Embed presentation
Downloaded 133 times

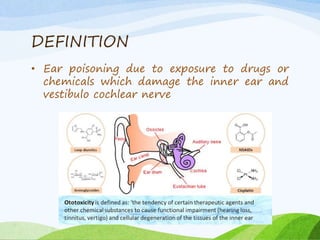





This document defines ototoxicity as ear poisoning caused by exposure to drugs or chemicals that damage the inner ear and vestibulocochlear nerve. It lists various drugs and chemicals that can cause ototoxicity, including quinine, salicylates, aminoglycosides, loop diuretics, antiepileptics, and betablockers. Signs of ototoxicity include tinnitus, imbalance, vertigo, and hearing loss. Diagnosis involves a health history, physical exam, electrocochleography, and electronystagmography. Management focuses on limiting ototoxic drugs, periodic exams, hearing aids, vestibular exercises, and treating underlying causes.





