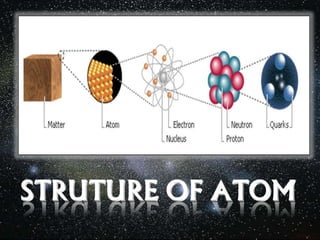
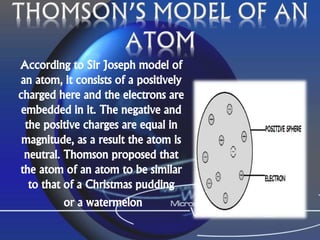
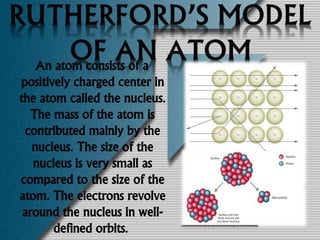
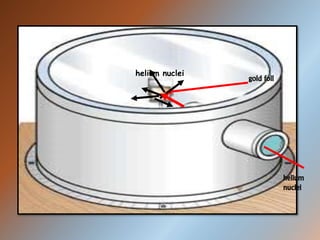
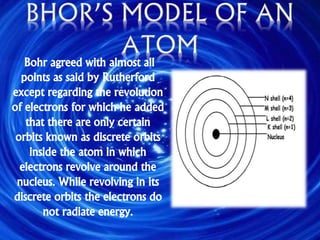
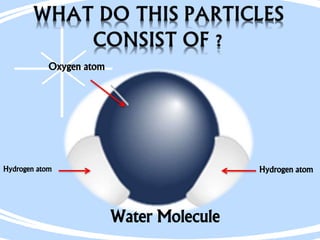
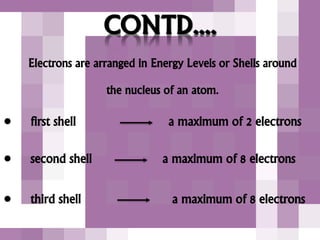
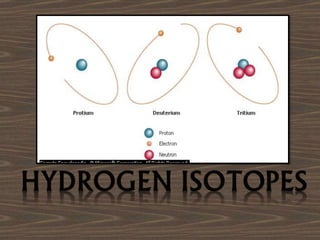
The document outlines the history and structure of atoms, detailing subatomic particles such as protons, neutrons, and electrons. It discusses key atomic models proposed by scientists like Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr, highlighting the organization of electrons in shells and the concepts of isotopes and isobars. Overall, it emphasizes that atoms are the fundamental building blocks of matter, exhibiting unique properties based on their composition.