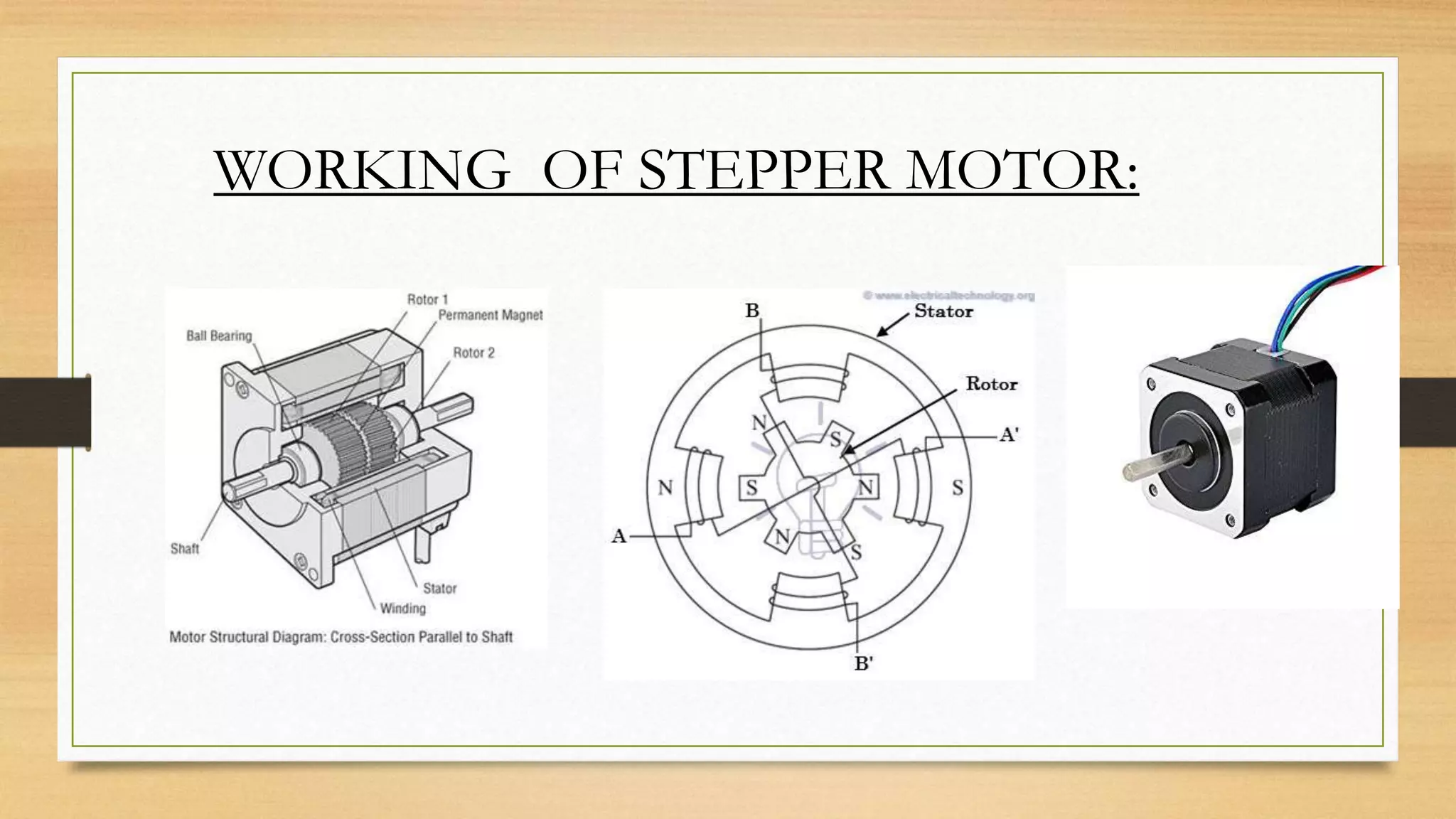
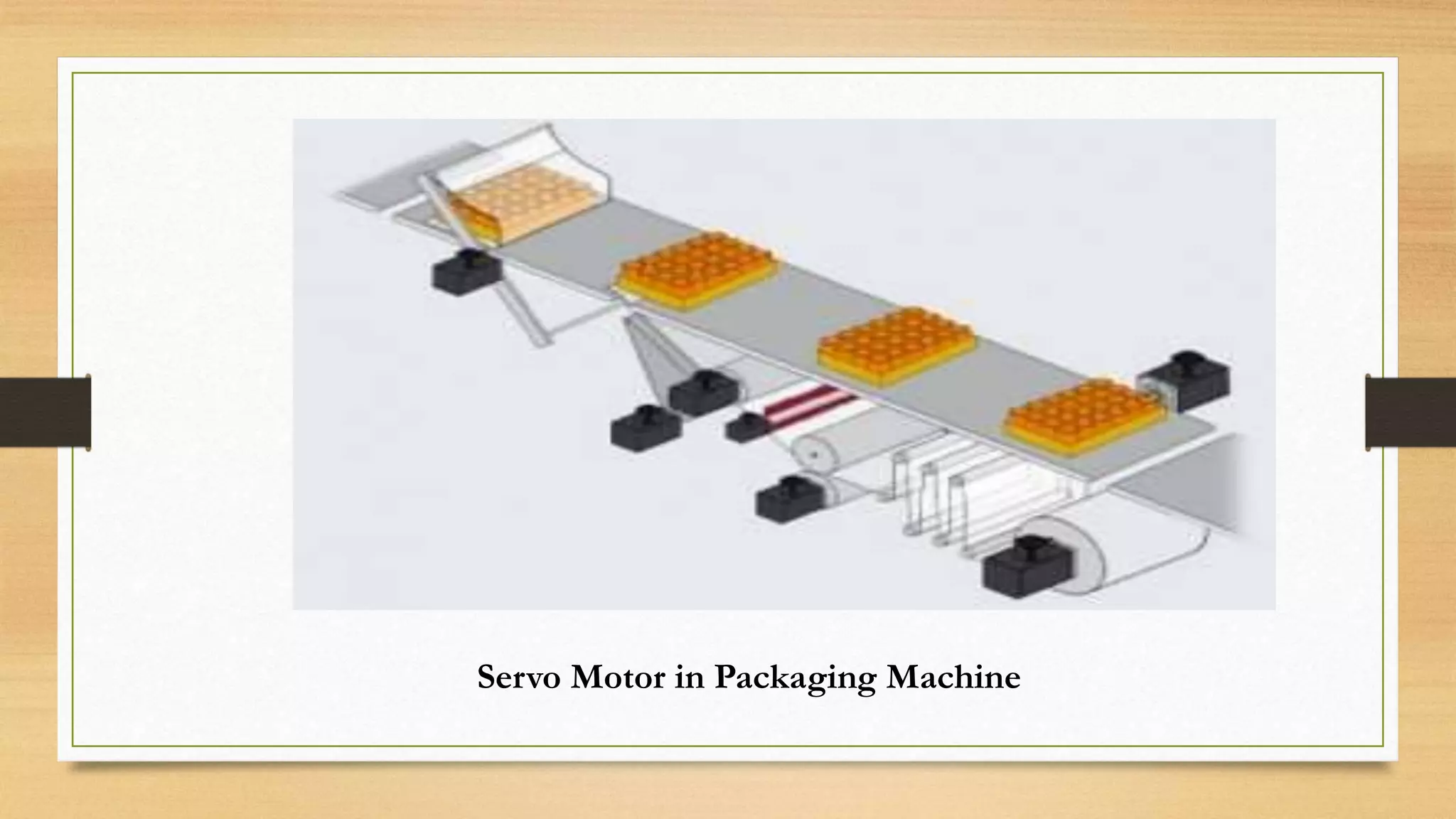
This document provides an overview of stepper motors and servo motors. It discusses the basic introduction, fundamentals of operation, and types of stepper motors, including permanent magnet, variable reluctance, and hybrid synchronous stepper motors. Applications of stepper motors include computer controlled positioning systems, lasers and optics equipment, and various industrial machinery. The document also introduces servo motors, listing types like DC, AC, positional rotation, continuous rotation, and linear servo motors. It describes the working principle of servo motors and their applications in areas like robotics, automation technology, home electronics, vehicles, and packaging machines. The document concludes by referencing several sources for additional information.