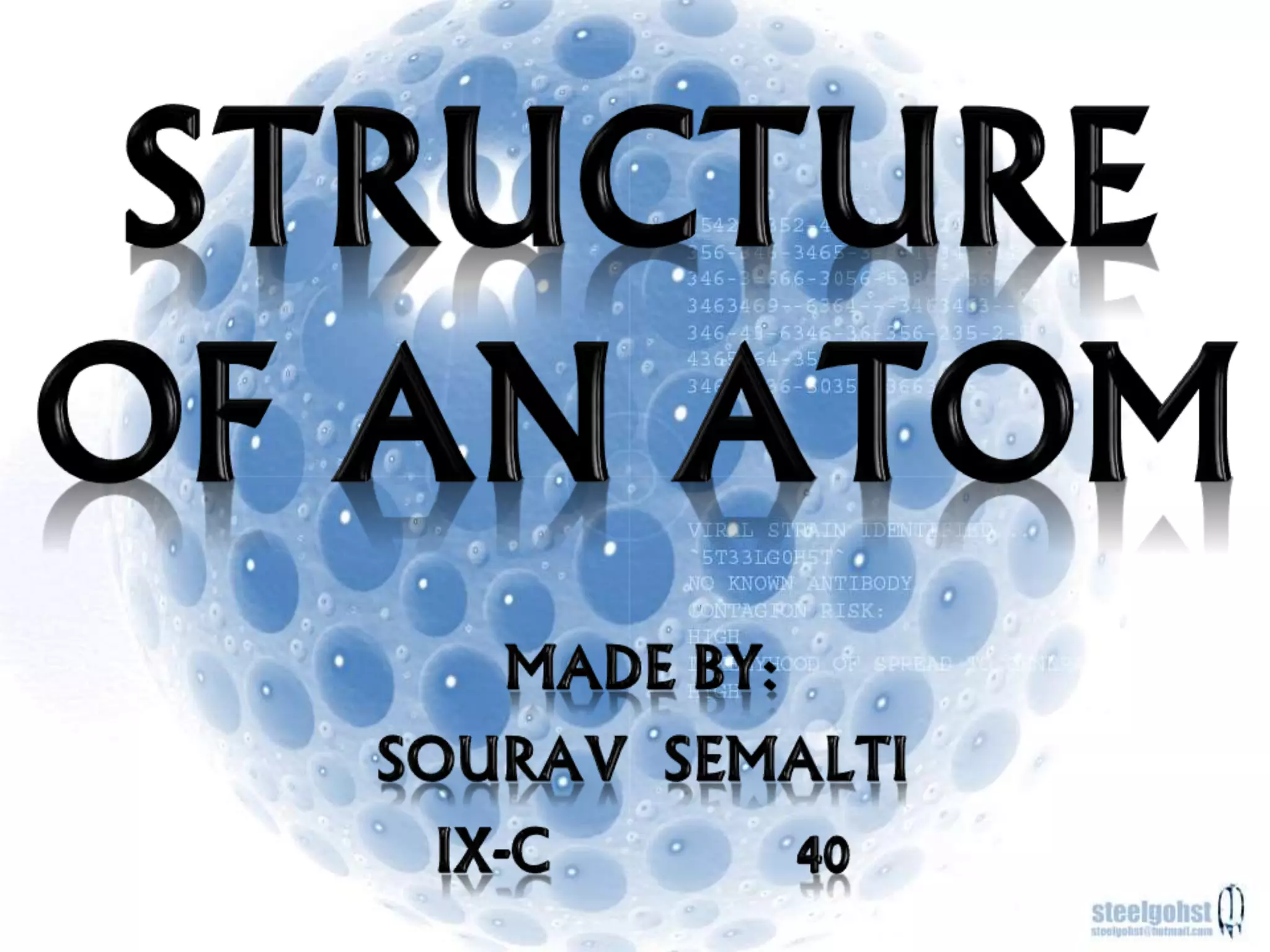
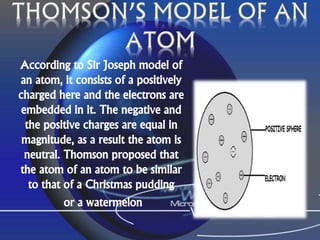
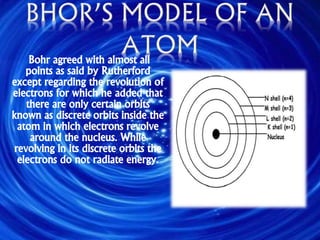
Democritus first proposed the idea of atoms in 460 BC, suggesting that all matter was made up of tiny spheres called atoms. An atom is the smallest particle of a chemical element that retains the properties of that element, and consists of a nucleus surrounded by a cloud of electrons. Atoms themselves are made up of even smaller subatomic particles - electrons, protons, and neutrons. The nucleus contains nearly all of an atom's mass and is very small compared to the size of the entire atom. Isotopes are variants of the same chemical element that differ in their number of neutrons.