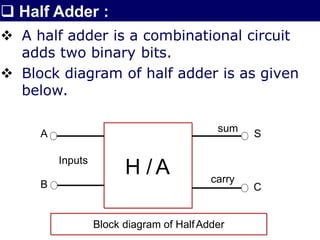
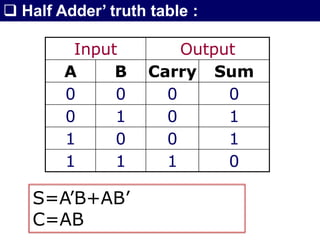
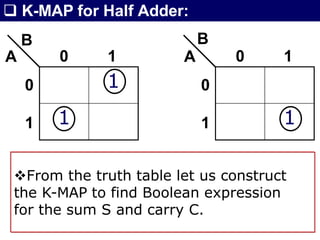
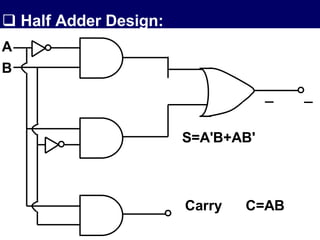
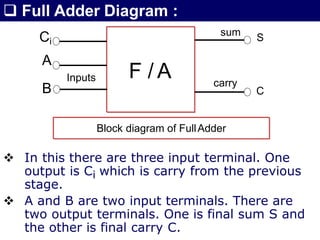
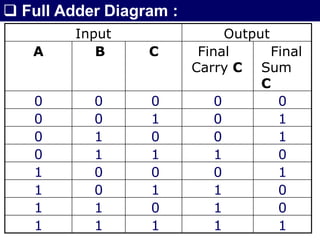
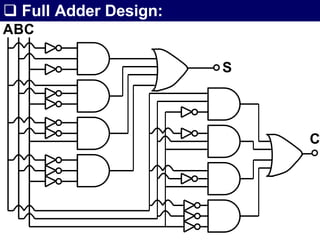
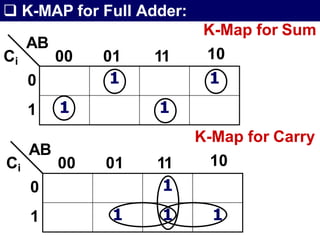
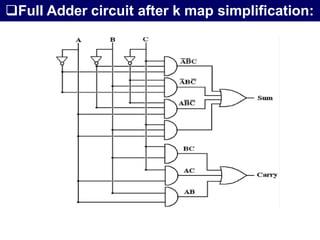
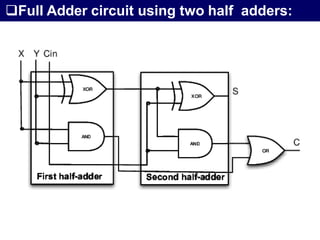
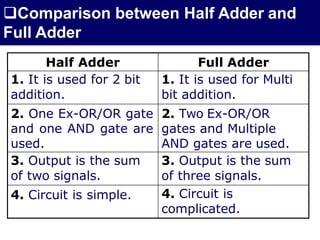
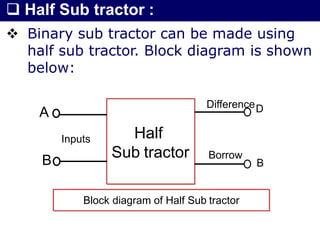
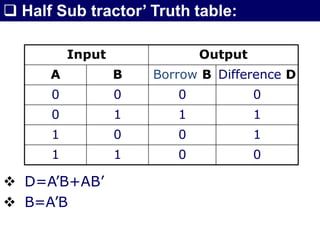
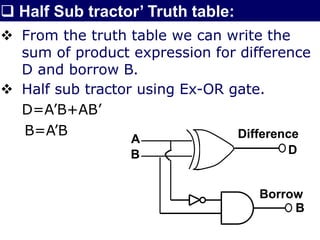
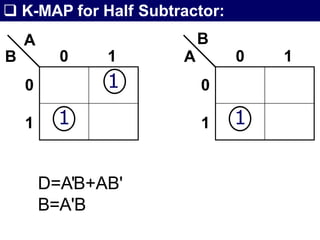
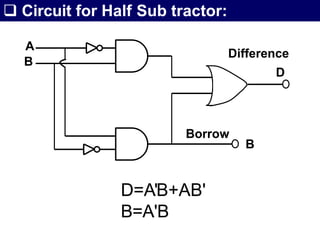
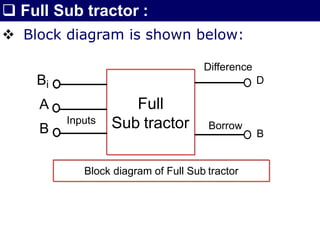
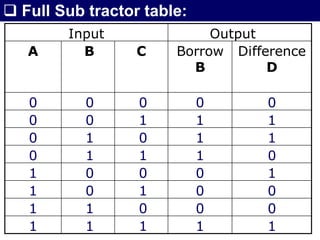
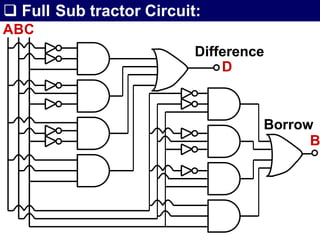
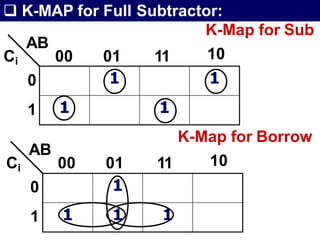
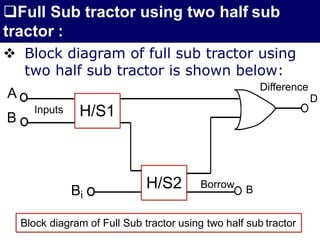
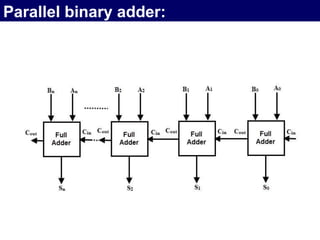
The document discusses combinational circuits, focusing on half adders and full adders, which are used for binary addition. It explains their structures, truth tables, and how they can be constructed using logic gates, along with differences between half and full adders. Additionally, it introduces half and full subtractors, highlighting their designs and functionalities in binary subtraction.