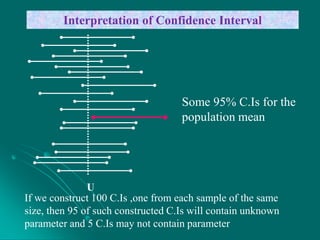
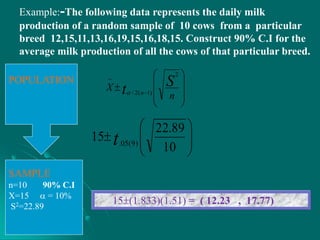
Statistical inference involves drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample. It has two main areas: estimation and hypothesis testing. Estimation uses sample data to obtain point or interval estimates of unknown population parameters. Hypothesis testing determines whether to accept or reject statements about population parameters. Confidence intervals give a range of values that are likely to contain the true population parameter, with a specified level of confidence such as 90% or 95%.