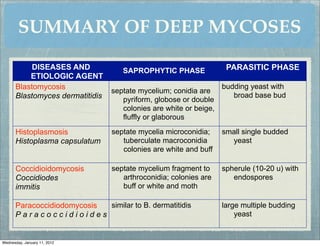
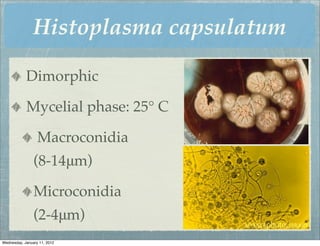
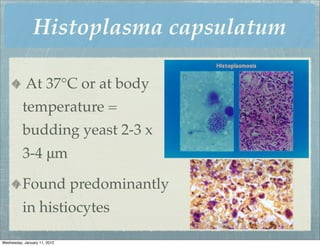
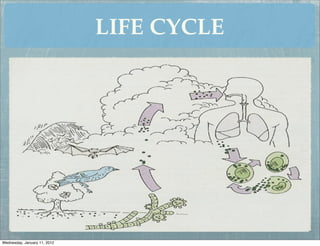
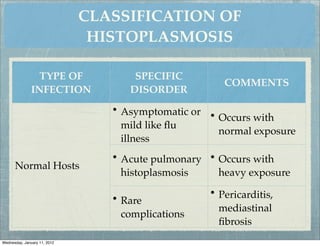
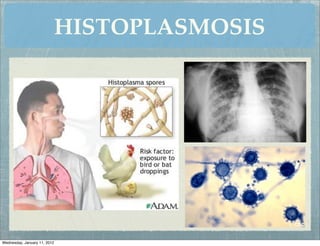
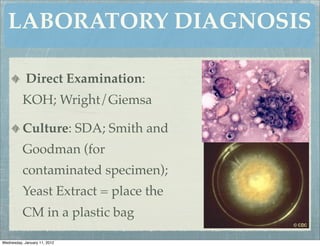
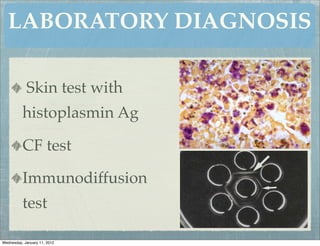
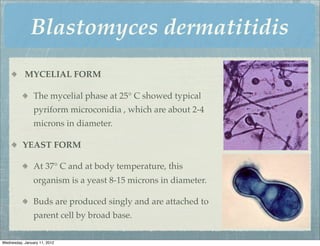
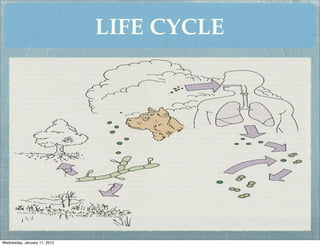
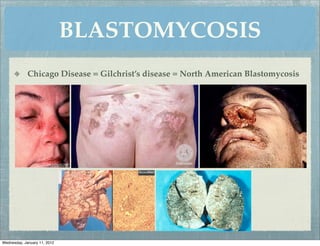
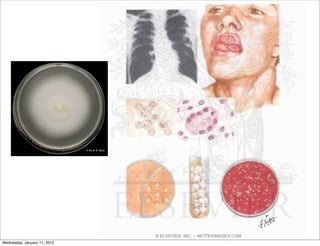
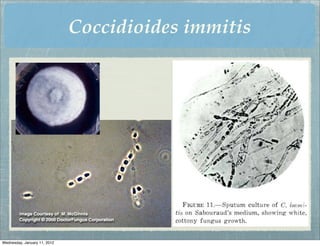
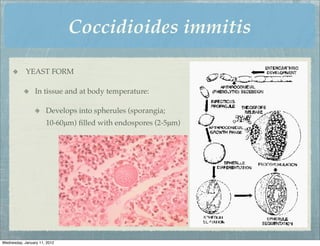
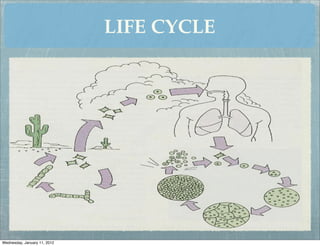
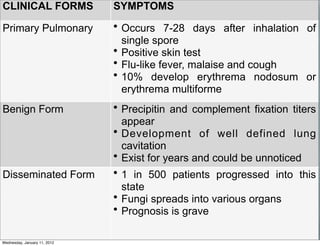
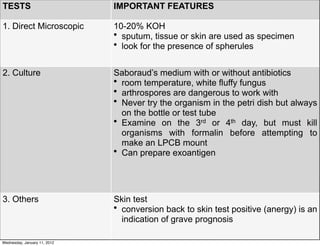
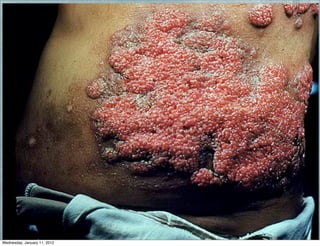
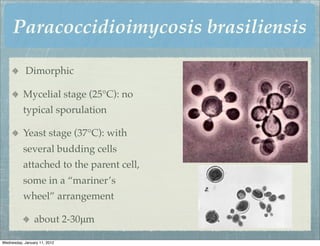
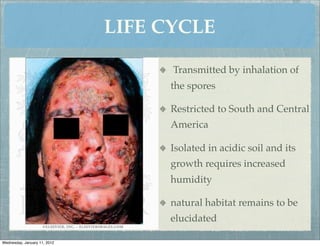
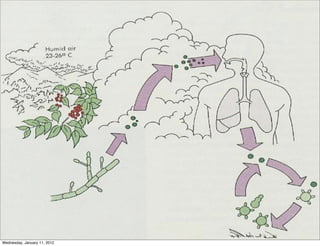
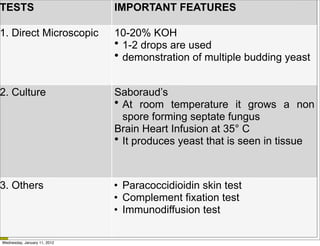
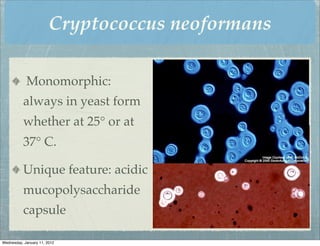
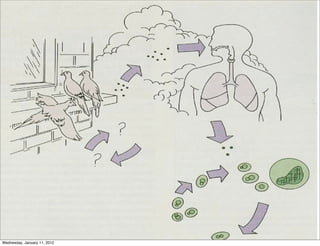
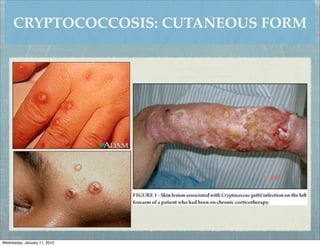
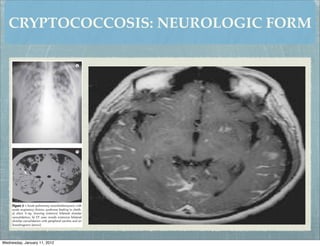
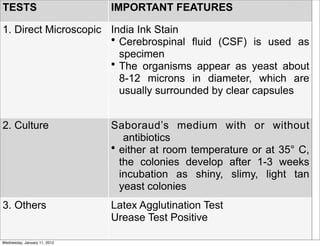
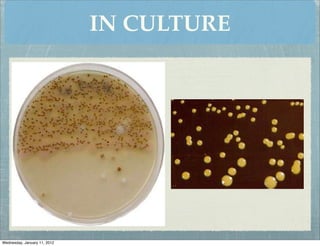
This document summarizes several systemic mycoses, including blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It describes the etiologic agents, life cycles, clinical presentations, and diagnostic approaches for each. Many of these fungi exhibit dimorphism, growing as mold-like mycelia at lower temperatures and yeast-like forms at human body temperature when infecting humans. Laboratory diagnosis may involve microscopy, culture, antigen detection and antibody tests. Treatment depends on the specific infection but may include antifungal drugs such as amphotericin B and itraconazole.