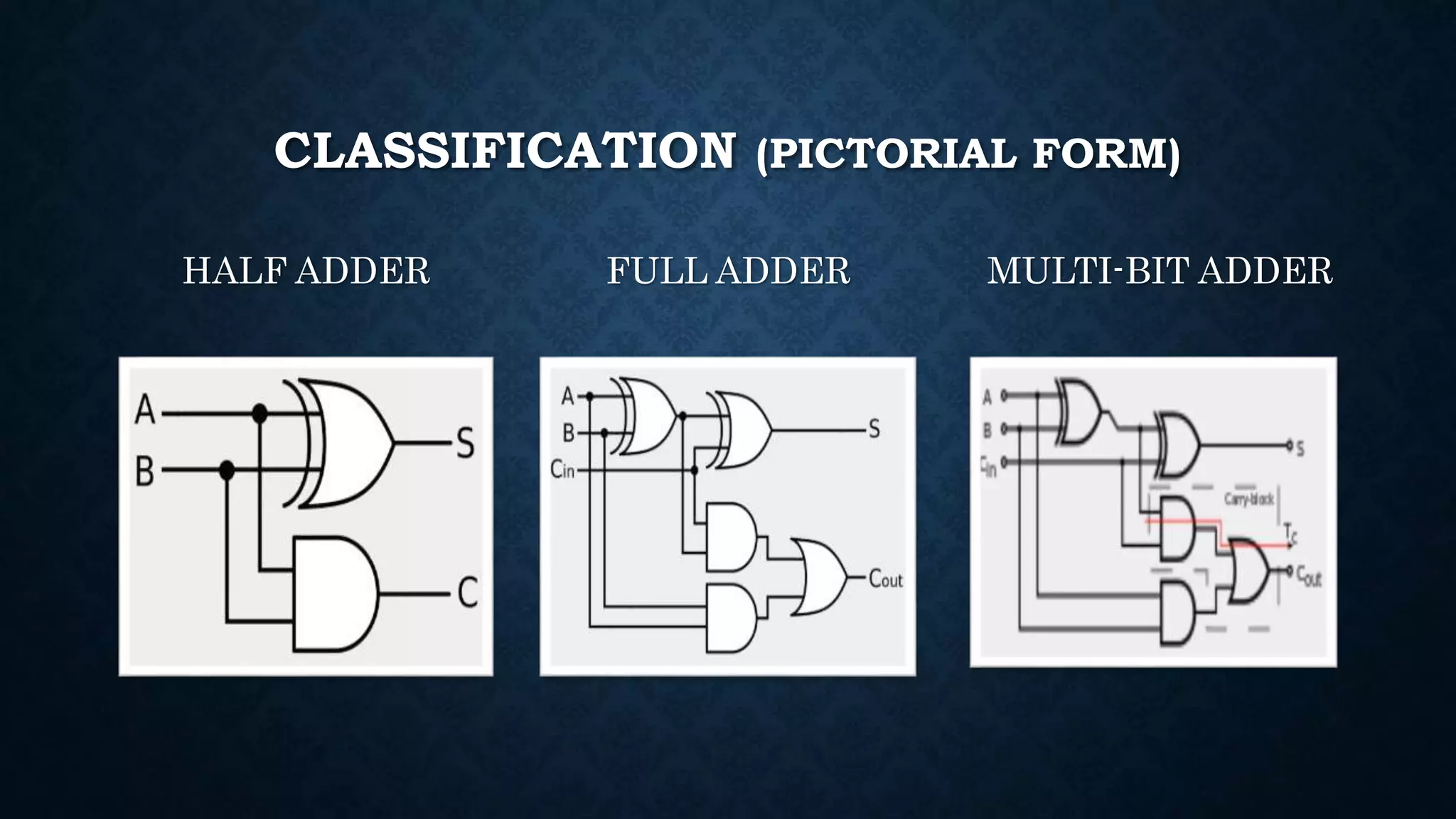
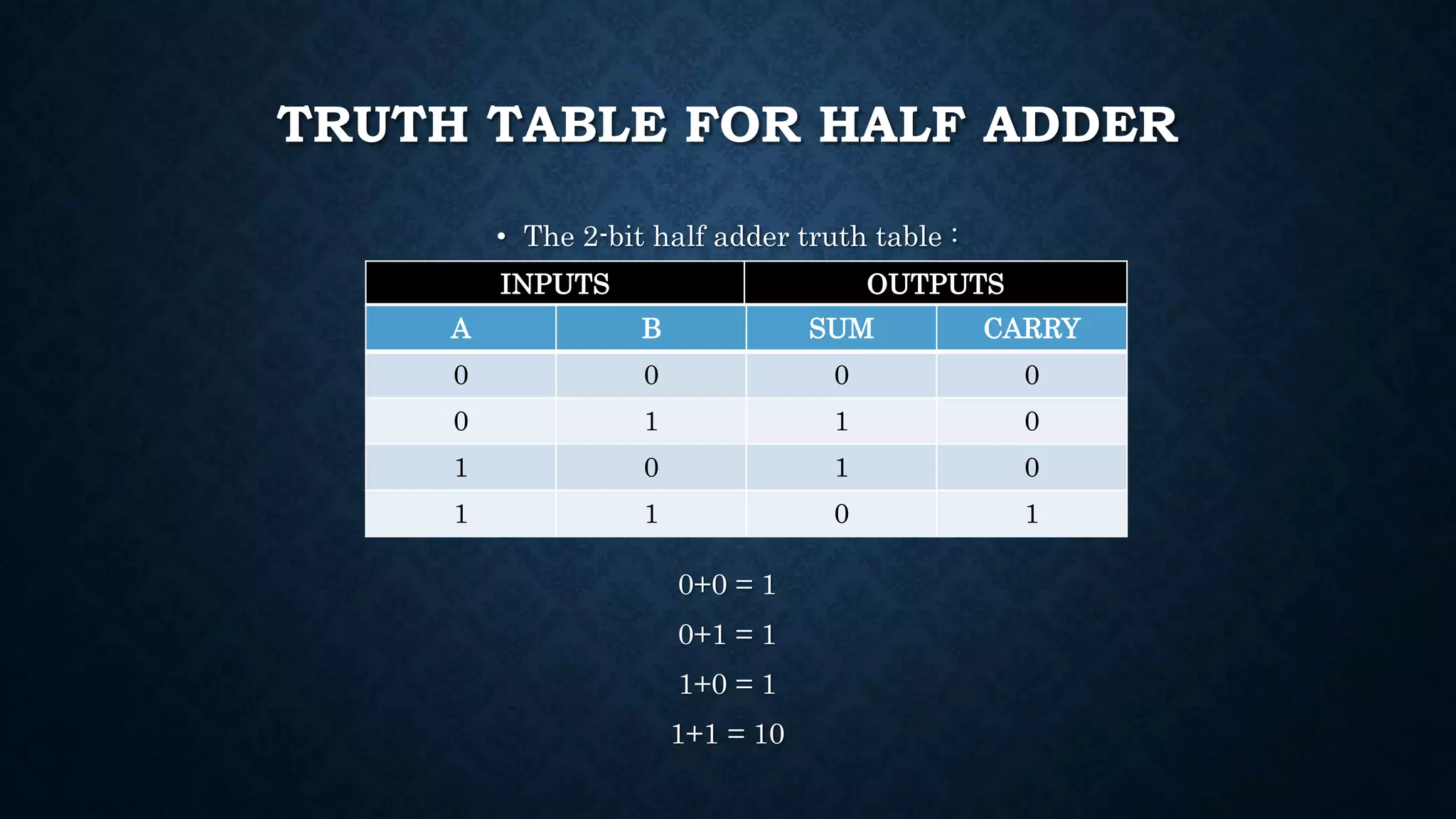
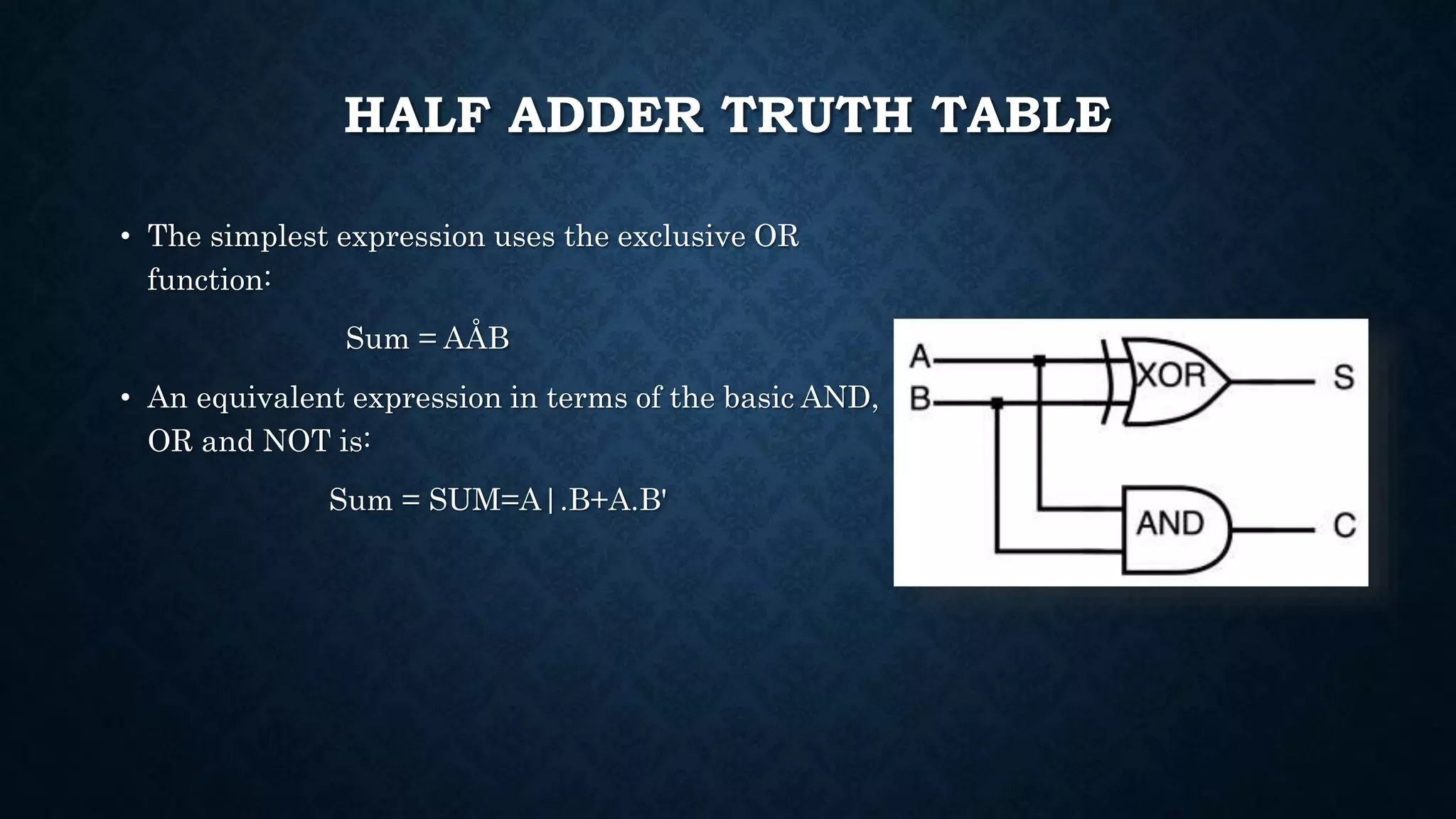
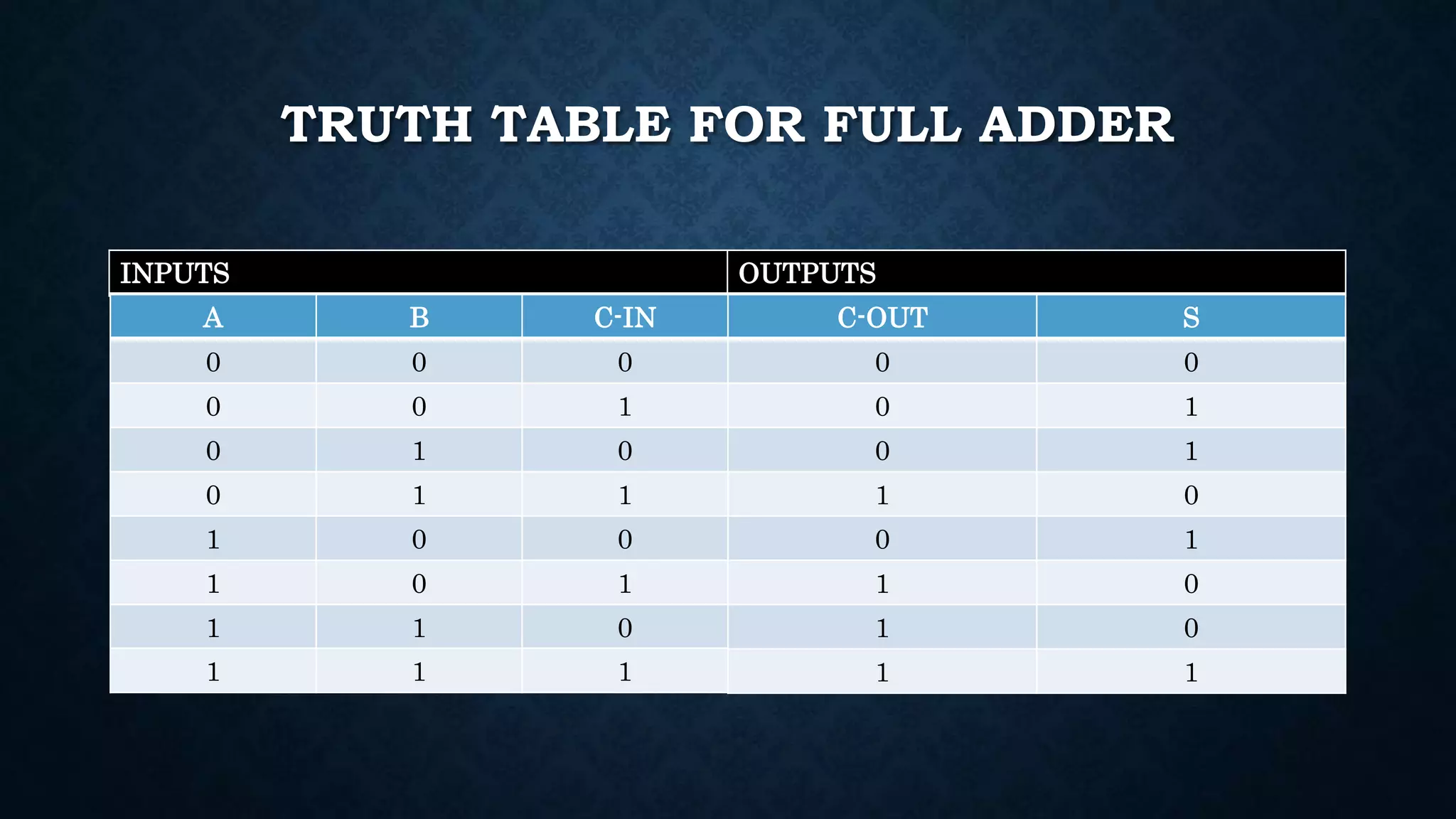
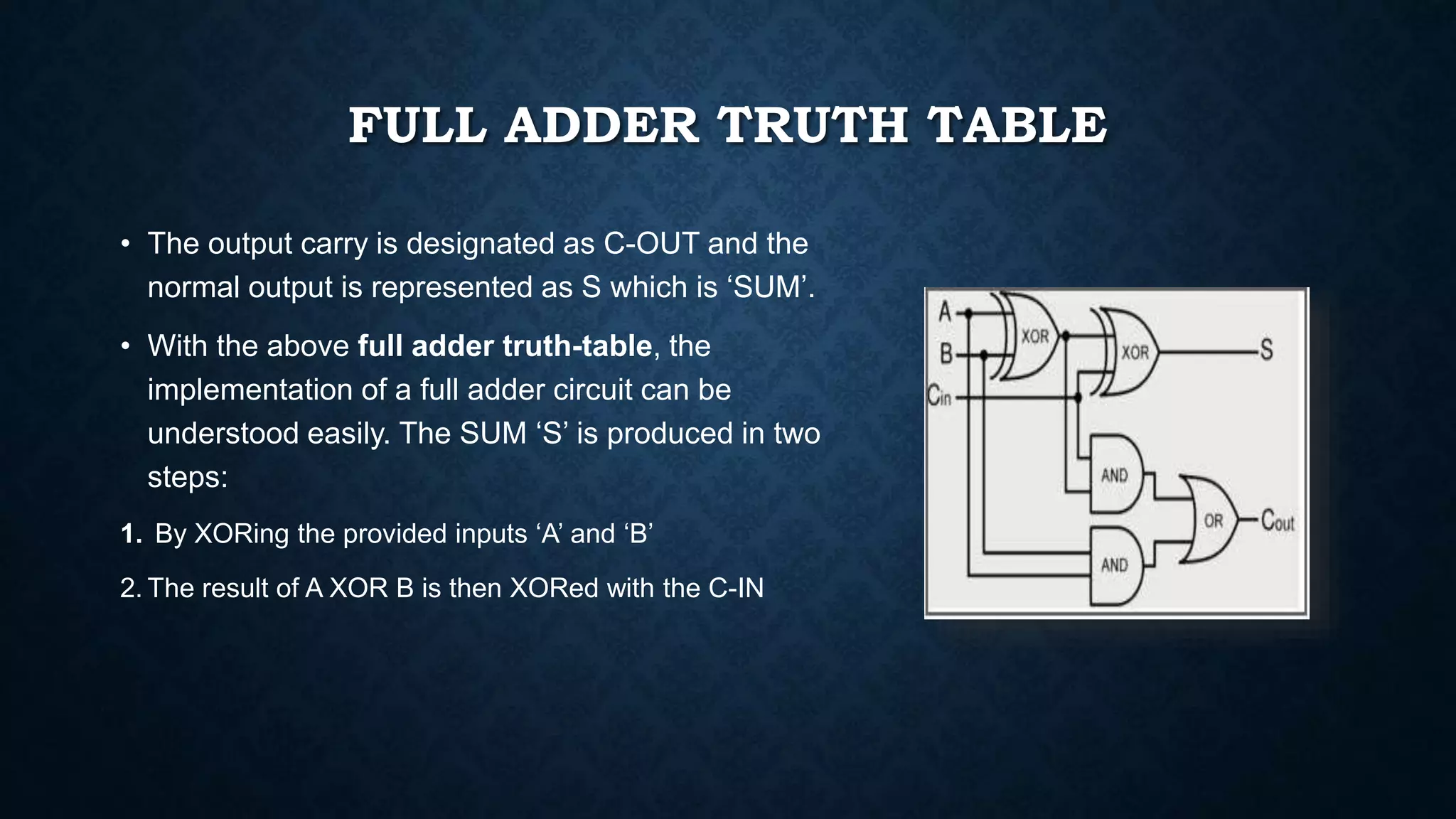
The document explains the function and classification of digital logic circuits known as adders, which are essential for performing addition in computers and processors. It details two main types of adders: half adders, which add two single-bit binary numbers, and full adders, which can add three one-bit binary numbers, often using two half adders. Additionally, it mentions multi-bit adders, which are combinations of full adders, used for more extensive addition tasks.