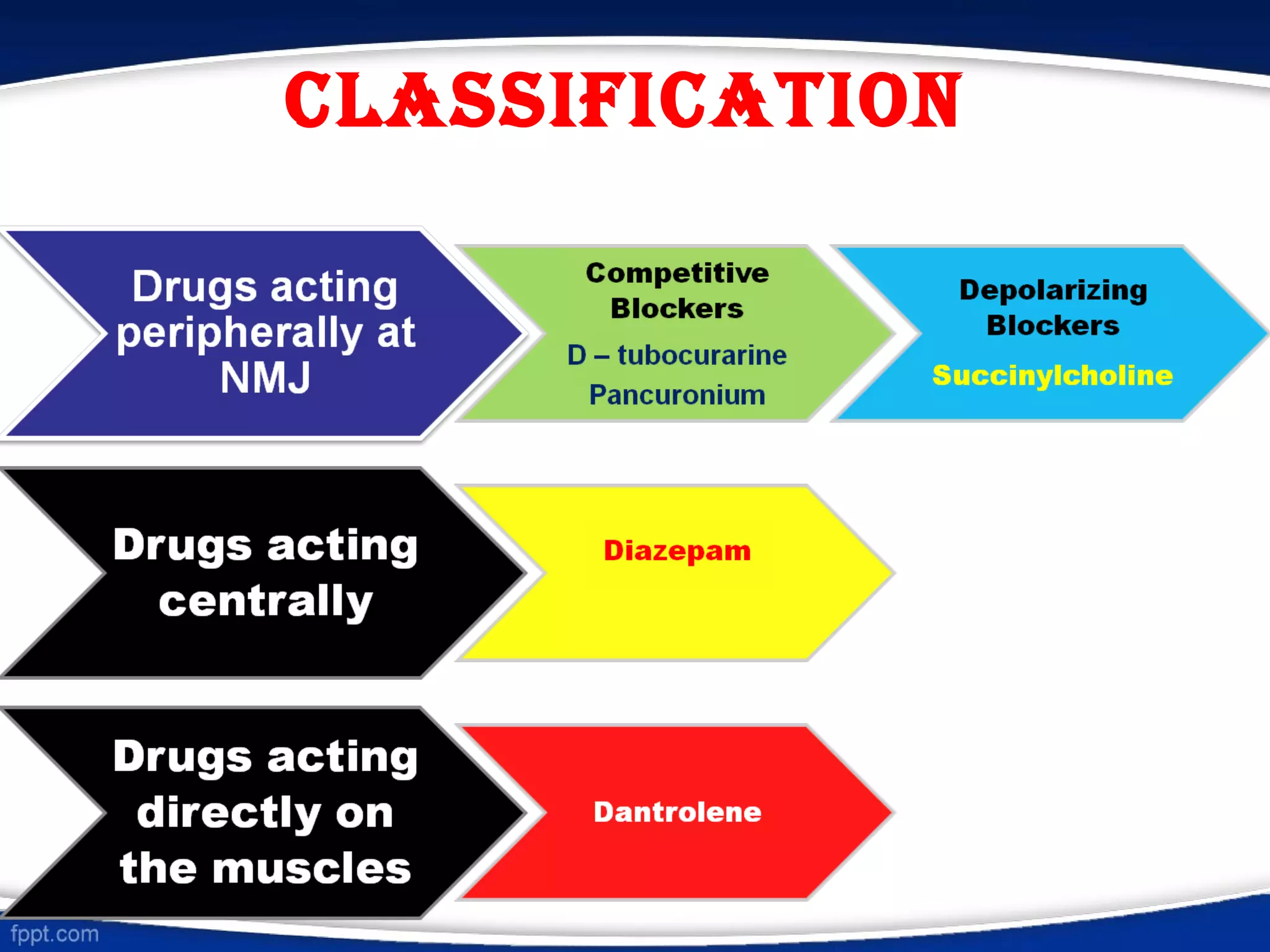
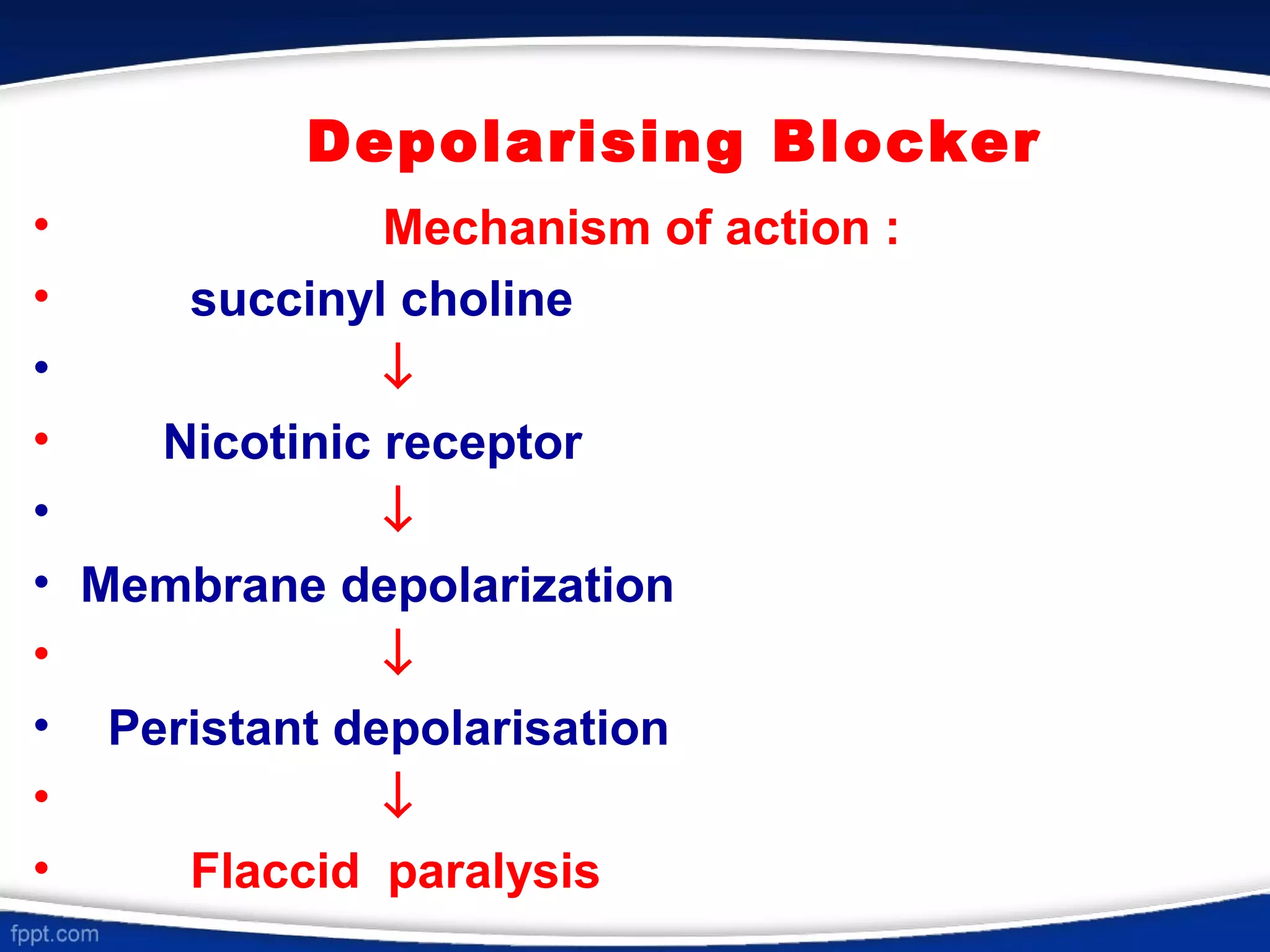
This document discusses skeletal muscle relaxants (SMRs), which are drugs that reduce muscle tone by acting at the neuromuscular junction or in the central nervous system. It classifies SMRs as peripherally or centrally acting. Peripherally acting SMRs include neuromuscular blockers like tubocurarine, which bind to nicotinic receptors and block the action of acetylcholine, causing paralysis. Succinylcholine is a depolarizing blocker that stimulates nicotinic receptors, causing depolarization and paralysis. Centrally acting SMRs like diazepam and baclofen decrease muscle tone by depressing polysynaptic reflexes in the spinal cord. SMR