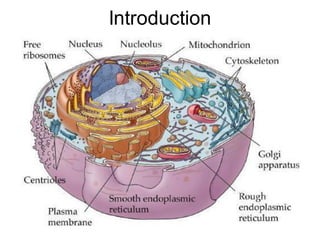
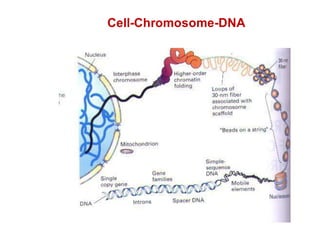
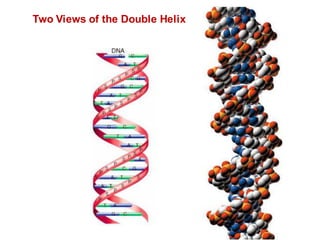
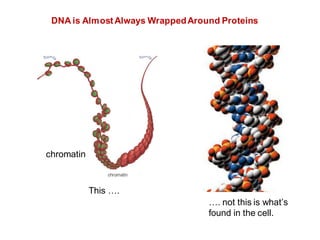
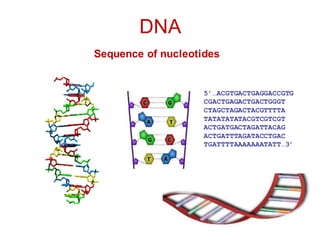
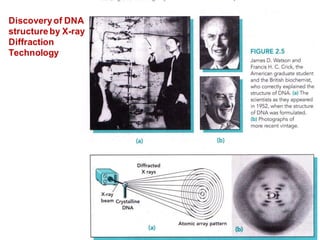
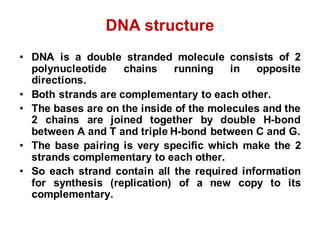
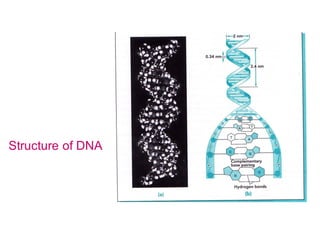
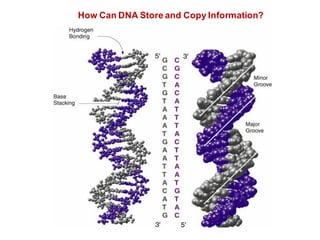
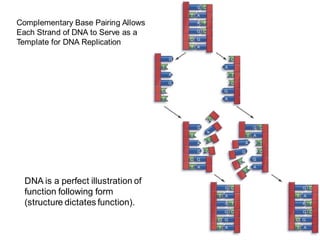
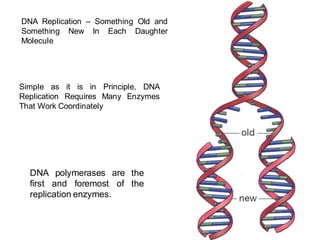
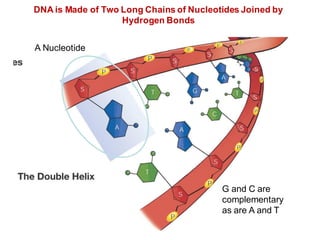
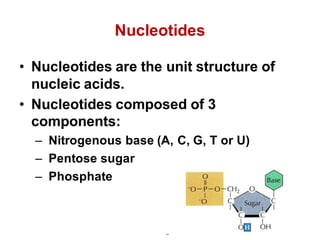
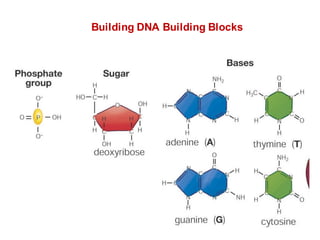
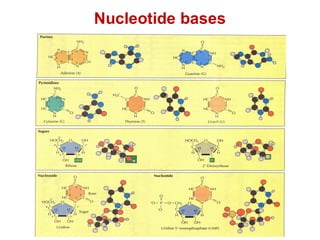
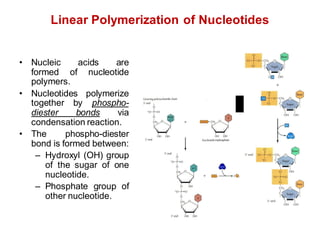
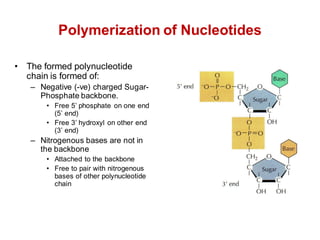
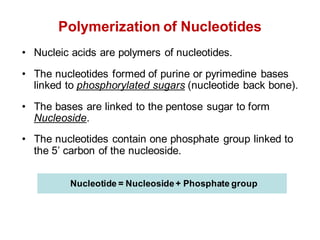
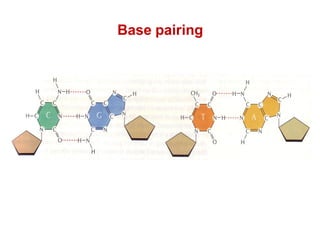
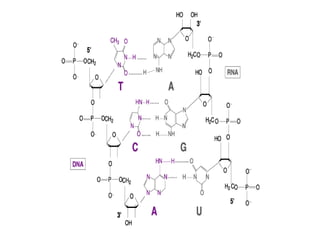
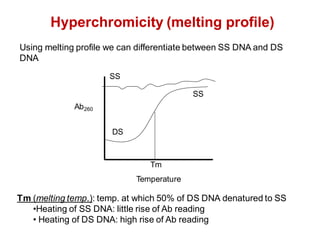
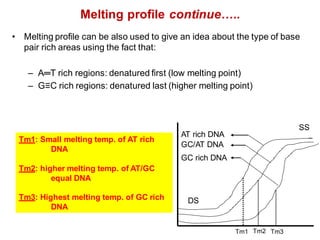
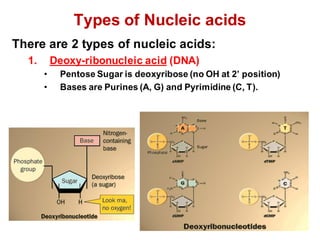
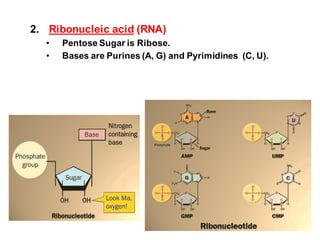
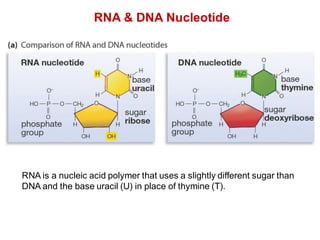
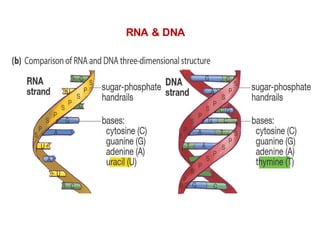
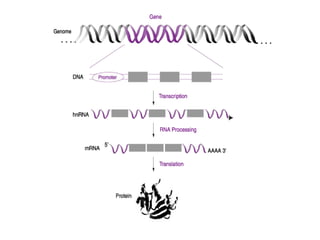
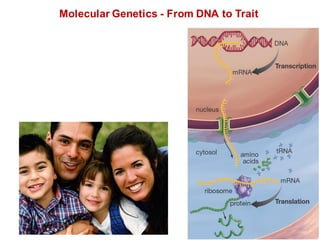
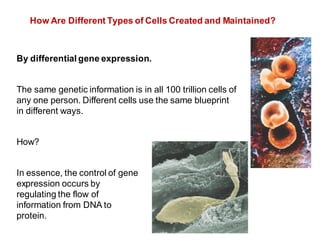
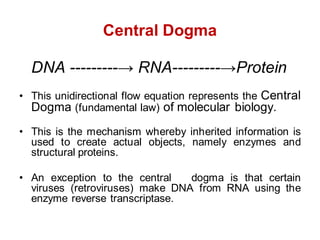
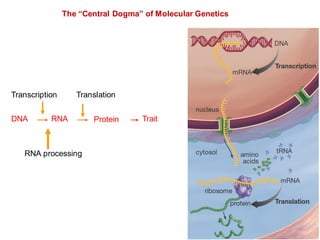
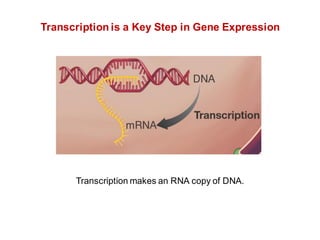
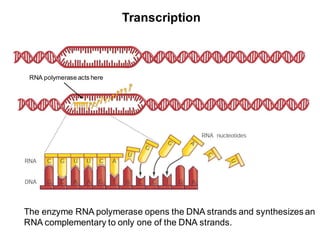
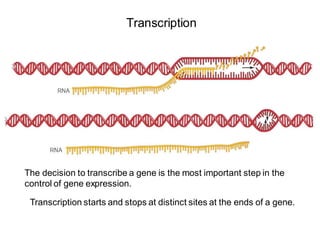
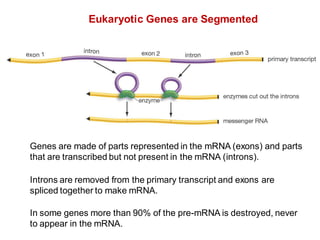
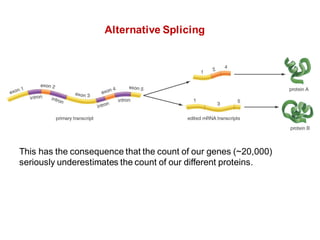
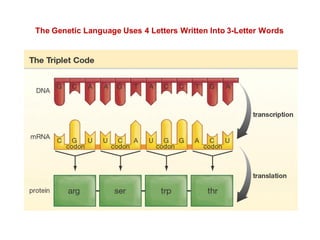
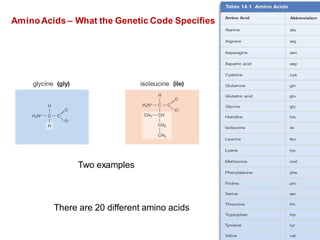
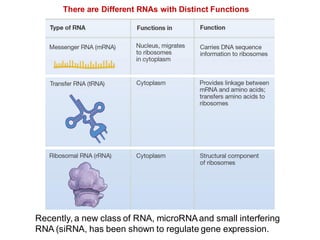
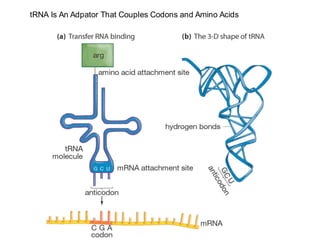
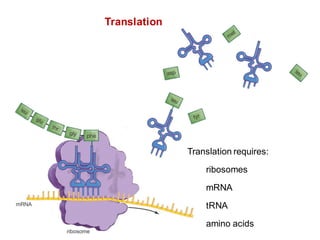
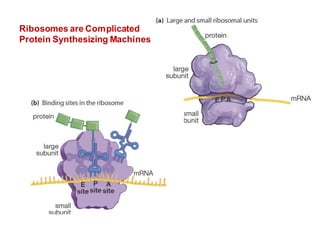
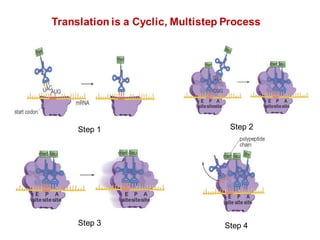
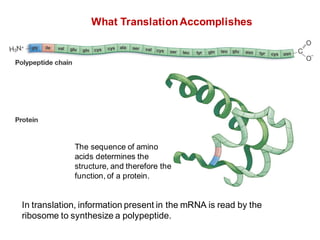
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that can store and copy information through its base-pairing properties. It is made up of two complementary strands held together by hydrogen bonds between nucleotide bases adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine. DNA can replicate itself using its base-pairing rules to create complementary daughter strands. Gene expression involves transcription of DNA into RNA and translation of RNA into protein. Differential gene expression allows cells to carry out specialized functions despite having the same DNA.