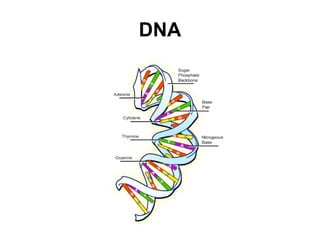
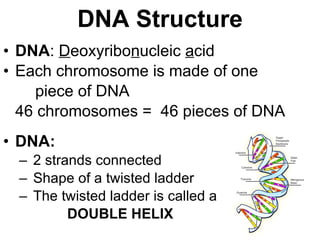
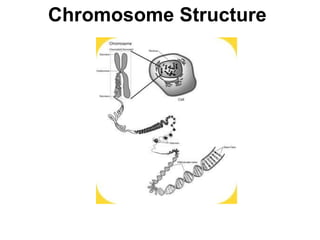
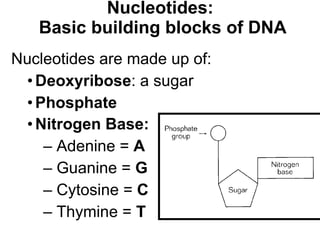
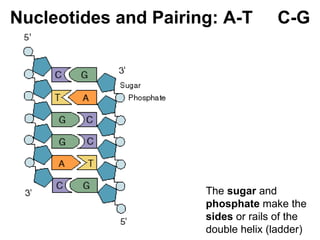
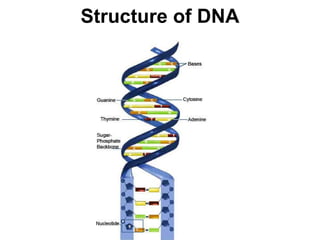
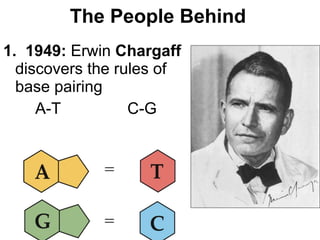
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, consists of 46 chromosomes each made of two strands forming a double helix that stores genetic information essential for controlling cellular activities. The basic building blocks of DNA, known as nucleotides, are composed of deoxyribose, phosphate, and nitrogenous bases which pair in specific ways (A-T, C-G). Key discoveries in the understanding of DNA's structure were made by Erwin Chargaff, Rosalind Franklin, and the duo of James Watson and Francis Crick.