Embed presentation
Downloaded 222 times








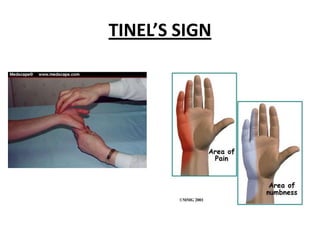
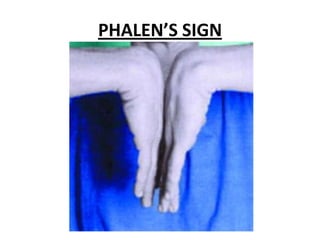






Peripheral nerve disorders are alterations in motor, sensory or autonomic peripheral nerves that can be caused by various metabolic, toxic, infectious or genetic factors. Symptoms include pain, numbness, weakness and sensory loss. Peripheral neuropathies can be classified as mononeuropathies affecting single nerves, mononeuropathies multiplex affecting multiple individual nerves, or polyneuropathies broadly affecting many nerves simultaneously. Clinical exams help identify affected nerves and patterns of injury.














