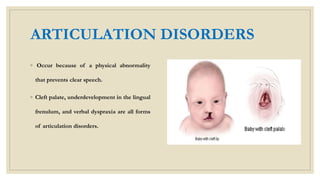
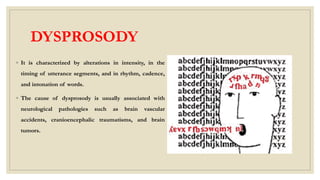
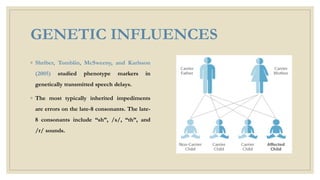
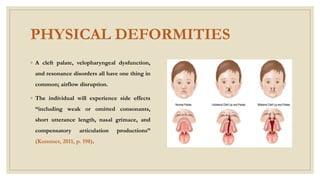
This document discusses speech disorders. It begins by defining speech disorders as problems with the actual production of sounds. It then outlines several types of speech disorders including dysfluency, articulation disorders, fluency disorders, resonance or voice disorders, apraxia, dysarthria, dysprosody, and muteness. Causes of speech disorders include genetic influences, physical deformities, and neurological malfunctions. Speech disorders can impact people's lives by affecting their social acceptance, confidence, and overall life satisfaction. The document concludes by stating that early identification and intervention can improve life for those with speech disorders.