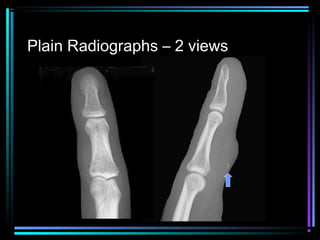
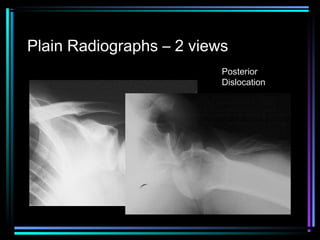
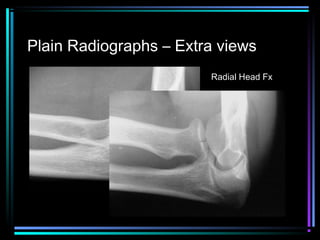
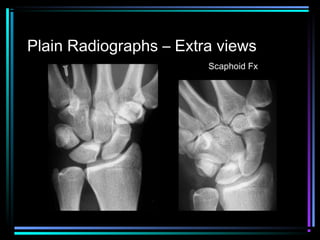
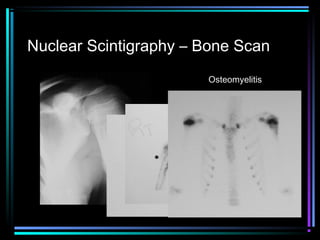
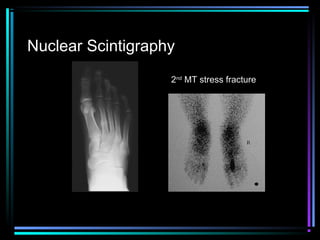
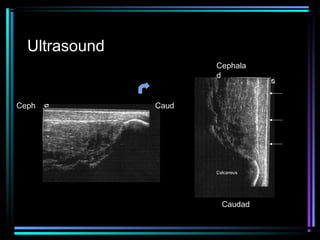
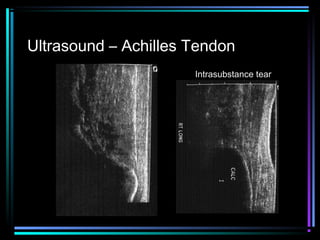
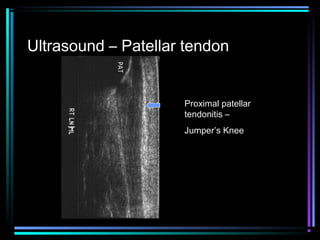
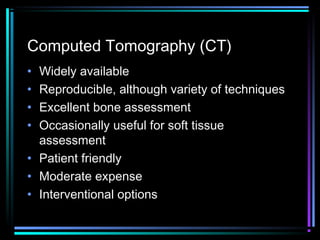
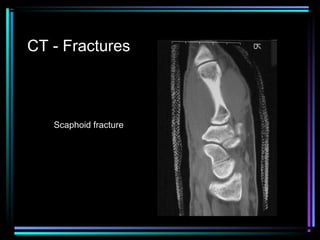
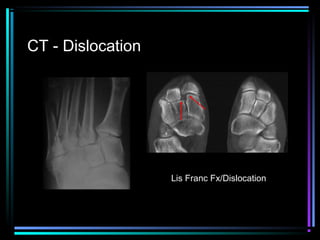
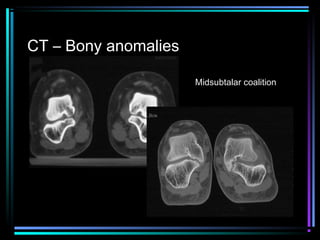
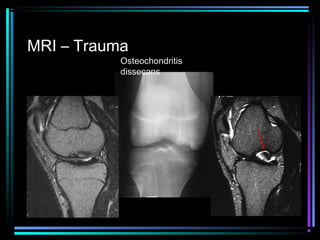
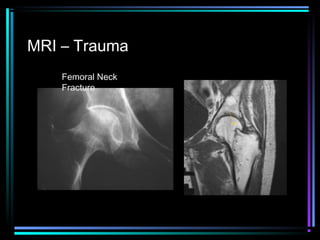
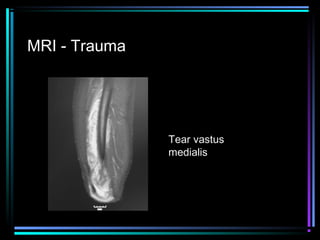
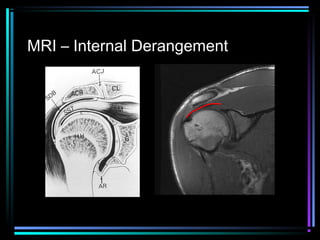
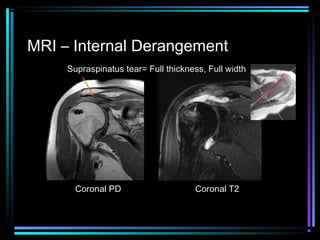
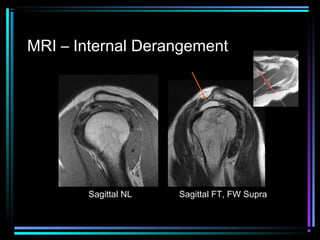
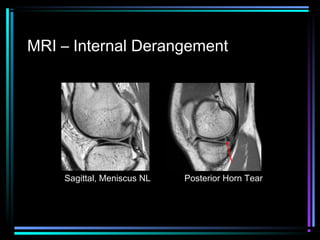
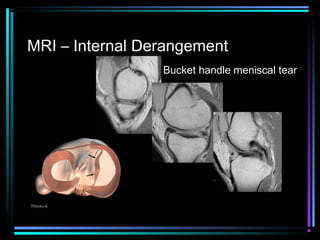
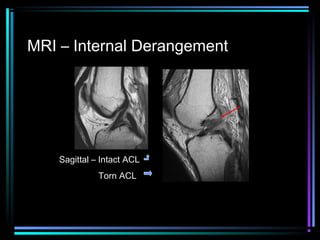
This document provides an overview of common musculoskeletal imaging modalities. It discusses plain radiography as usually the primary modality due to its wide availability, low cost, and ability to assess bone. Nuclear scintigraphy is described as sensitive for skeletal pathology but nonspecific. Ultrasound is noted to be useful for superficial soft tissues. CT is presented as excellent for bone assessment. MRI is outlined as the best modality for soft tissues but more expensive and less patient-friendly. Specific clinical examples are given to illustrate findings on each imaging type.