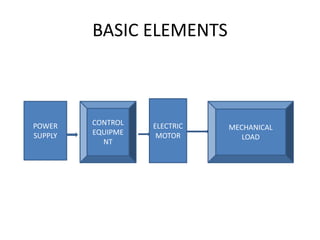
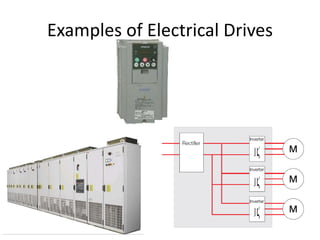
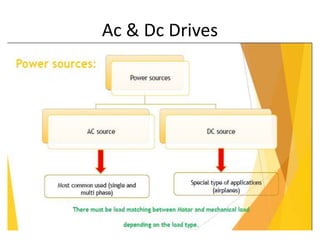
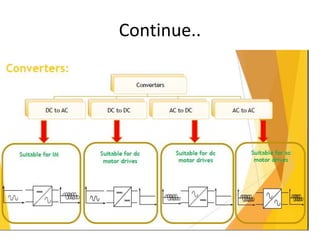
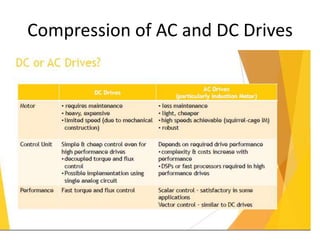
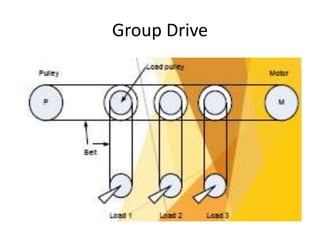
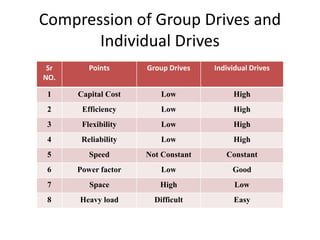
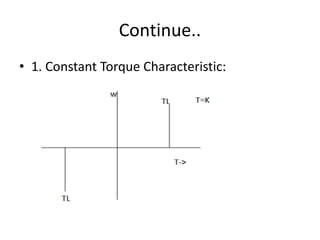
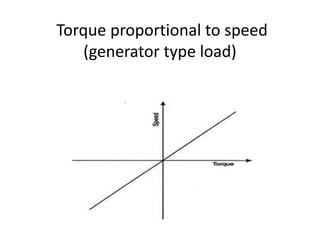
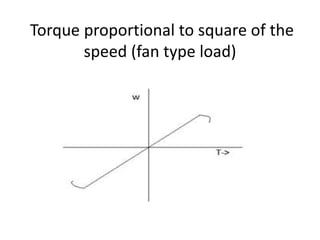
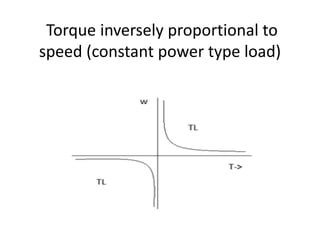
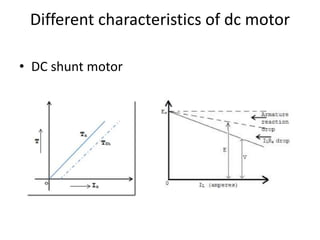
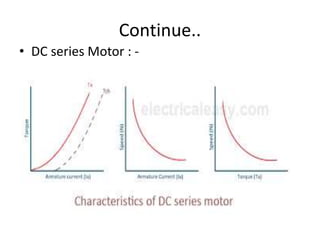
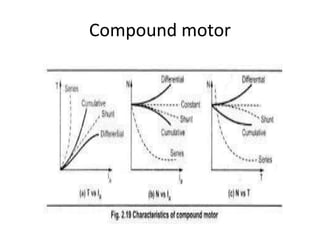
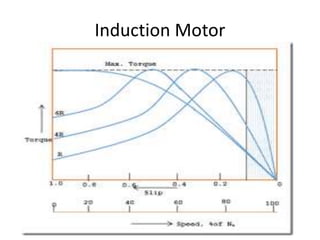
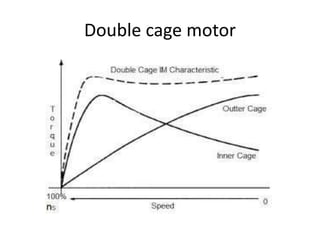
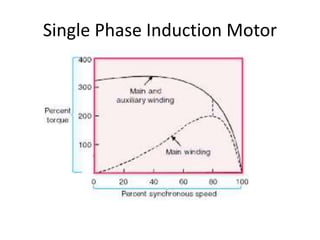
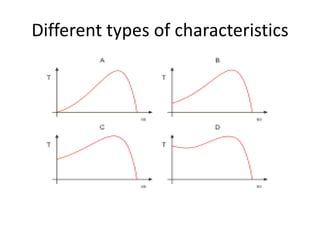
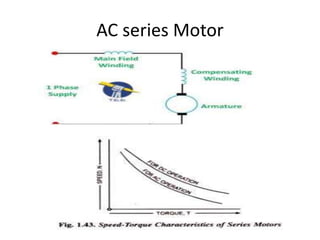
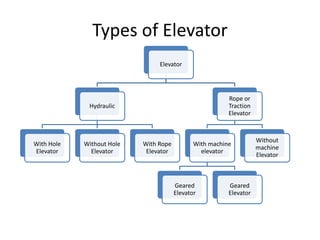
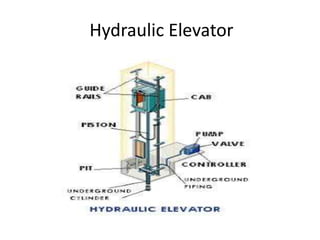
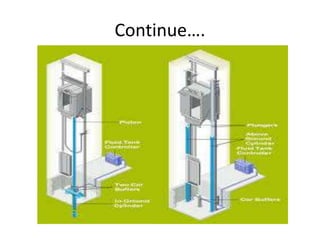
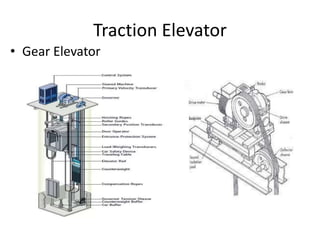
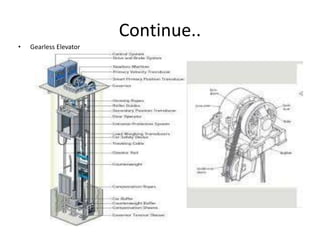
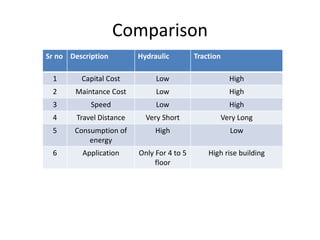
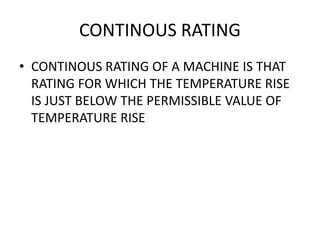
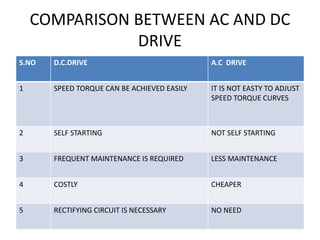
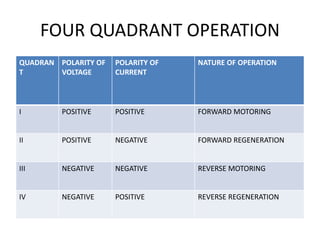
The document discusses electrical drives and control. It defines an electrical drive as a unit consisting of an electric motor, energy transmitting shaft, and control equipment. Drive systems combine electrical drives with corresponding loads. Advantages of electrical drives include feasible control characteristics, wide speed and torque ranges, higher efficiency, lower noise, and easier maintenance. Examples of electrical drives include AC and DC drives. Types of electrical drives include group drives, individual drives, and multimotor drives. Group drives have one motor driving multiple machines while individual drives have one dedicated motor per machine. Selection of motors depends on the load characteristics.