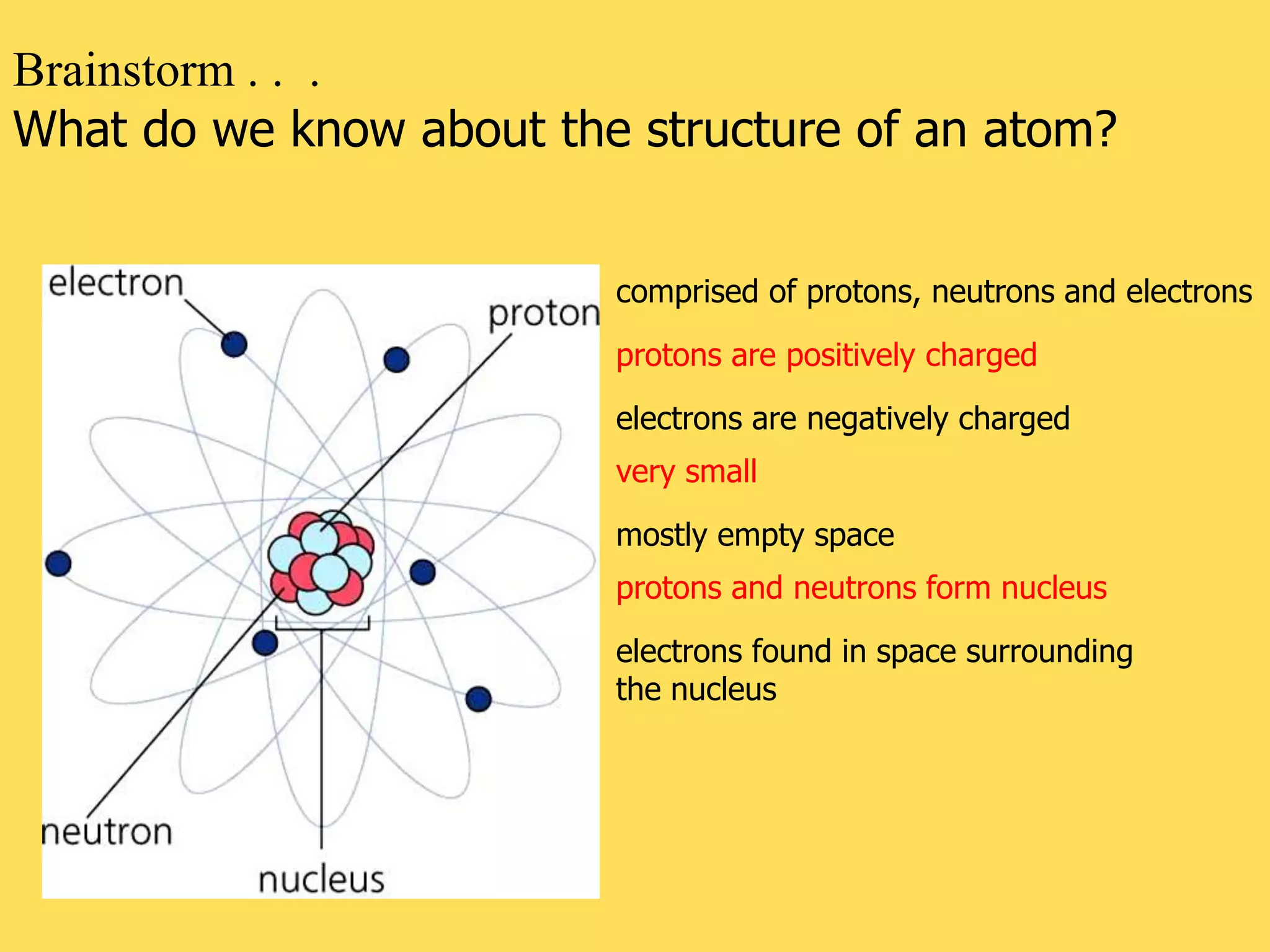
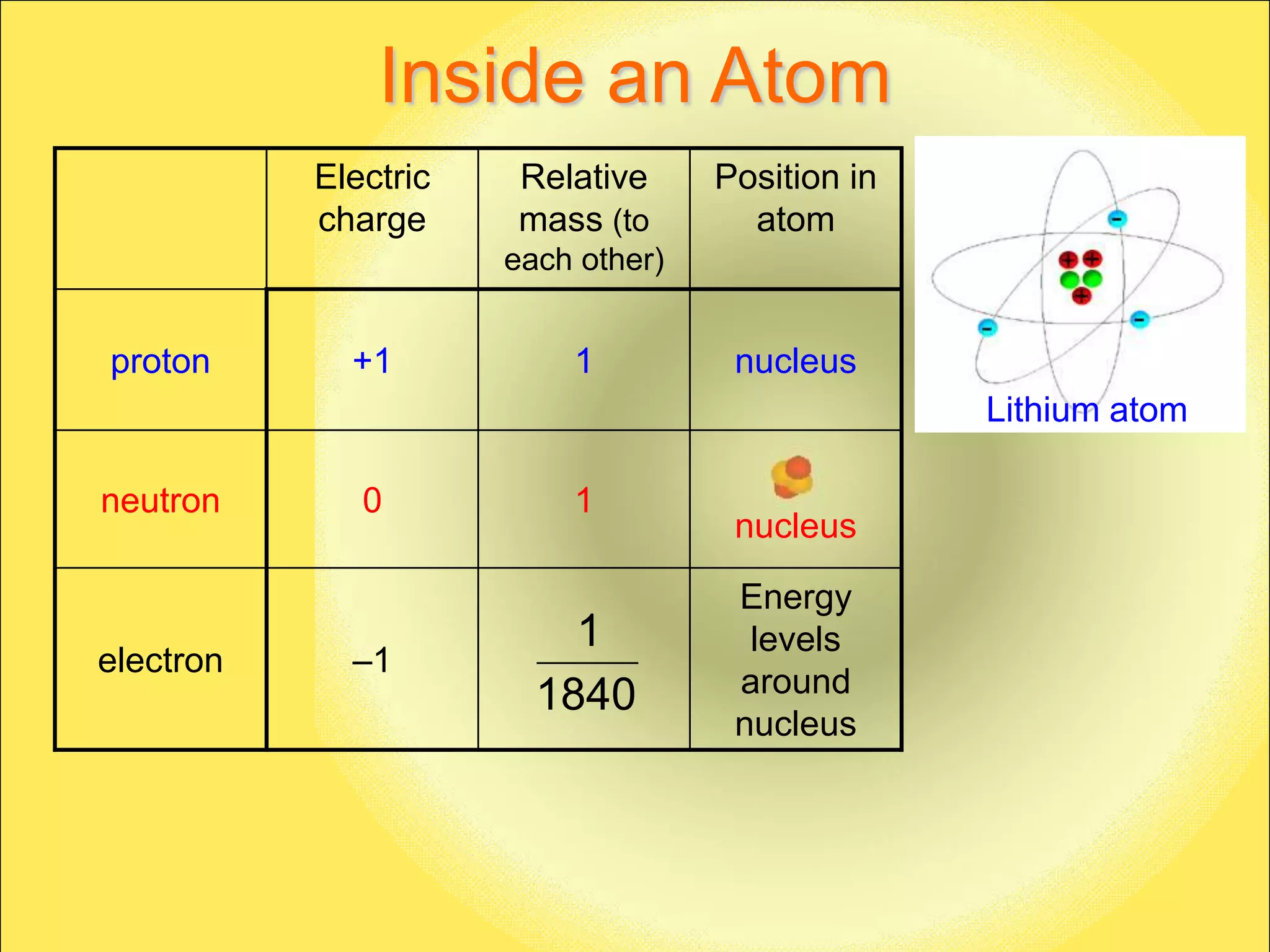
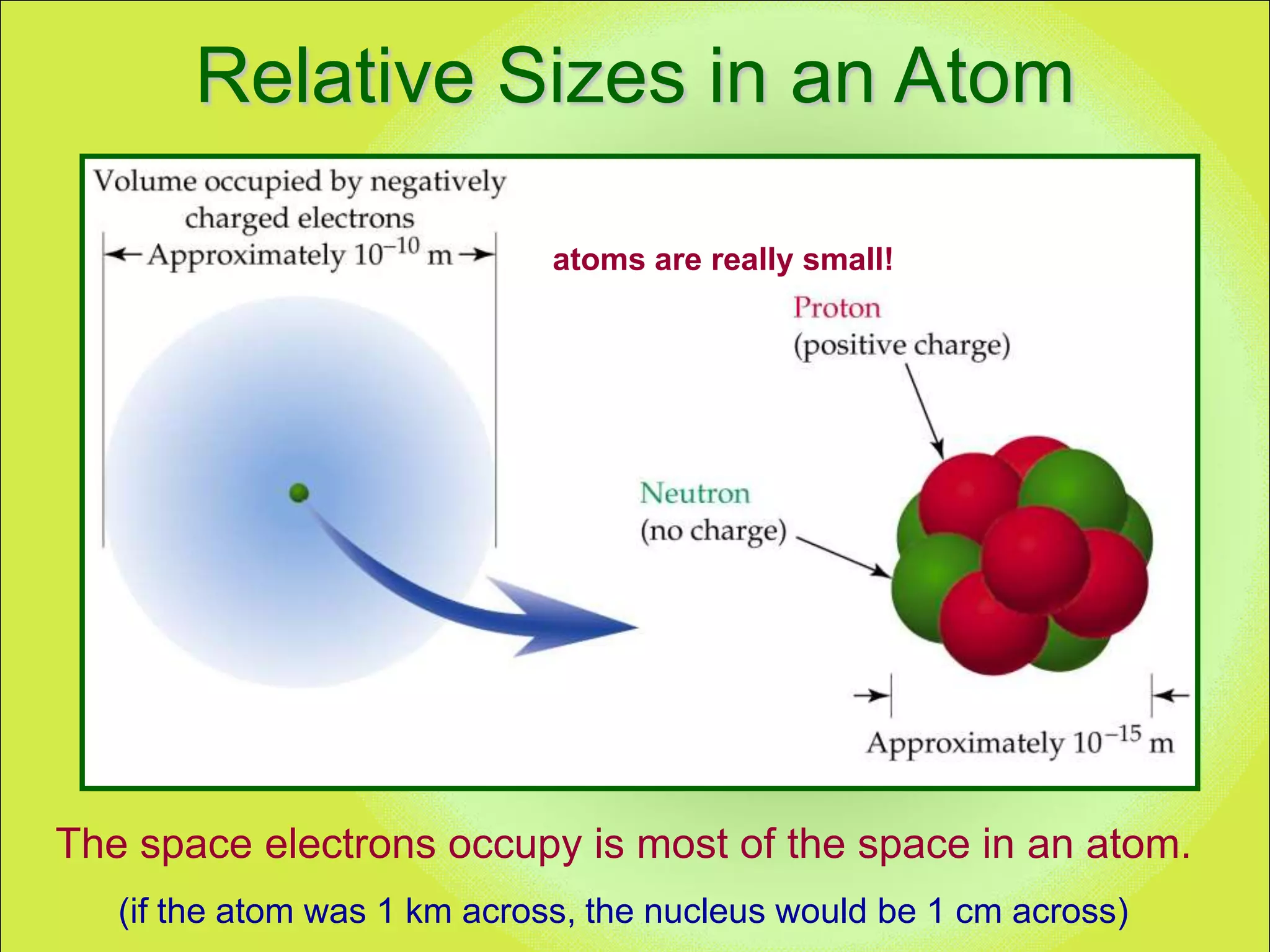
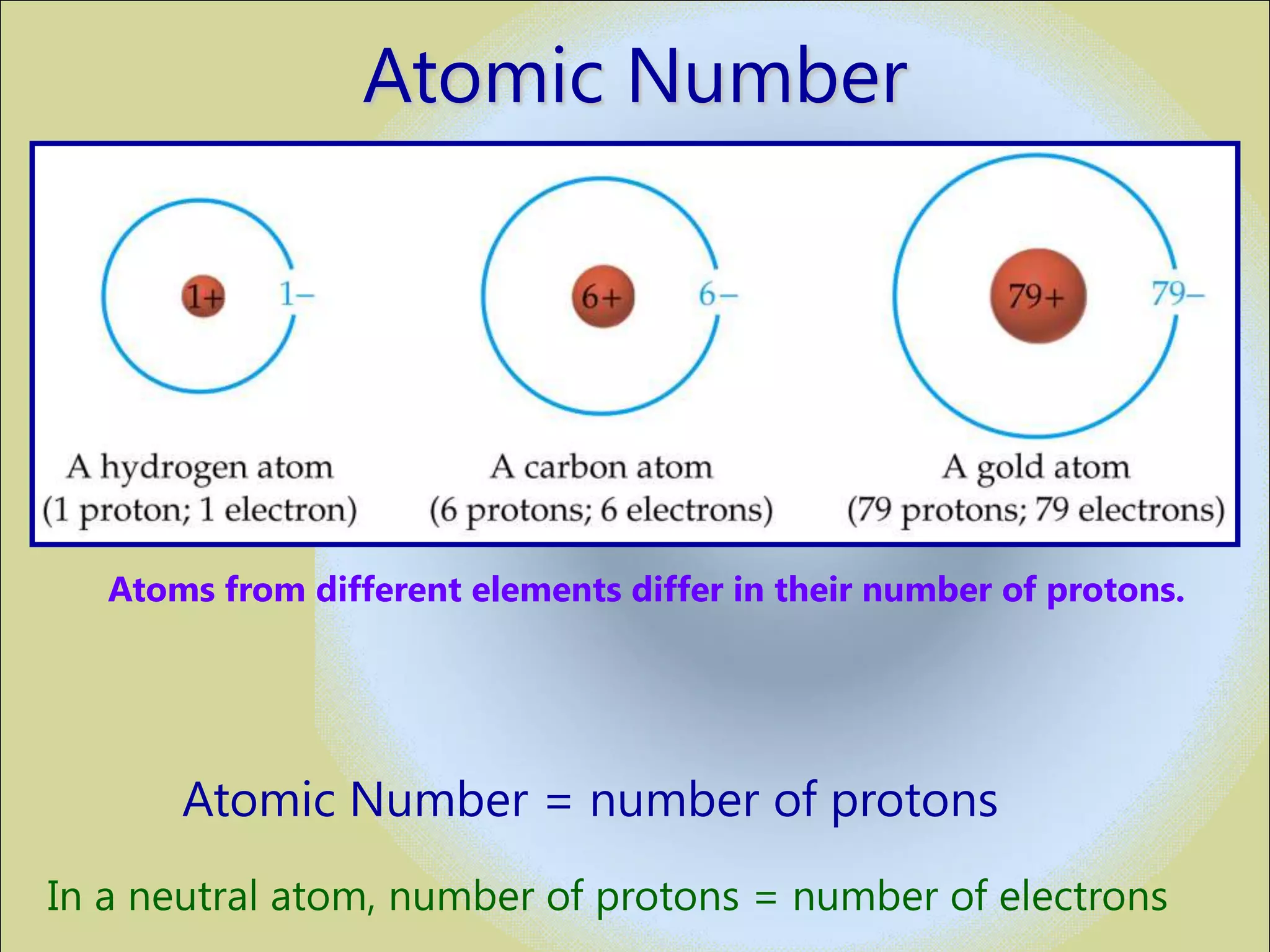
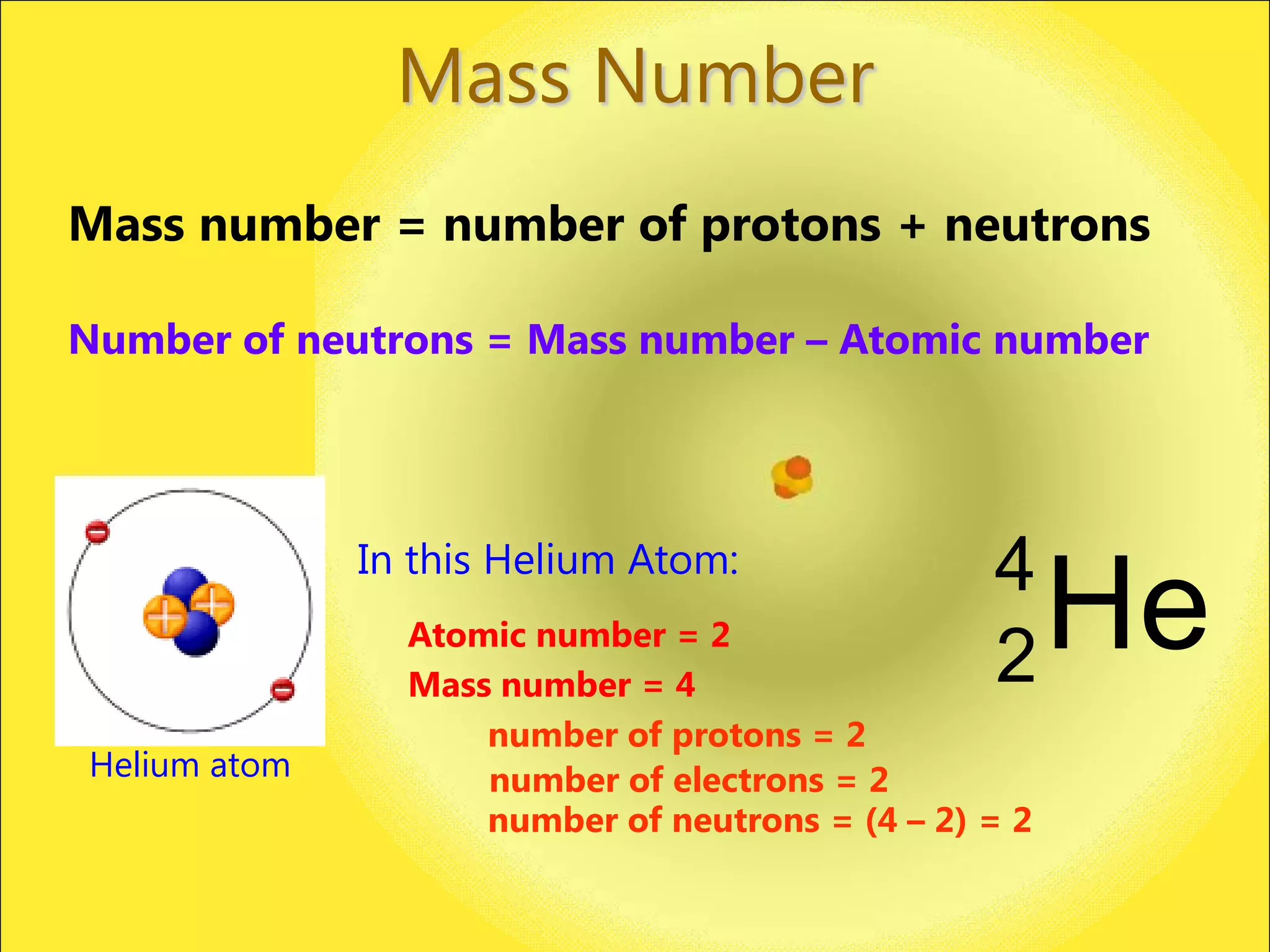
The document discusses the atomic model and structure of atoms. It states that atoms are comprised of protons, neutrons, and electrons, with protons and neutrons located in the central nucleus and electrons surrounding it in empty space. Protons are positively charged, electrons are negatively charged, and neutrons have no charge. The sizes of atoms and their components are described, with the nucleus being very small compared to the mostly empty space occupied by electrons. A brief history of atomic models is also provided.