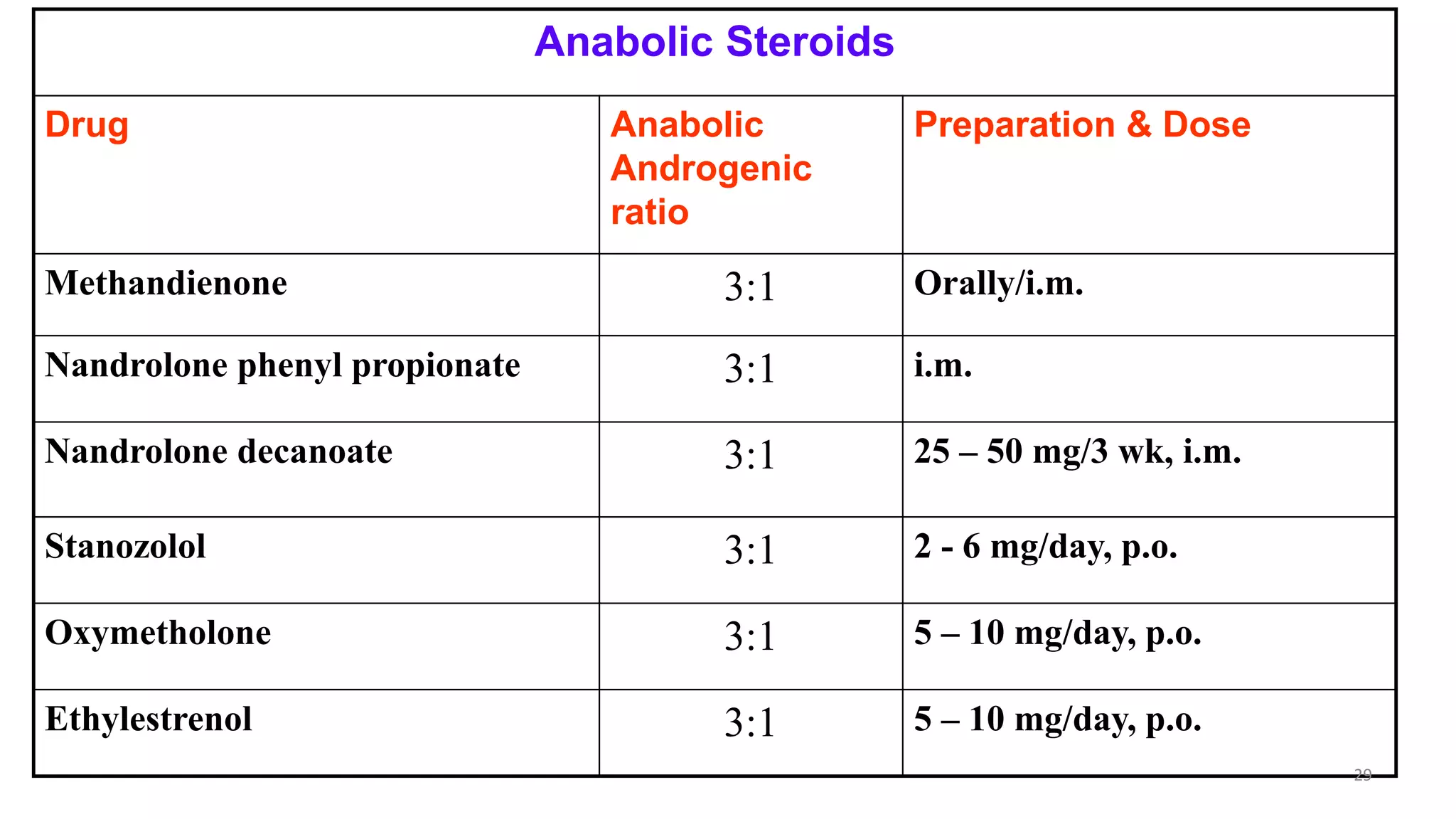
This document summarizes corticosteroids, including their biosynthesis, regulation, classification, mechanisms of action, effects, and therapeutic uses. Corticosteroids are synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex under ACTH control. They are classified as mineralocorticoids and glucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids such as cortisol regulate carbohydrate and protein metabolism and have anti-inflammatory effects. Prolonged corticosteroid use can cause HPA axis suppression and metabolic side effects like hyperglycemia. Therapeutic uses include replacing cortisol in adrenal insufficiency and treating inflammatory/autoimmune conditions.