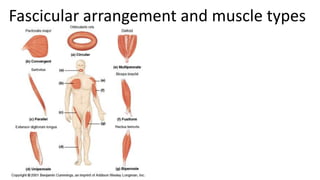
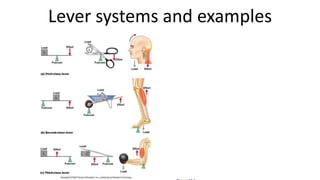
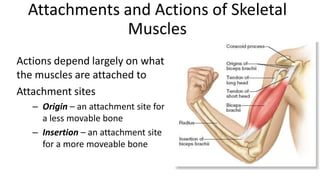
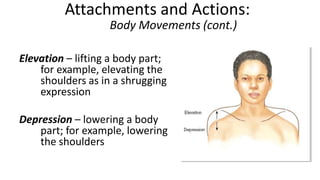
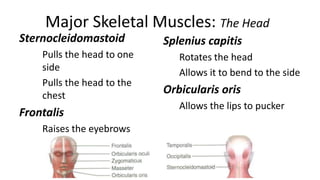
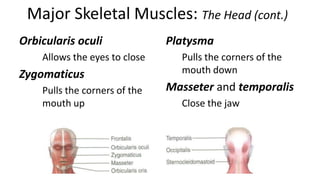
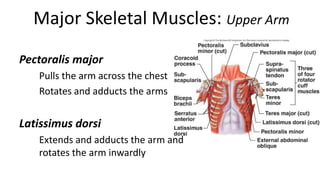
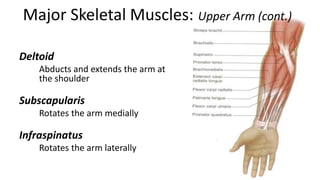
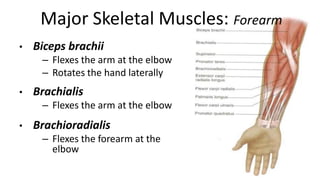
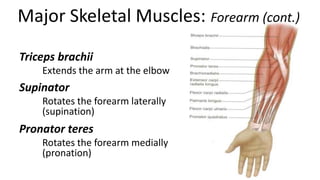
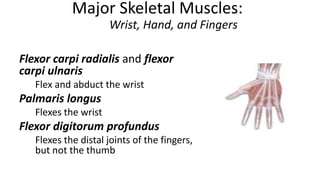
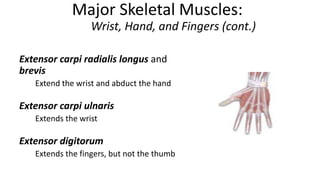
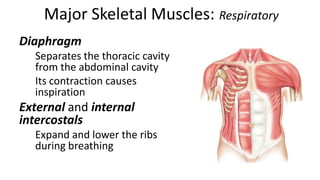
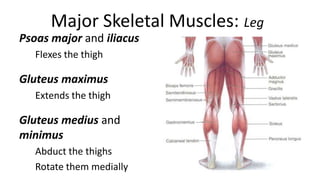
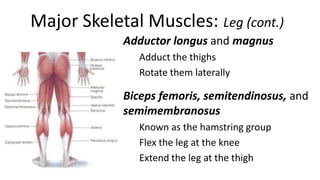
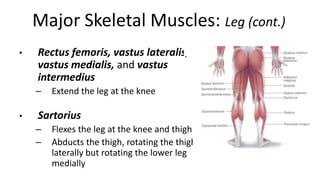
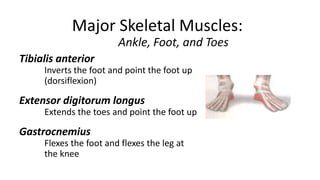
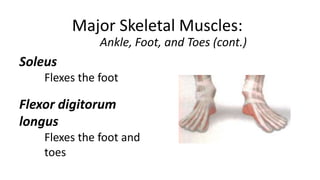
This document provides an overview of the muscular system, including muscle types, actions, and examples of lever systems. It describes how muscle attachments determine their actions and lists common movement terms. Finally, it details the major skeletal muscles in the head, upper arm, forearm, hand, respiratory system, abdomen, pectoral girdle, leg, ankle, and foot. It concludes with a brief overview of common muscular system diseases.