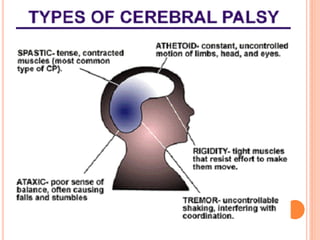
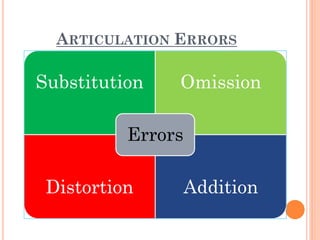
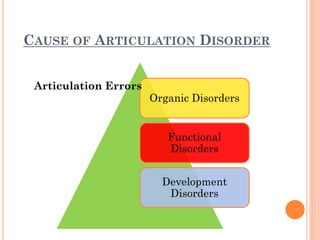
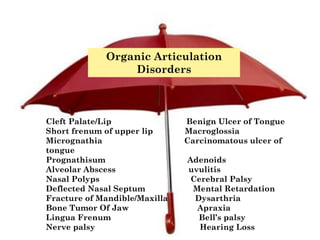
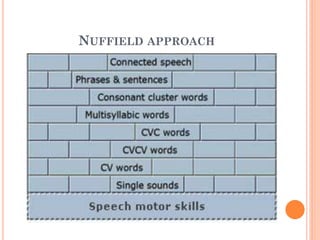
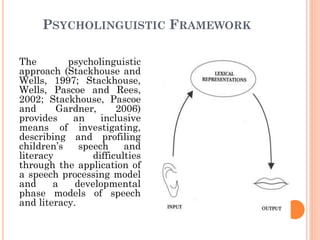
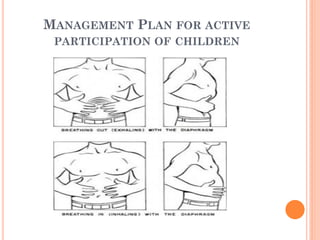
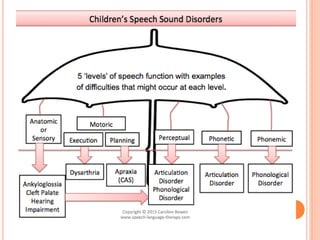
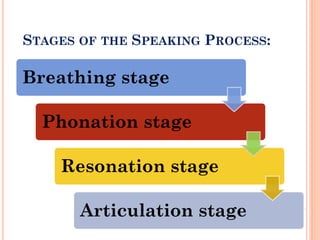
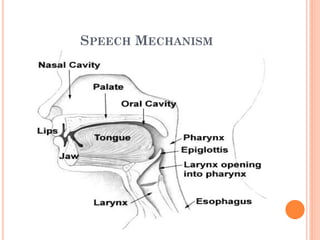
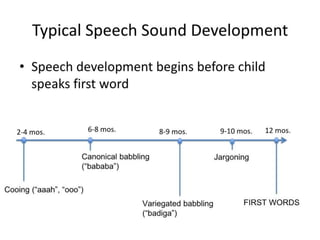
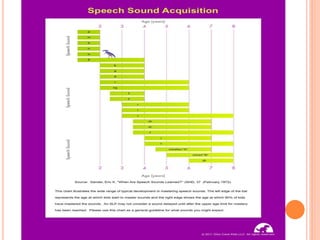
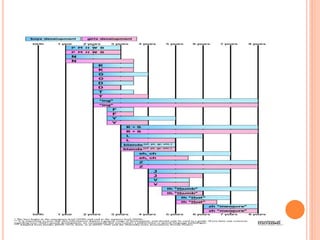
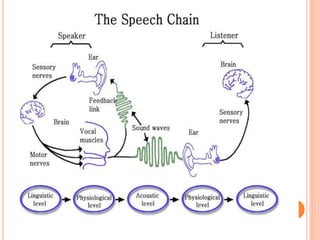
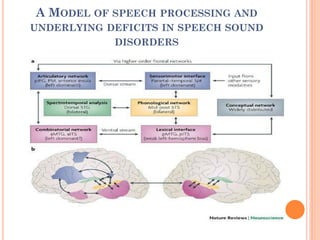
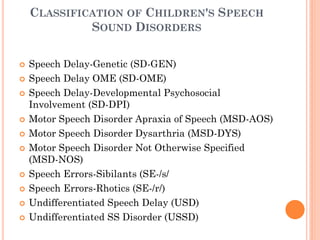
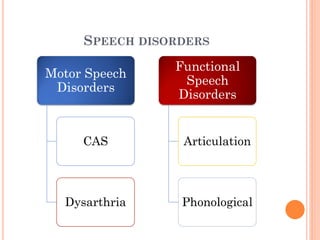
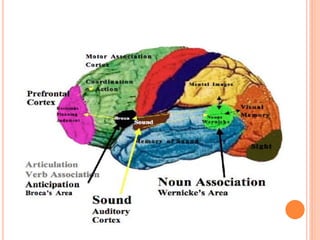
The document provides information about a workshop on speech sound disorders presented by Fouzia Saleemi. It discusses various types of speech sound disorders including articulation disorders, phonological disorders, childhood apraxia of speech, and dysarthria. It outlines the stages of the speaking process and various classification systems and intervention approaches for treating speech sound disorders in children, including core vocabulary therapy, cycles therapy, dynamic temporal and tactile cueing, and minimal pair therapies.














![HOW IS CHILDHOOD APRAXIA OF SPEECH
DIAGNOSED?
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders, 5th Edition (American Psychiatric
Association [APA], 2013) uses the term verbal
dyspraxia to describe this disorder and discusses
it within the Speech Sound Disorders category,
under the subheading, "Associated Features
Supporting Diagnosis." Verbal dyspraxia is
described in the DSM-5 as a disorder in which
"other areas of motor coordination may be
impaired as in developmental coordination
disorder."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/speechsounddisorders-160926041451/85/Speech-sound-disorders-27-320.jpg)