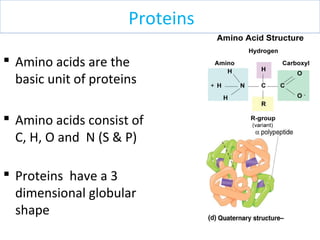
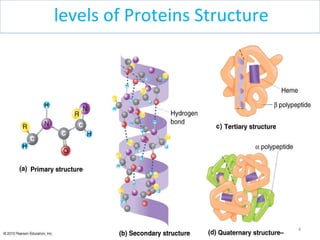
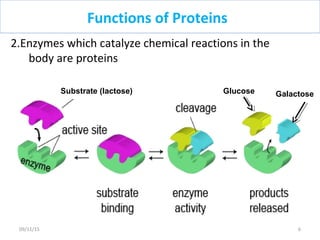
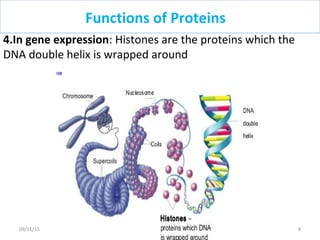
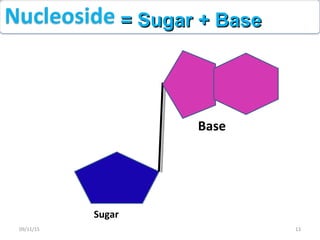
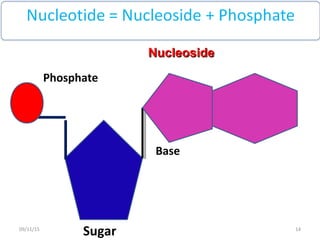
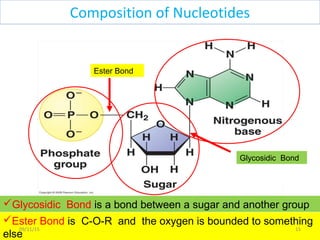
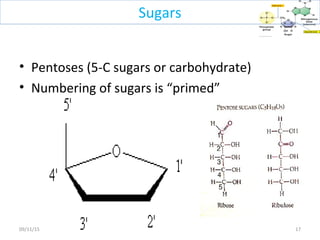
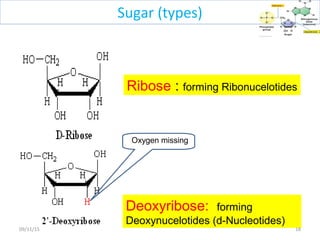
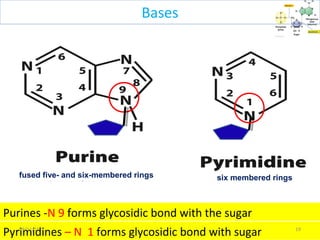
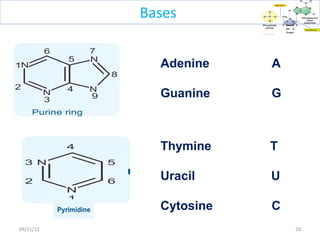
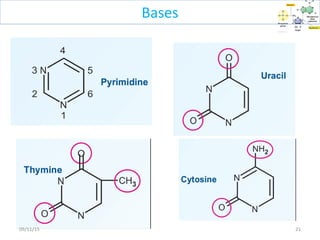
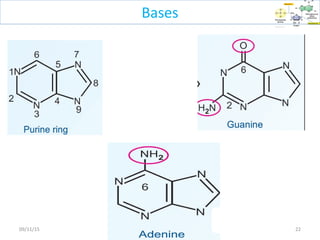
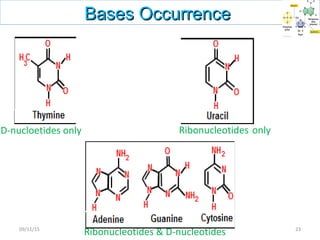
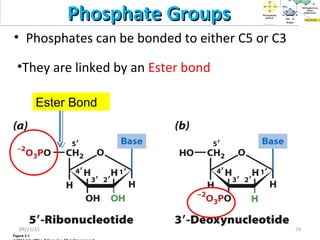
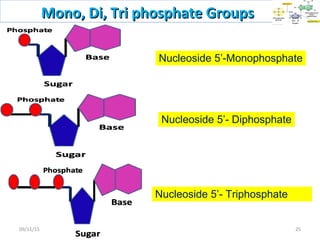
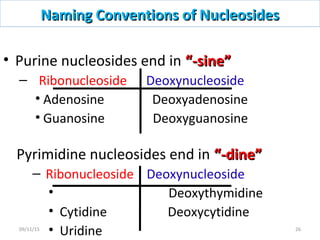
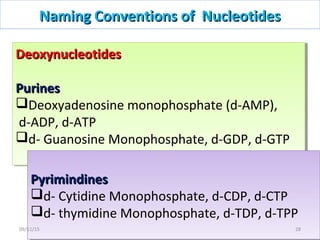
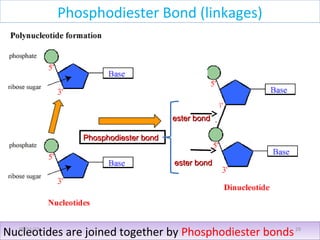
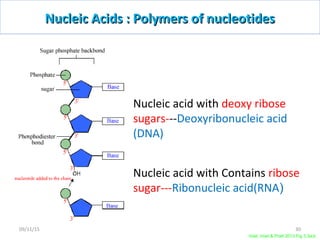
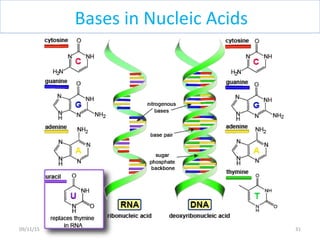
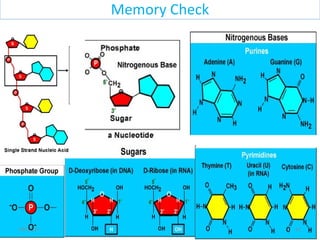
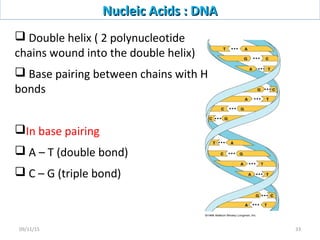
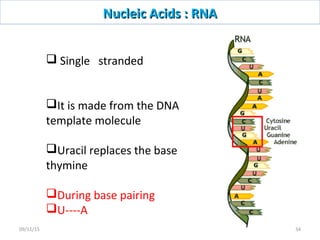
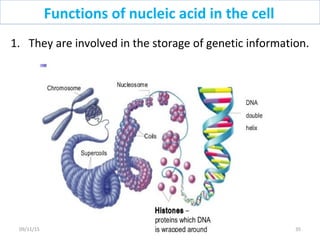
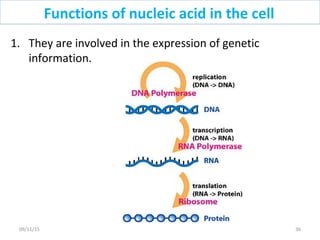
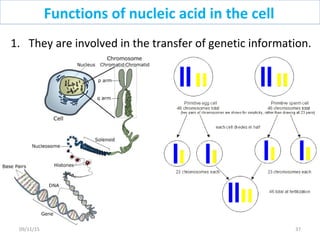
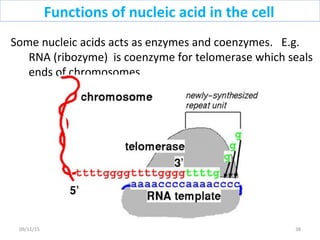
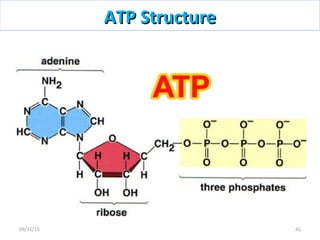
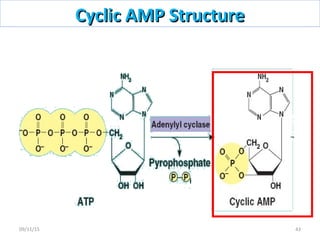
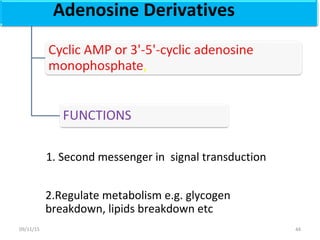
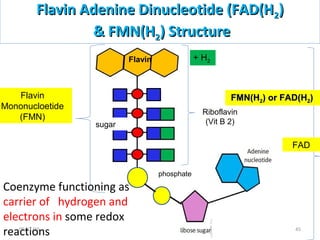
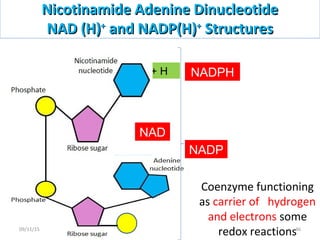
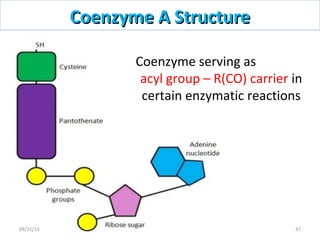
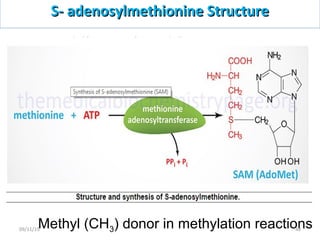
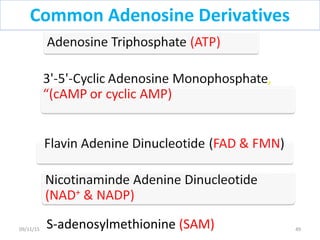
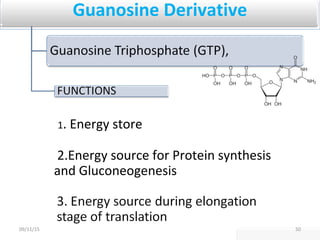
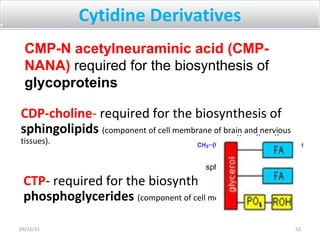
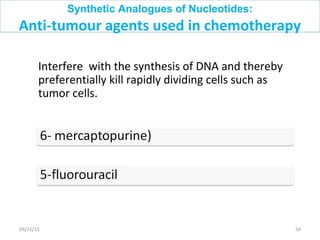
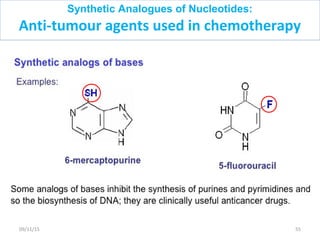
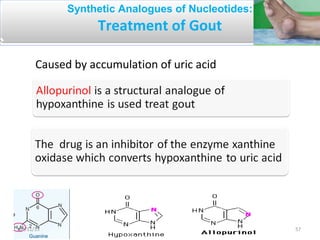
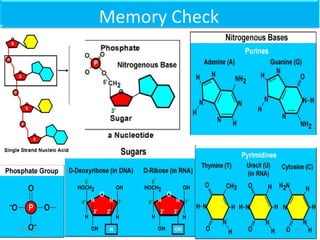
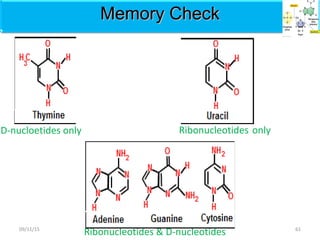
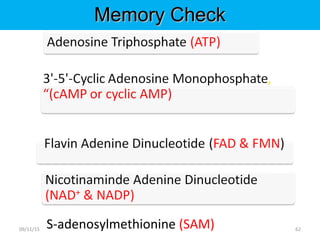
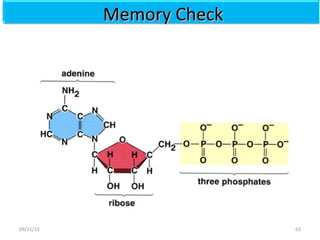
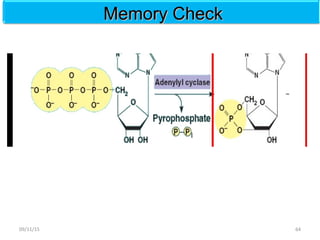
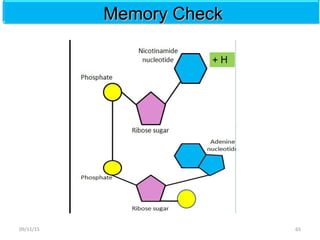
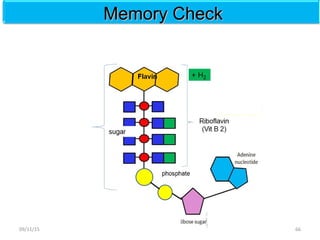
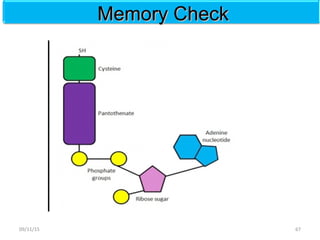
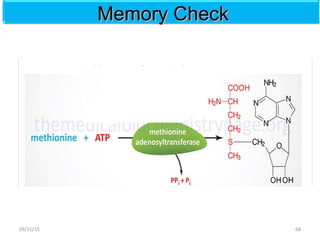
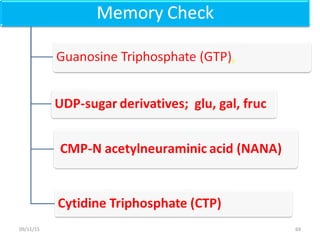
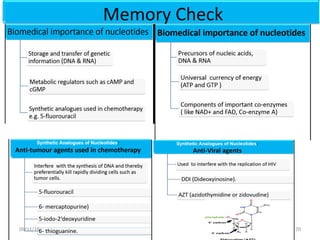
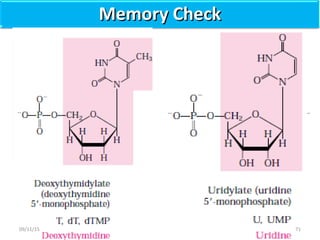
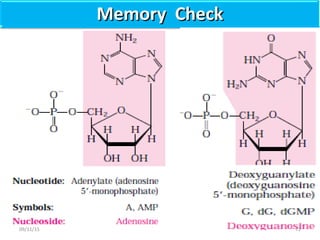
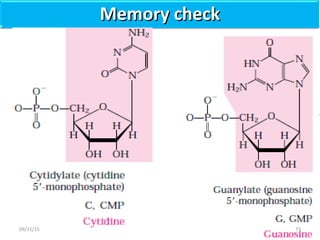
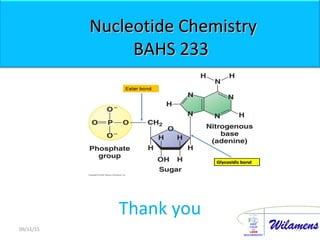
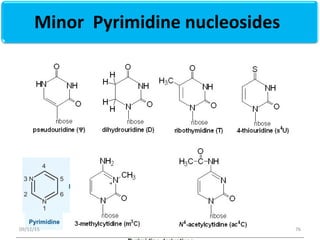
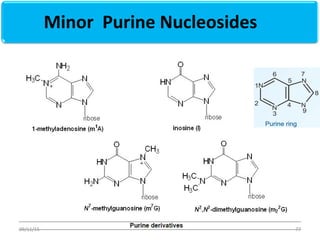
The document discusses proteins and nucleic acids. It defines that proteins are made up of amino acids connected by peptide bonds, and that nucleic acids are made up of nucleotides connected by phosphodiester bonds. The document outlines various functions of proteins including transport, enzymes, defense, gene expression, nutrients, and structural roles. It also discusses the structure of nucleotides including sugars, bases, and phosphate groups. Various nucleic acid functions are described such as storage and transfer of genetic information.