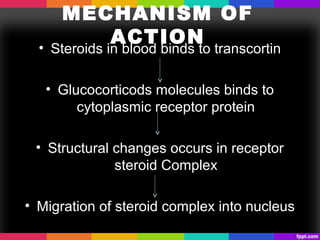
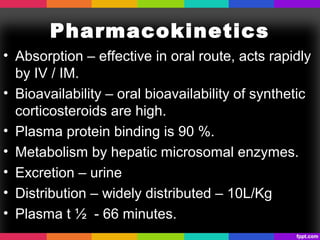
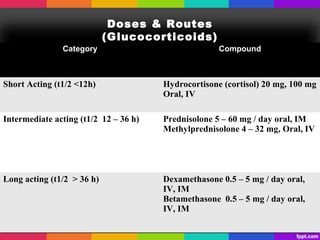
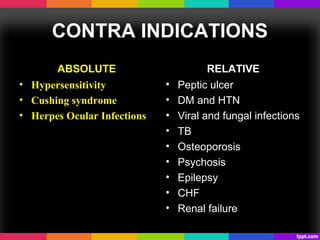
The document discusses corticosteroids and anabolic steroids. Corticosteroids are produced in the adrenal cortex and include glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. They regulate processes like stress response, immune response, and inflammation. Anabolic steroids are synthetic derivatives of testosterone that promote muscle and bone growth. Both have important therapeutic uses but also carry health risks with prolonged or improper use such as infections, liver damage, and psychological side effects.