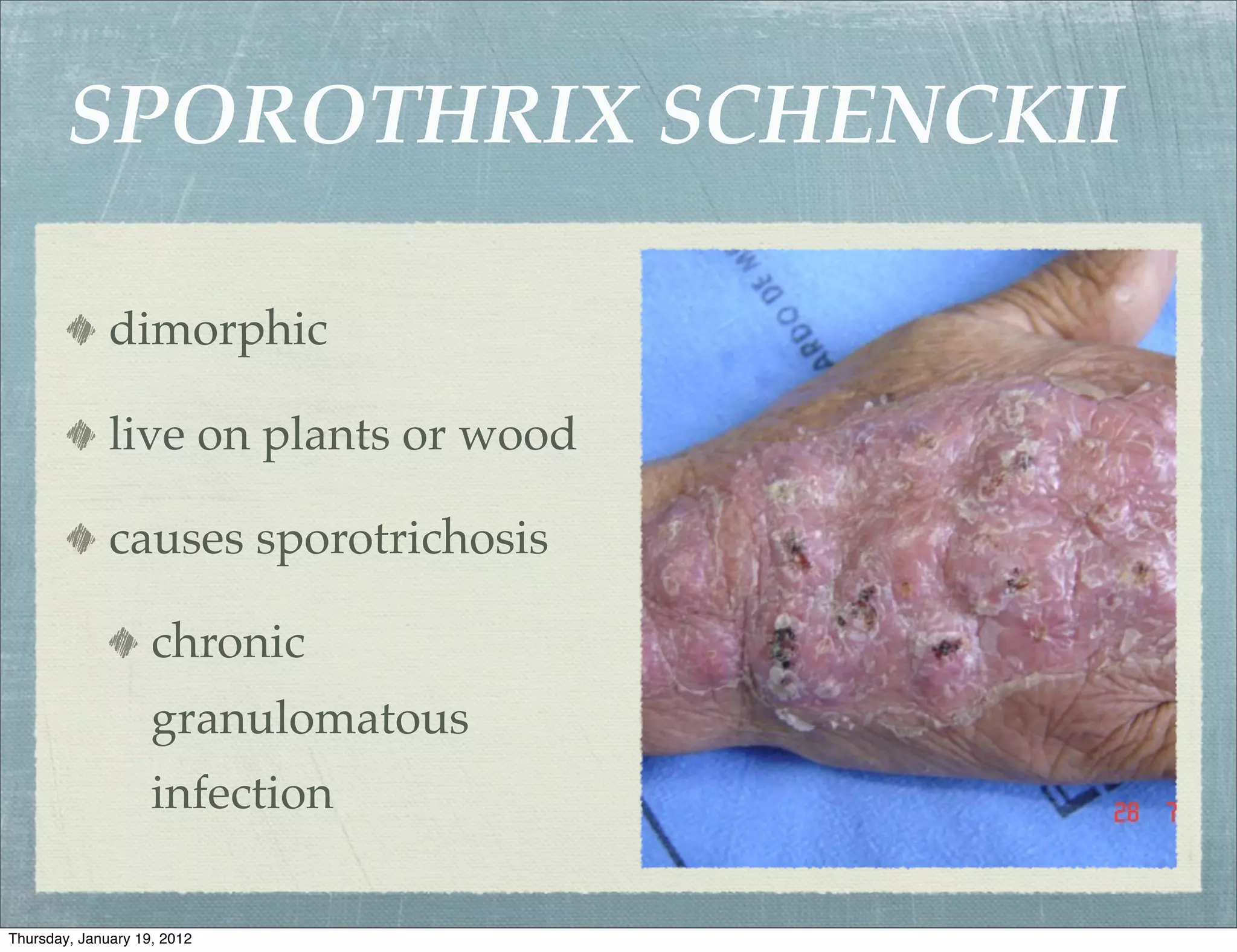
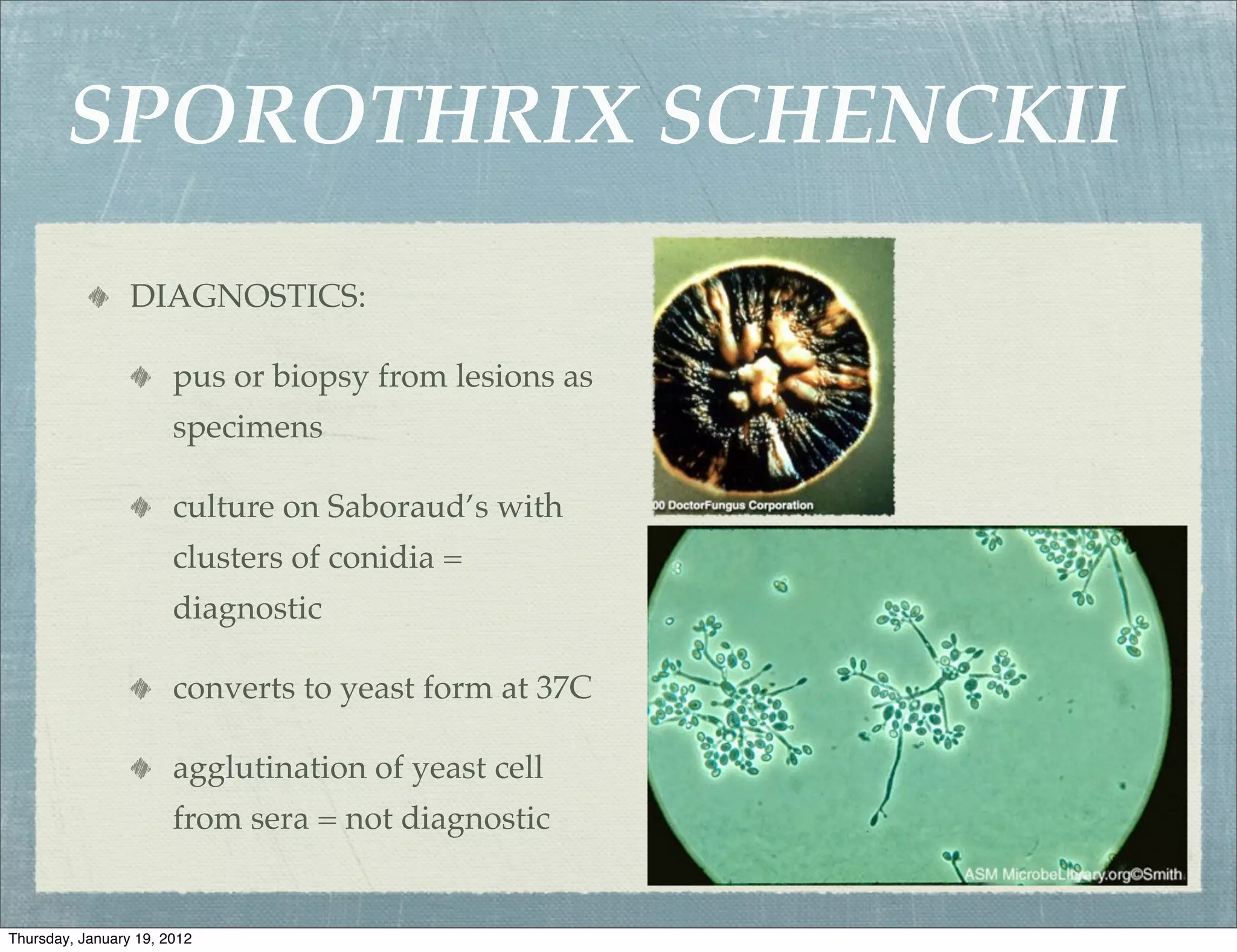
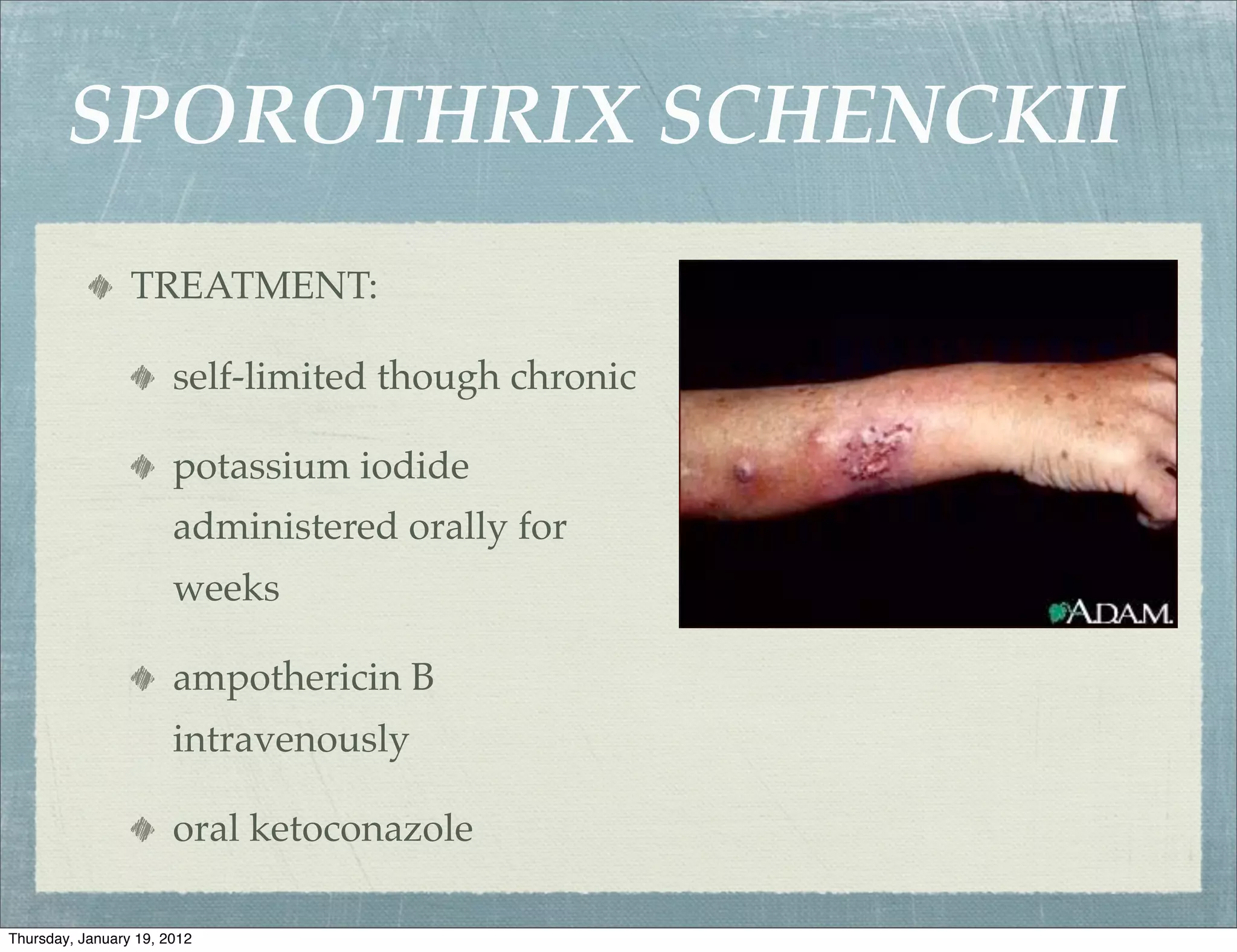
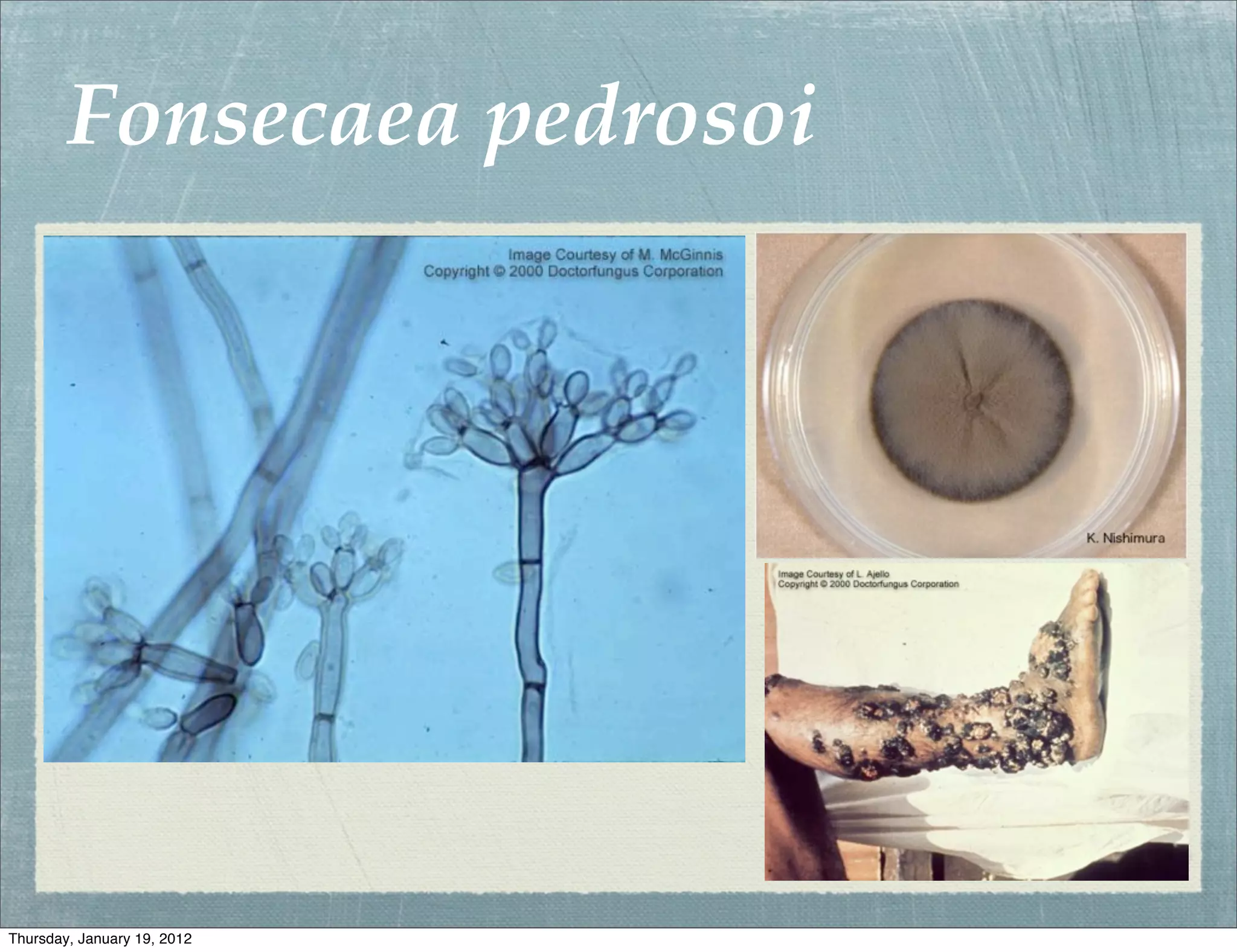
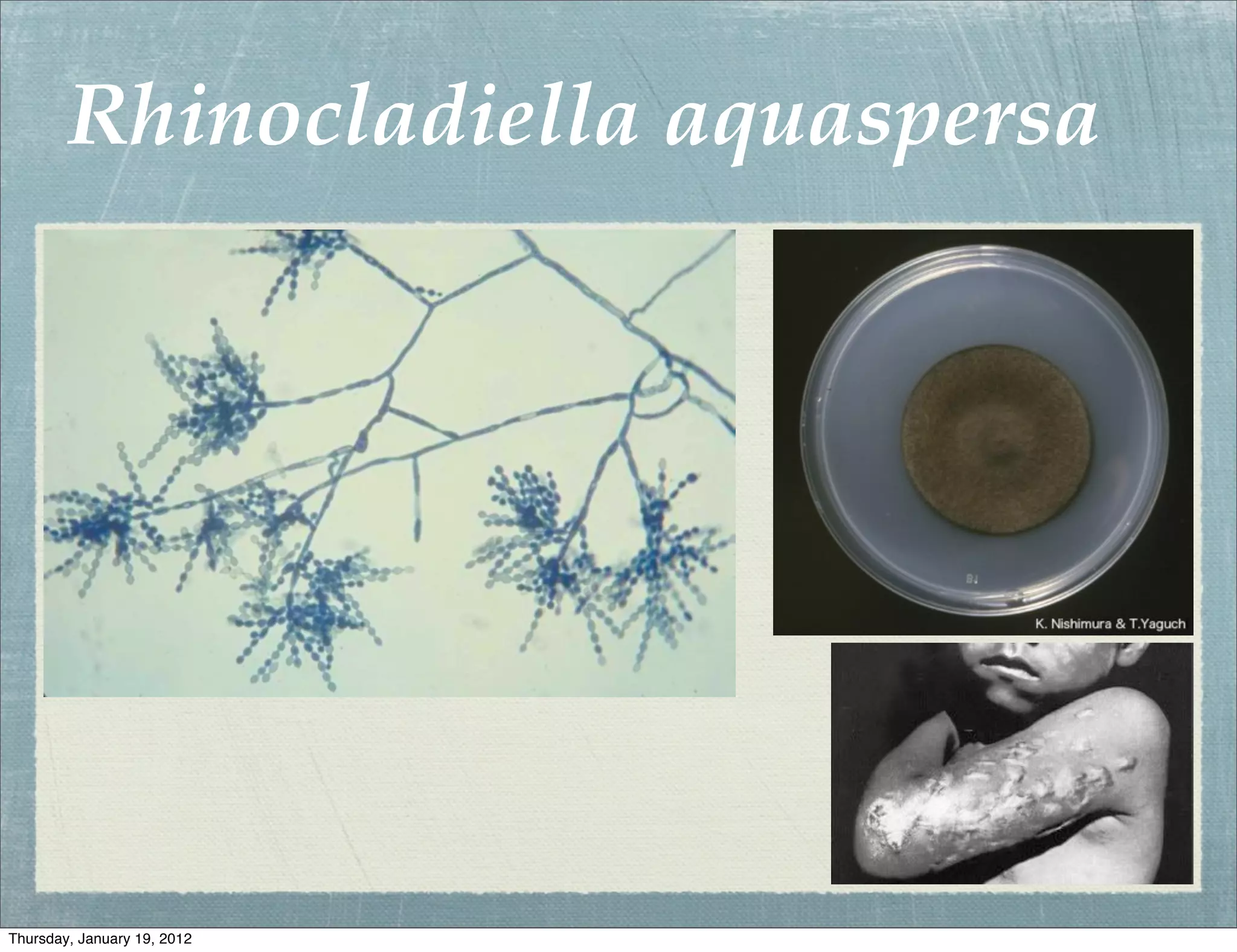
Subcutaneous mycoses are fungal infections that grow on soil or decaying vegetation. They must be introduced into subcutaneous tissue to cause disease. Lesions generally spread slowly from the area of implantation via lymphatics, except in cases of sporotrichosis where spread may be faster. Sporothrix schenckii is a dimorphic fungus that lives on plants or wood and causes sporotrichosis, a chronic granulomatous infection. Diagnosis involves culturing samples from lesions on Sabouraud's medium, where clusters of conidia indicate S. schenckii. Treatment includes oral antifungals like potassium iodide, amphotericin B, or ketocon