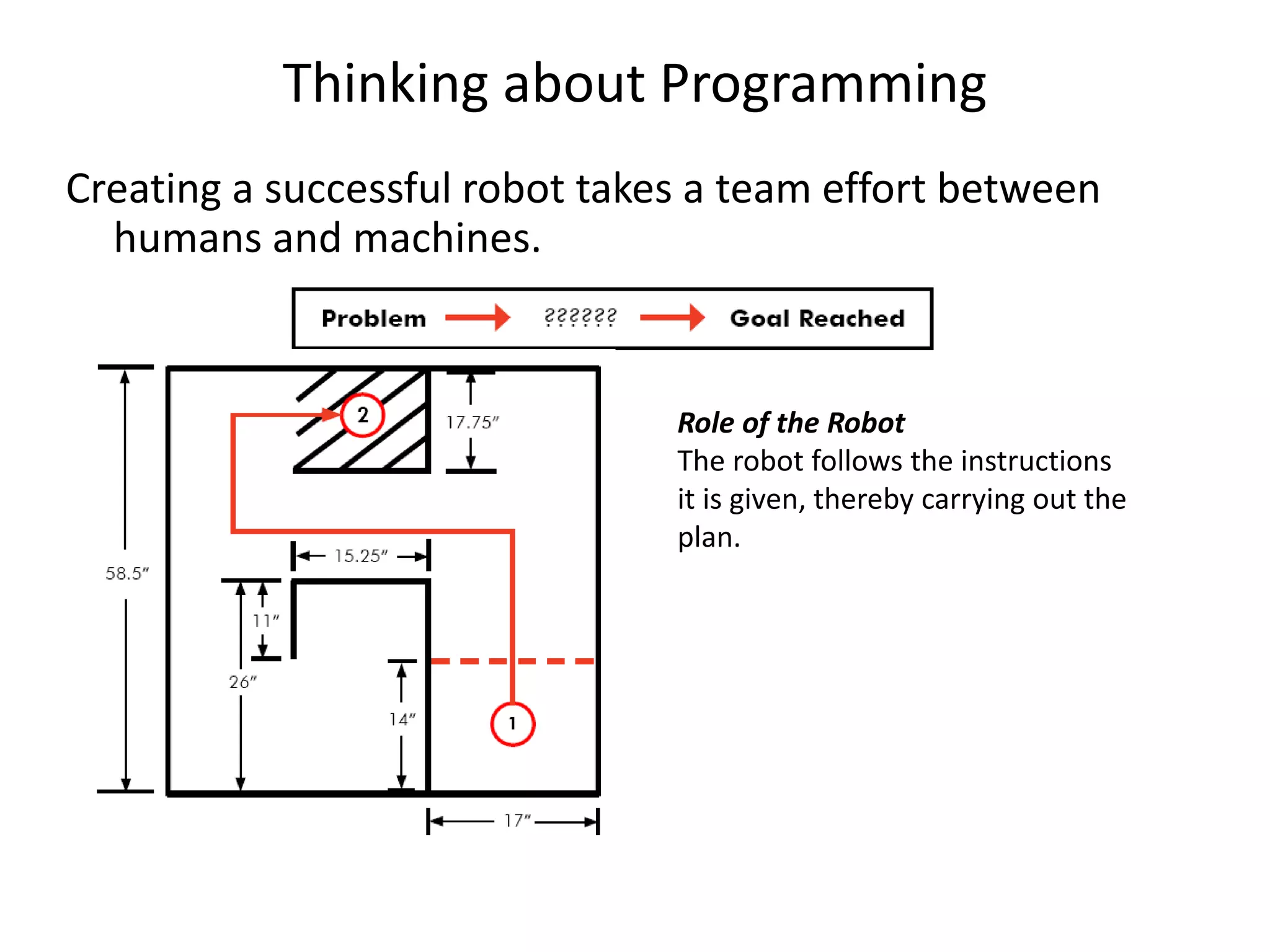
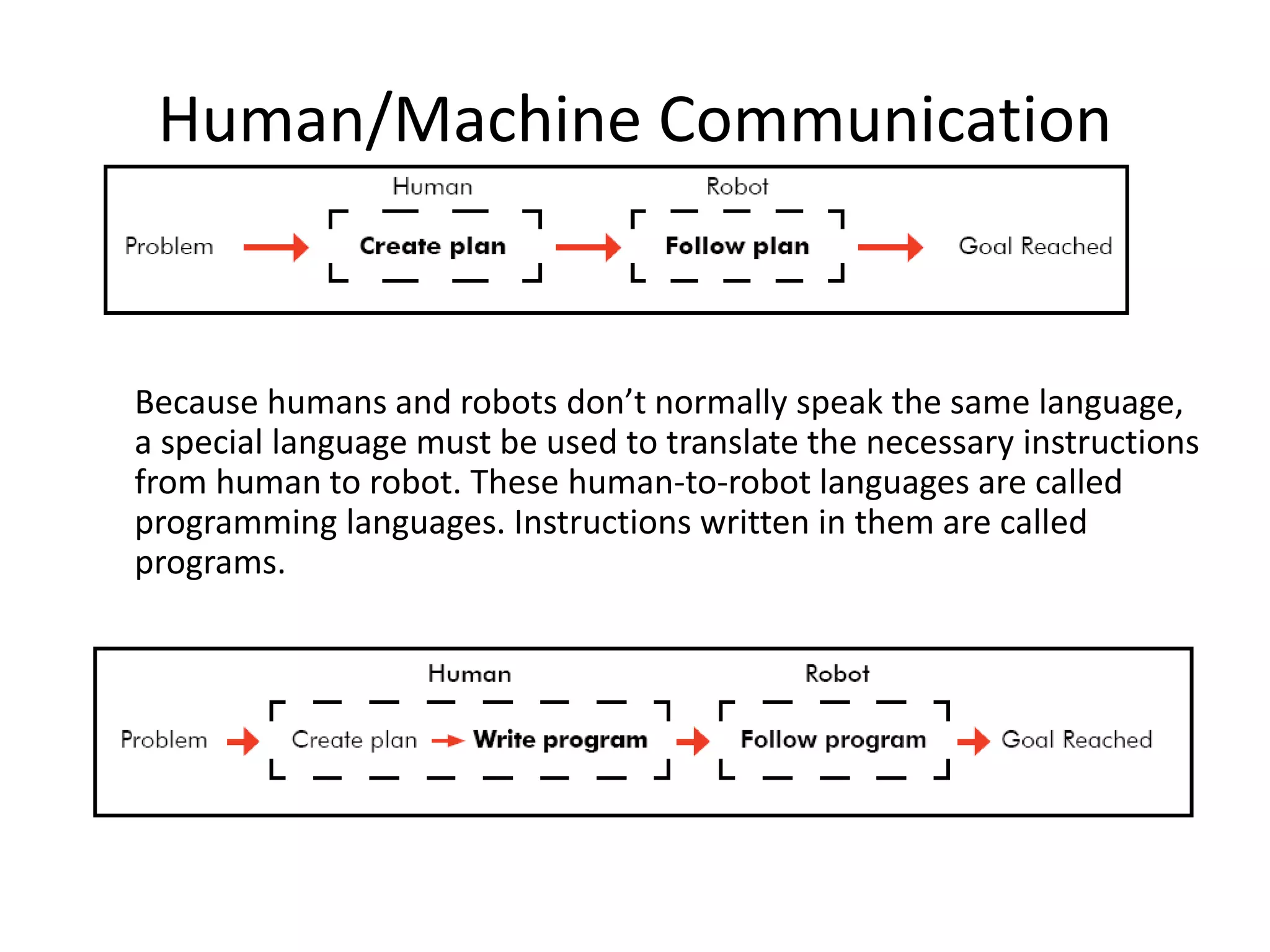
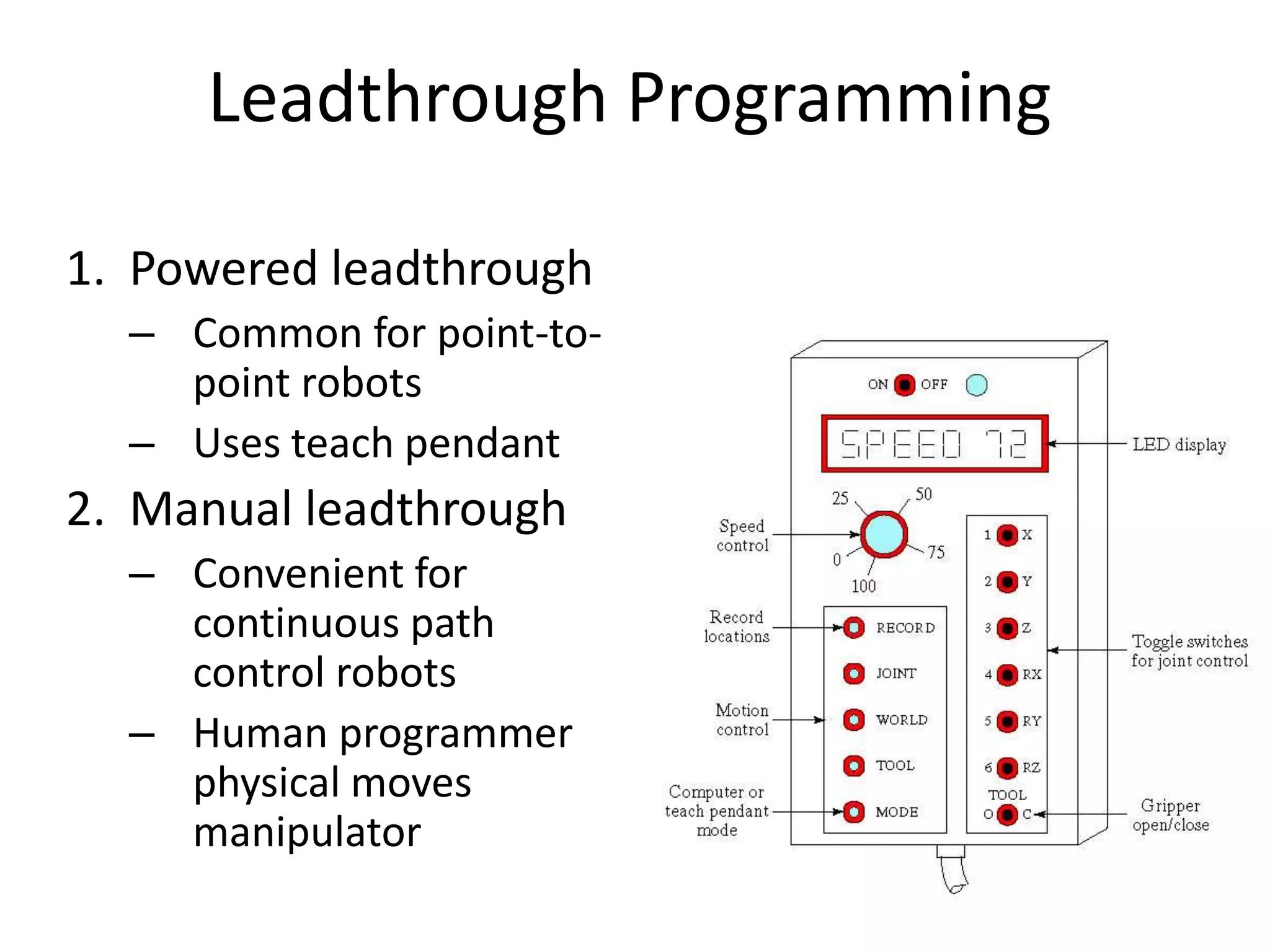
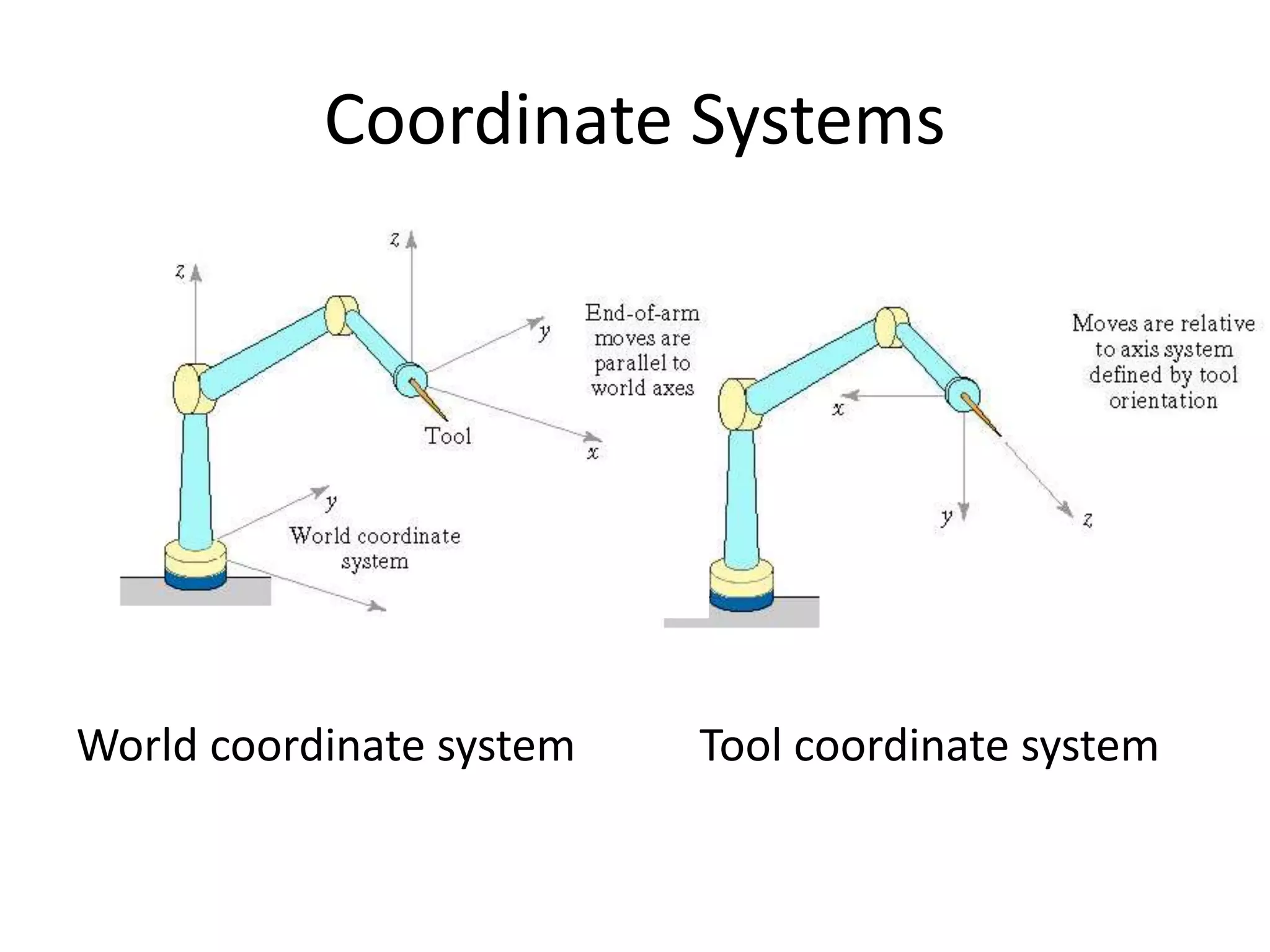
This document discusses robot programming methods. It describes leadthrough programming where the robot is taught motions by physically moving it through the required cycles. It also discusses using textual programming languages to enter commands into the robot controller. Additionally, it explains simulation and off-line programming where the program is prepared remotely and downloaded to the robot without using leadthrough methods. Finally, it provides examples of motion commands, interlock/sensor commands, and coordinate systems used in robot programming.