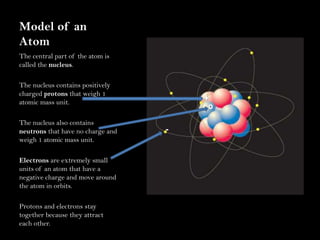
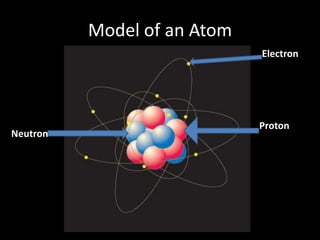
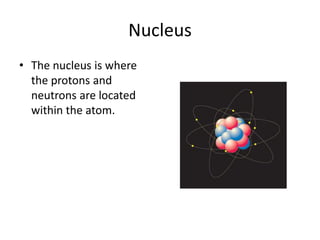
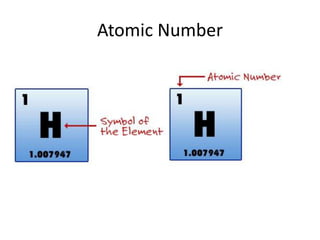
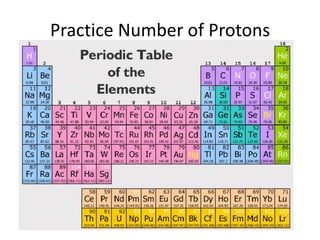
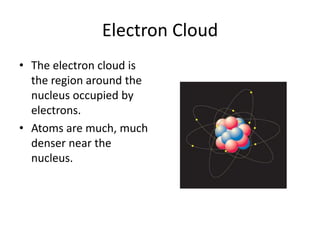
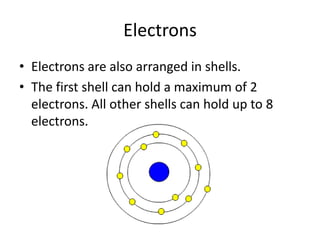
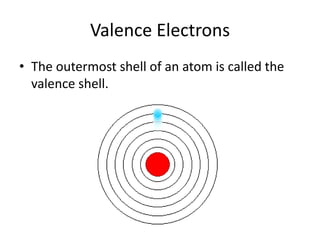
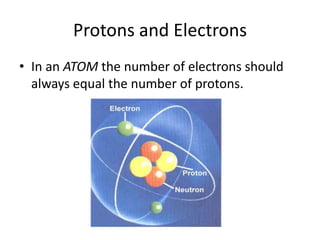
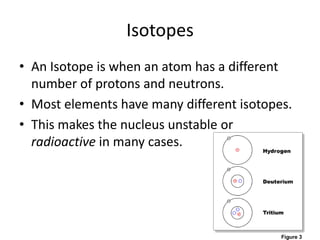
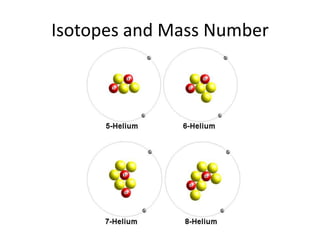
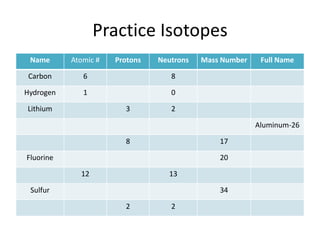
Scientists have been studying atoms since the 1800s using models to understand their structure and behavior. Early philosophers proposed the idea of atoms, while scientists like Dalton, Thomson, Rutherford, and Bohr developed atomic models through experiments. They discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a small, dense nucleus at the center containing protons and neutrons, and electrons orbiting the nucleus. The number of protons determines the element, while isotopes of an element have different numbers of neutrons.