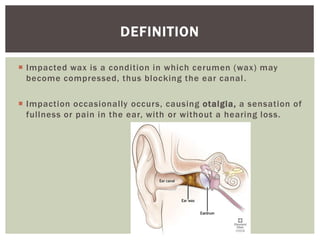
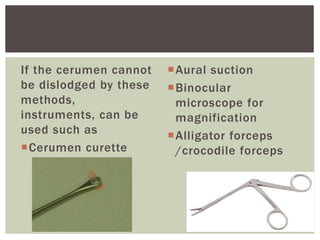
Impacted earwax occurs when earwax becomes compressed in the ear canal, blocking it. This can cause symptoms like ear pain, fullness, and hearing loss. People more prone to impacted earwax include those with hairy ear canals, who work in dusty environments, the elderly, and hearing aid users. Impacted earwax is typically treated first with ear drops to soften the wax, and then removal either on its own or with irrigation. Nursing care involves examining the ears, assessing any impaction, educating on prevention of insertion of objects in the ear, and examining high-risk groups like the elderly.