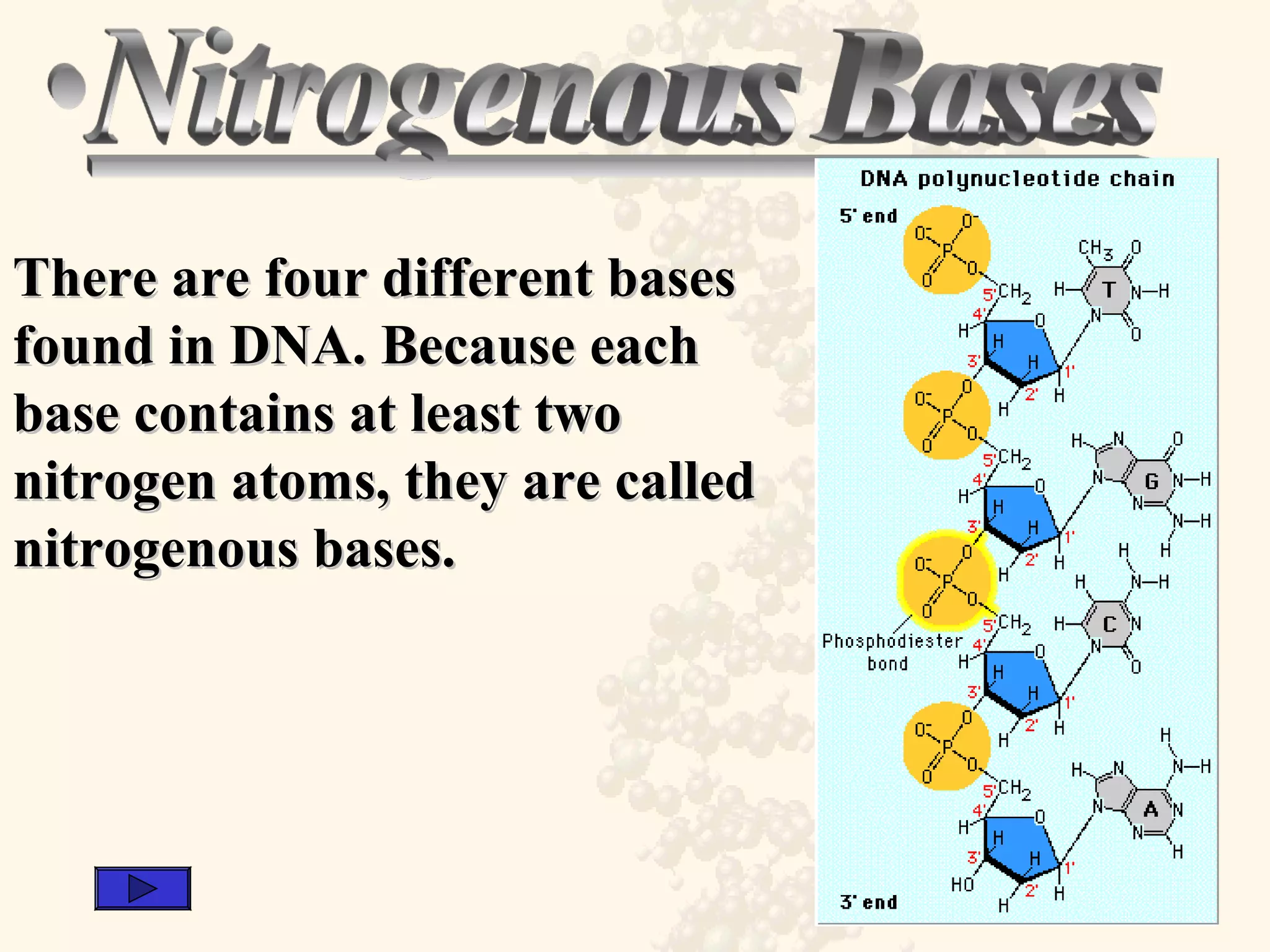
DNA is a long, double-stranded nucleic acid made of nucleotides, functioning as the primary informational molecule for storing genetic information about polypeptides. It consists of two complementary polynucleotide chains forming a double helix, held together by hydrogen bonds between nitrogenous bases. RNA serves various roles in protein synthesis and, in some viruses, acts as the primary genetic material instead of DNA.