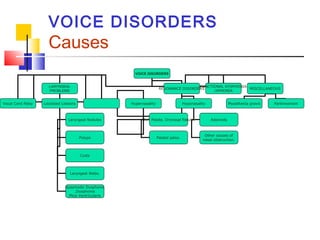
This document provides an introduction and overview of speech therapy. It defines key terms like speech therapist and speech therapy. It describes various communication disorders that speech therapists treat, including stuttering, voice disorders, language disorders, aphasia, articulation disorders, dysarthria, and dysphagia. It outlines the roles and therapeutic techniques of speech therapists for each disorder. The document emphasizes that speech therapy aims to help people with communication difficulties reach their maximum communication potential.