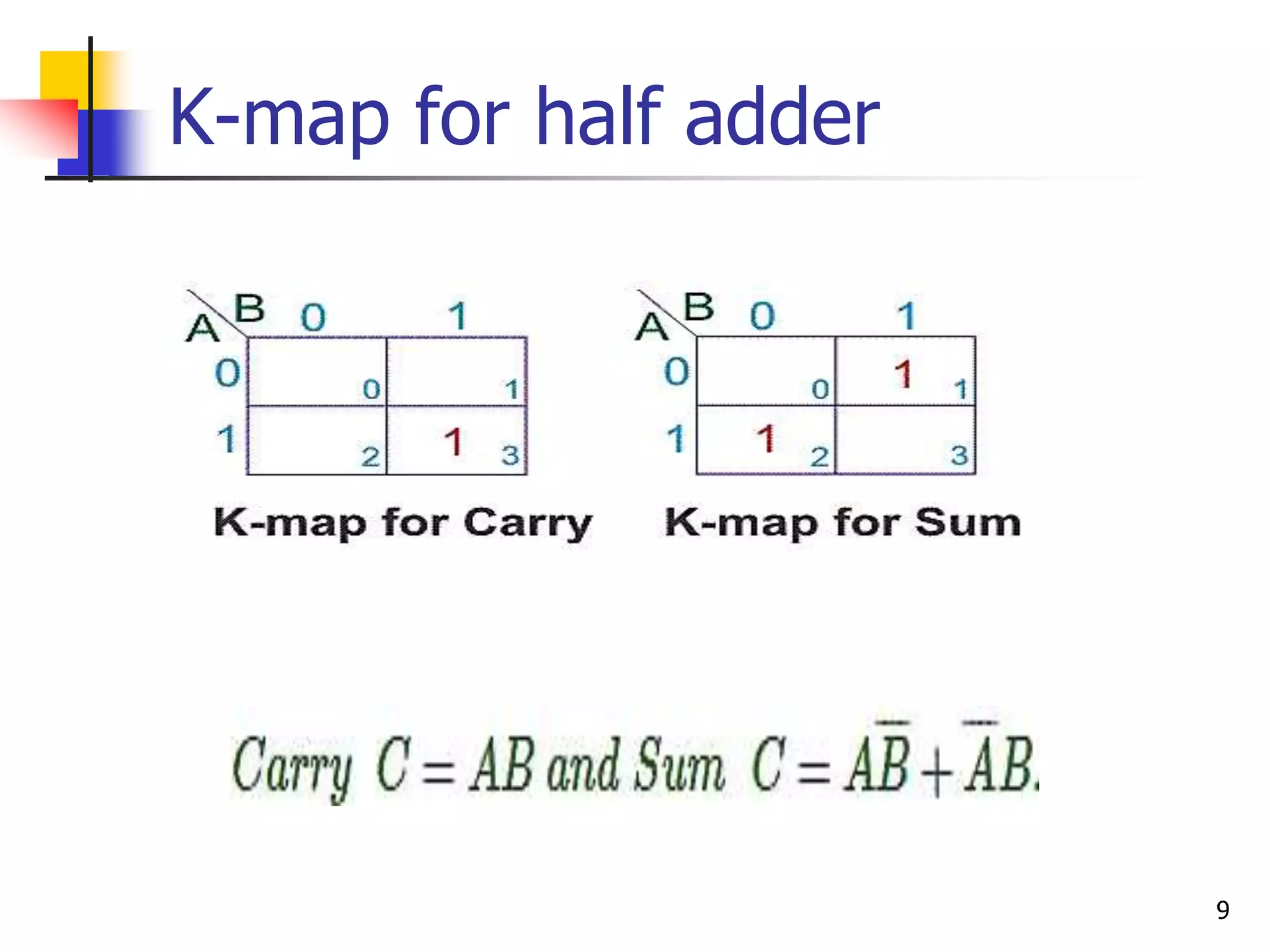
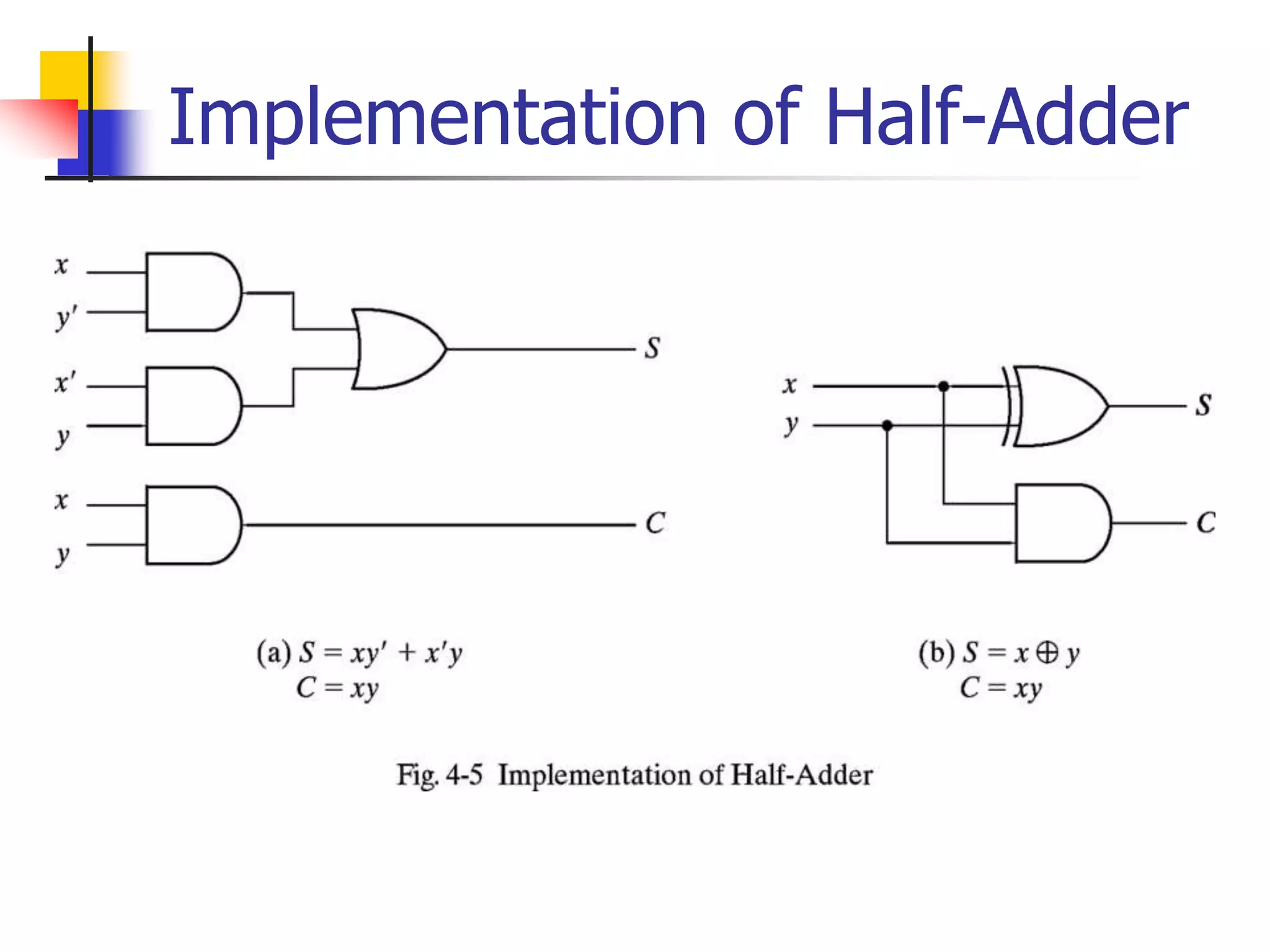
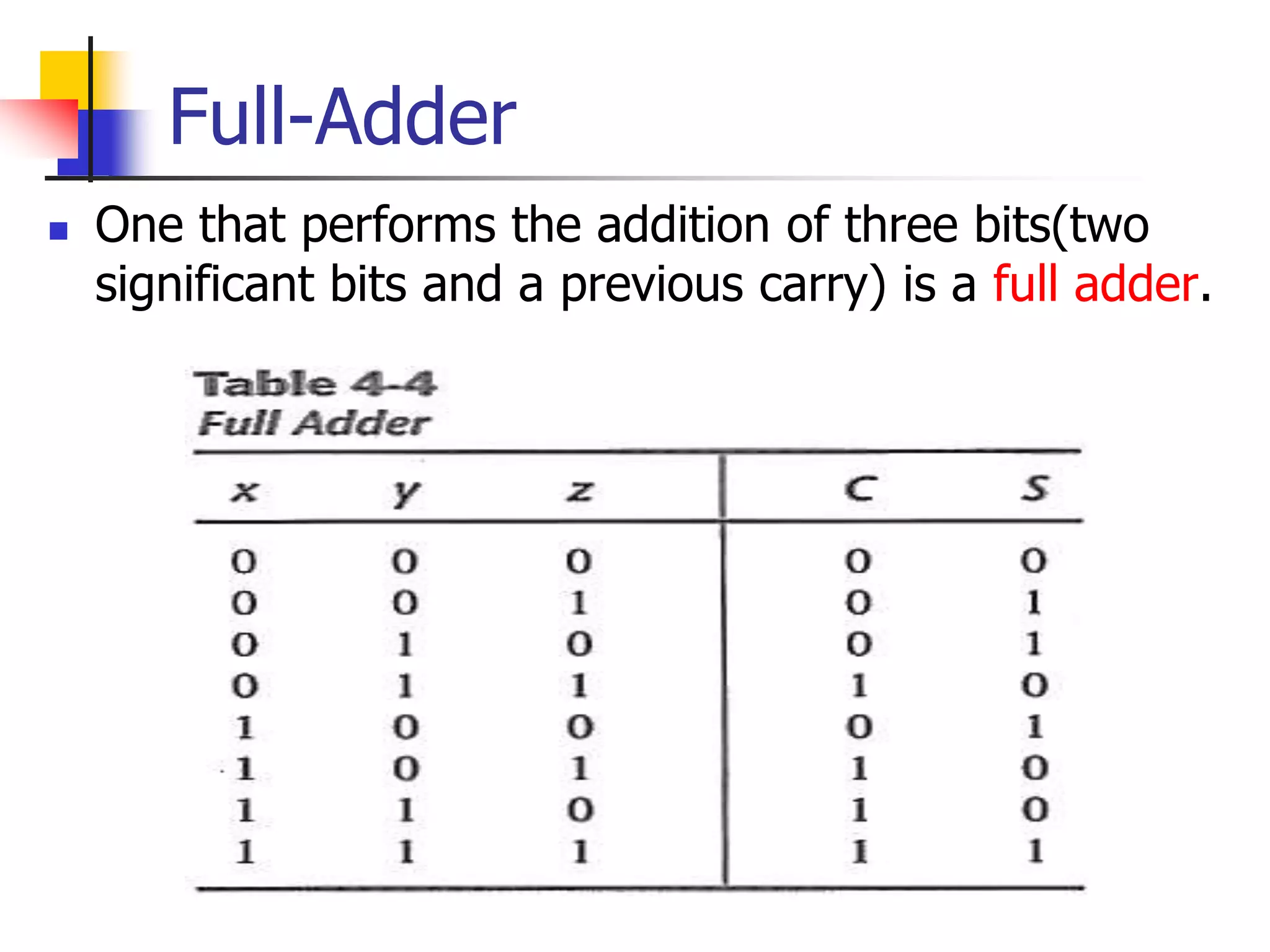
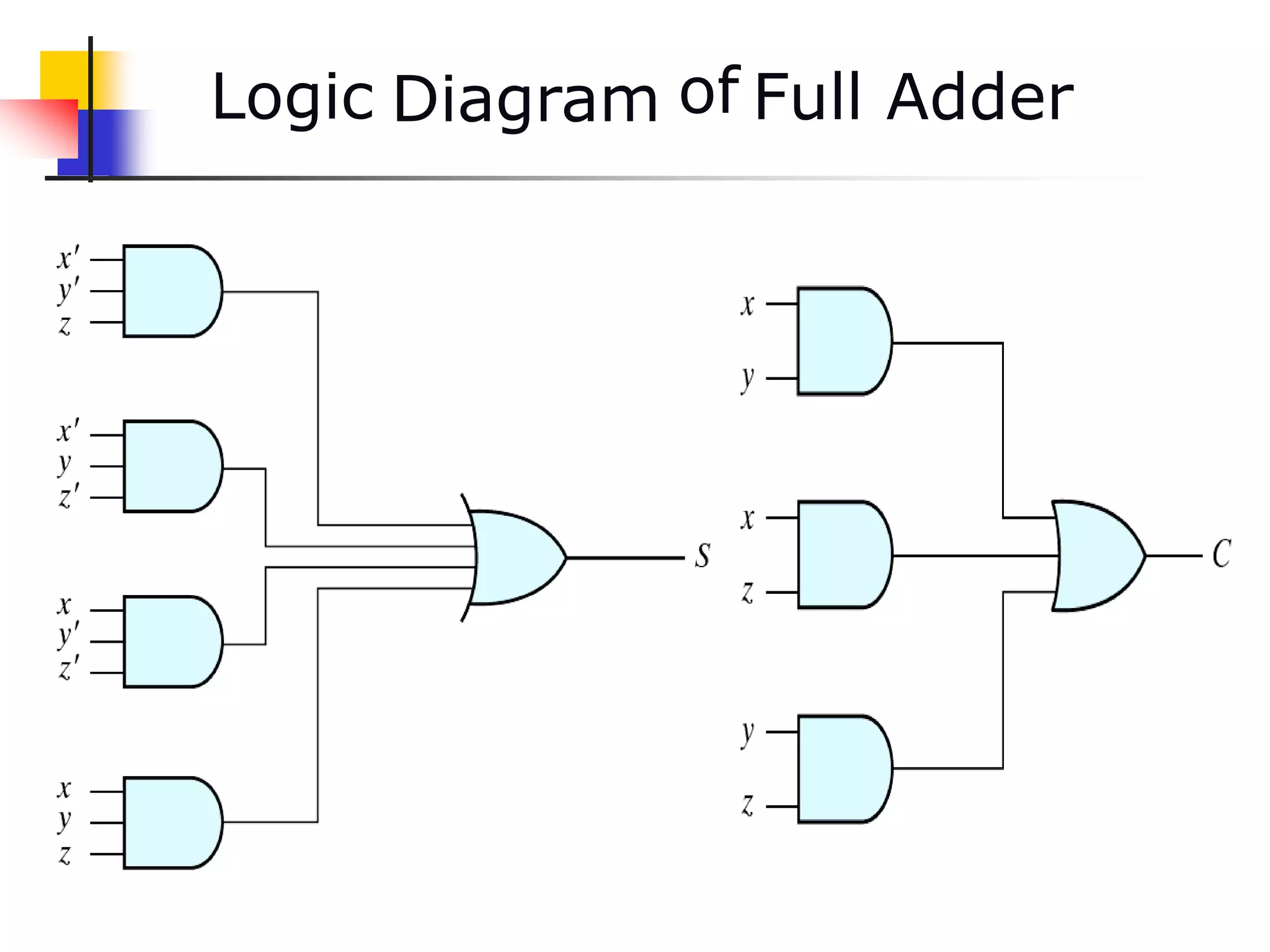
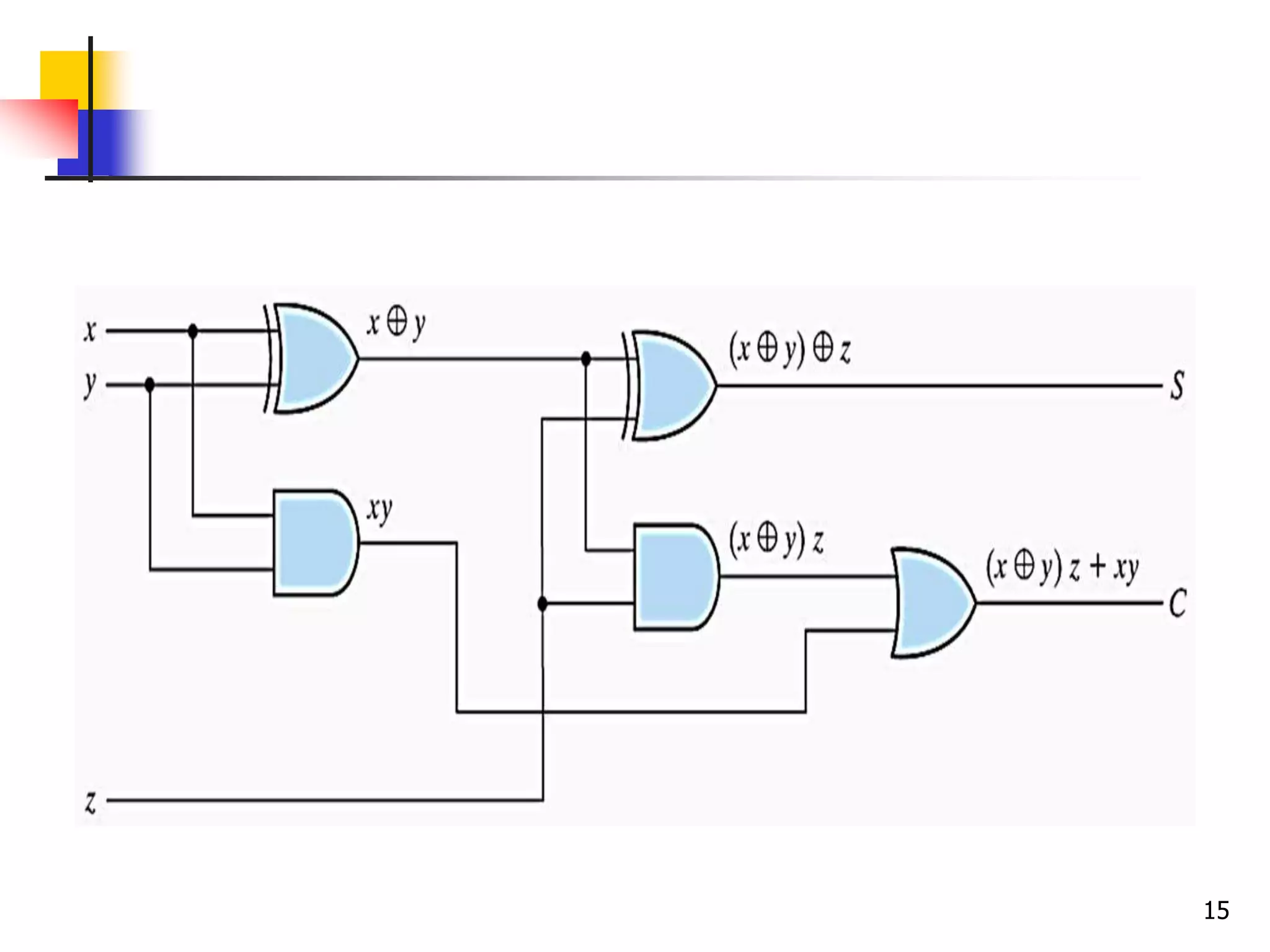
2) A half adder adds two bits and produces a sum and carry output. A full adder adds three bits by taking two input bits and a carry bit as input.
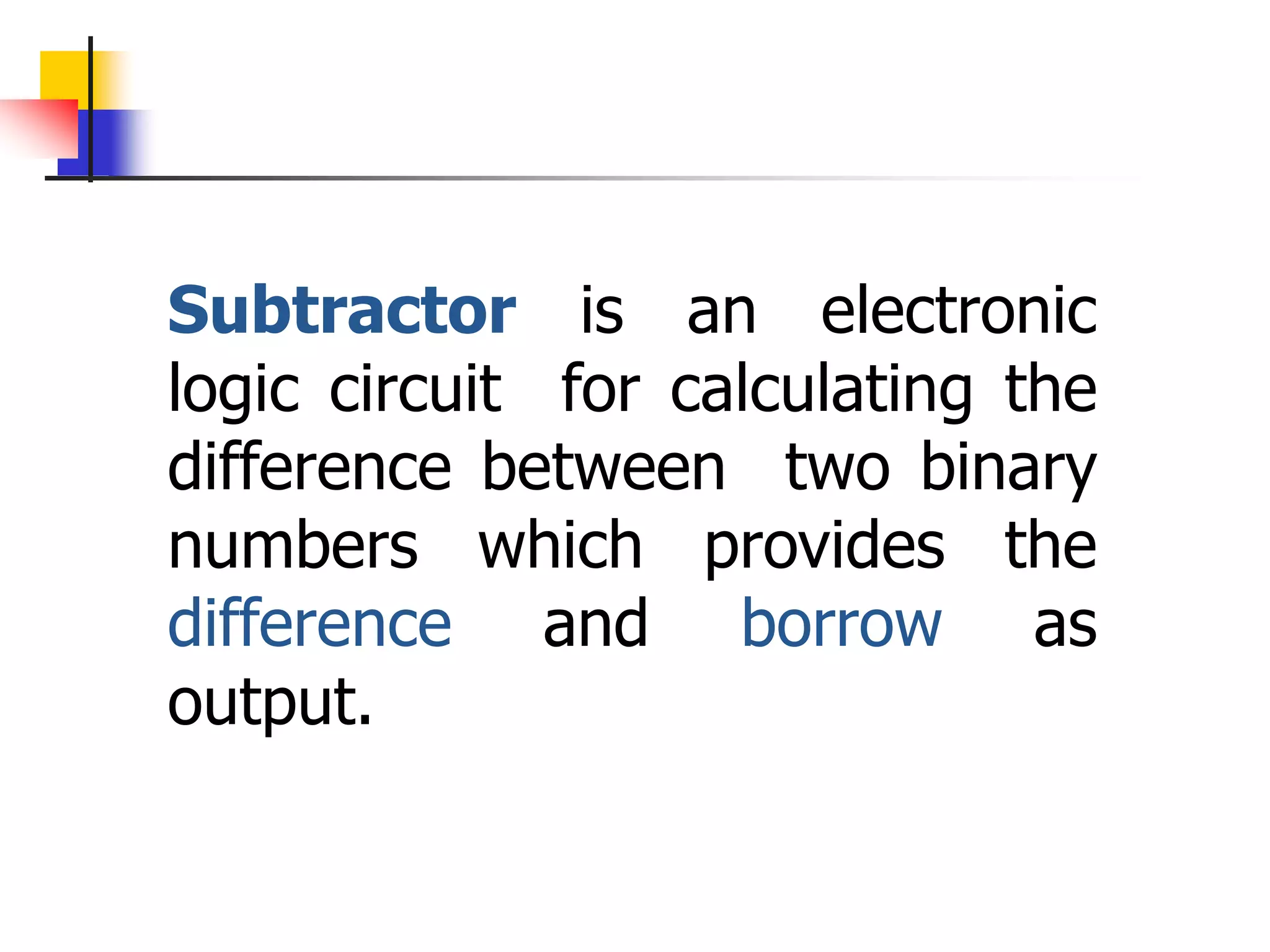
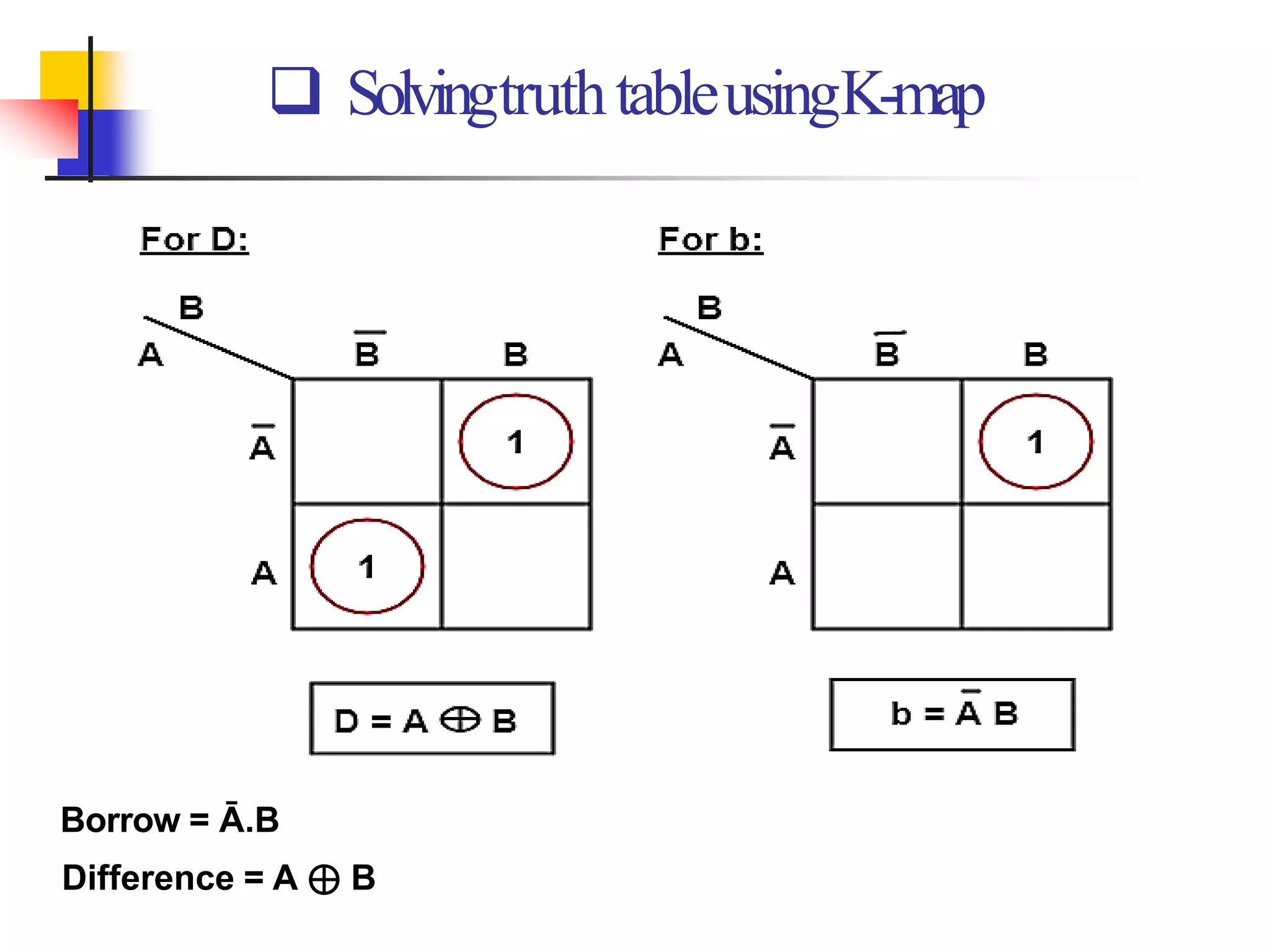
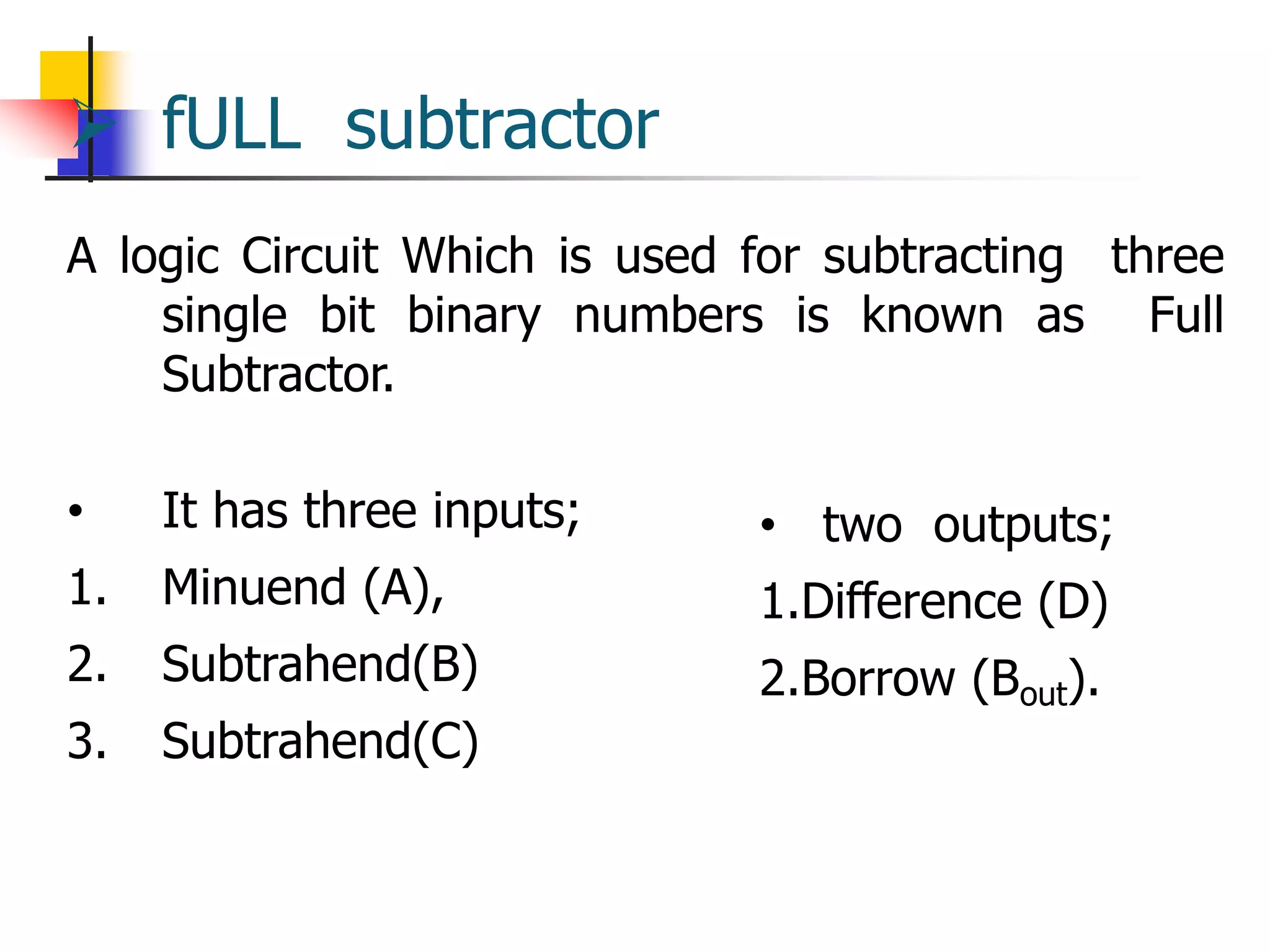
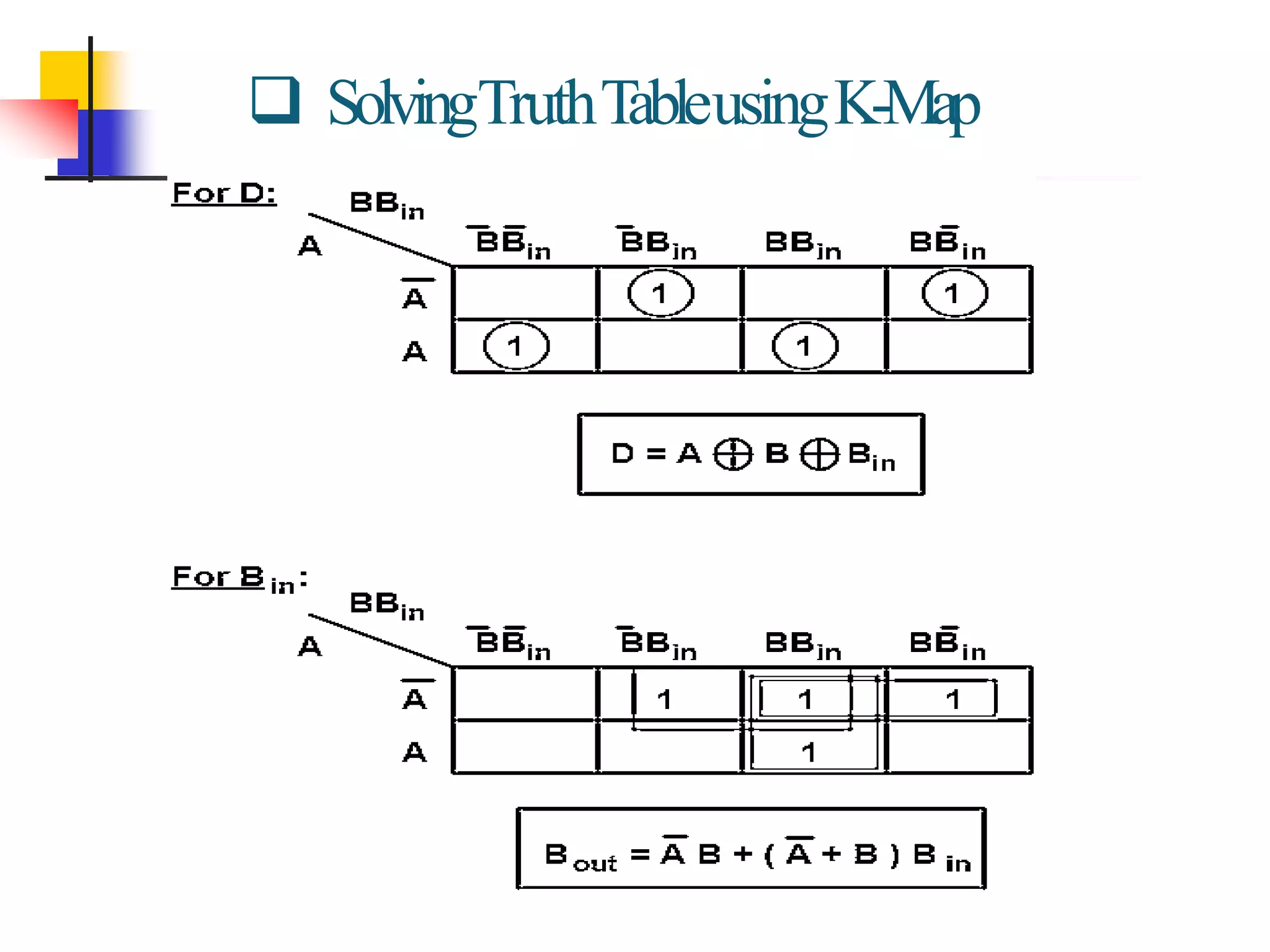
3) A half subtractor and full subtractor are also discussed, which take inputs of minuend, subtrahend, and optionally a carry bit, and produce a difference and borrow output. Truth tables and logic diagrams are provided for the subtractor circuits.