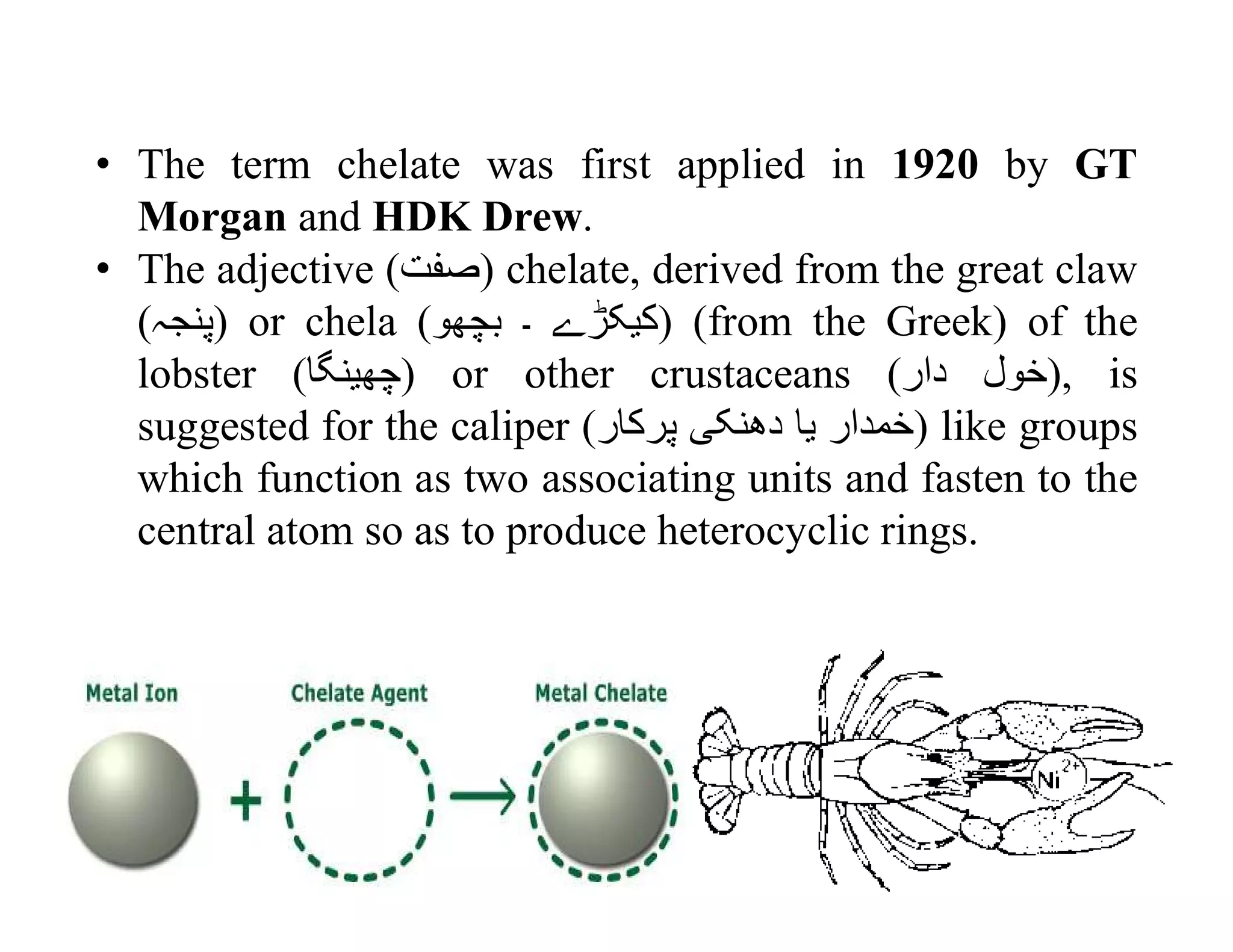
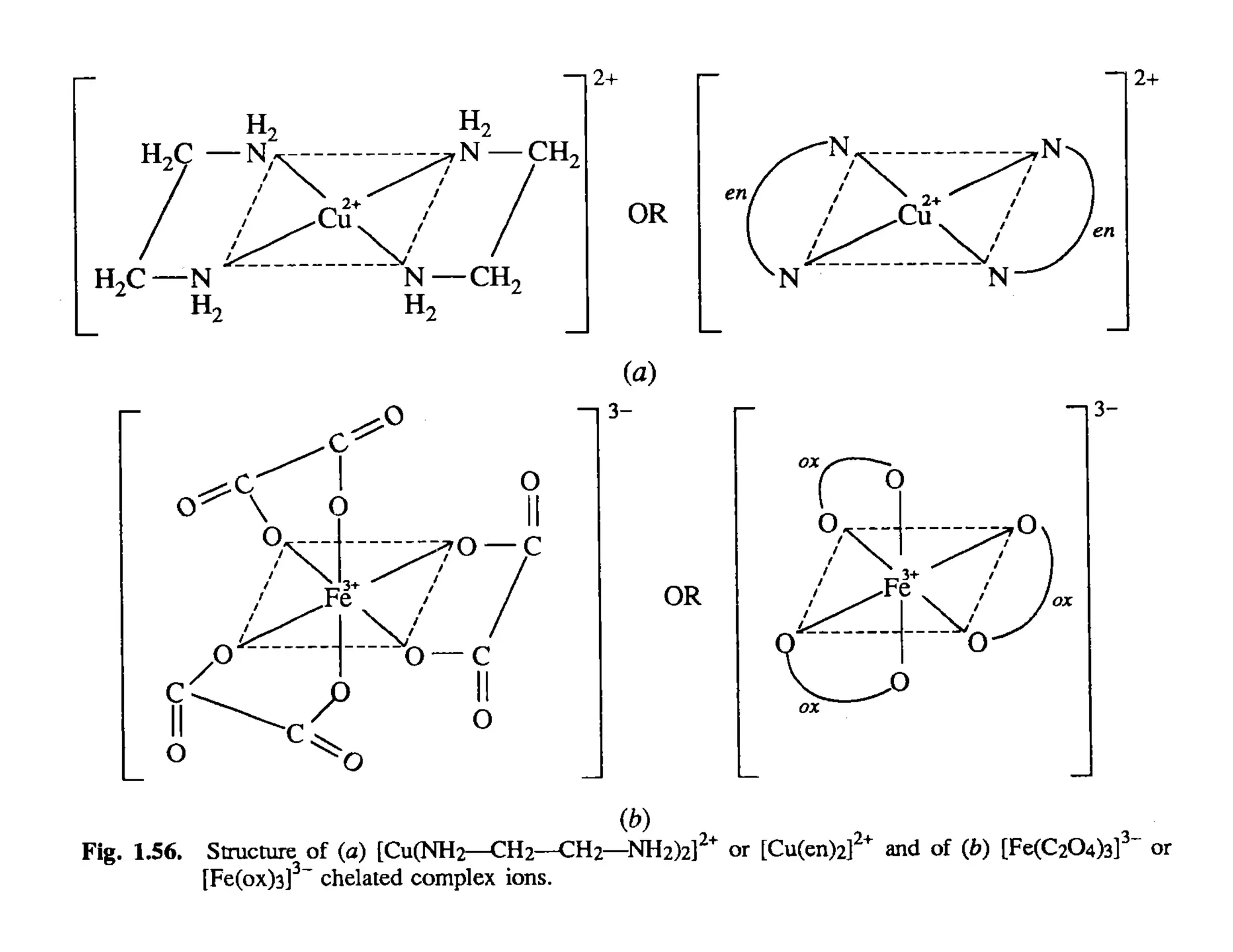
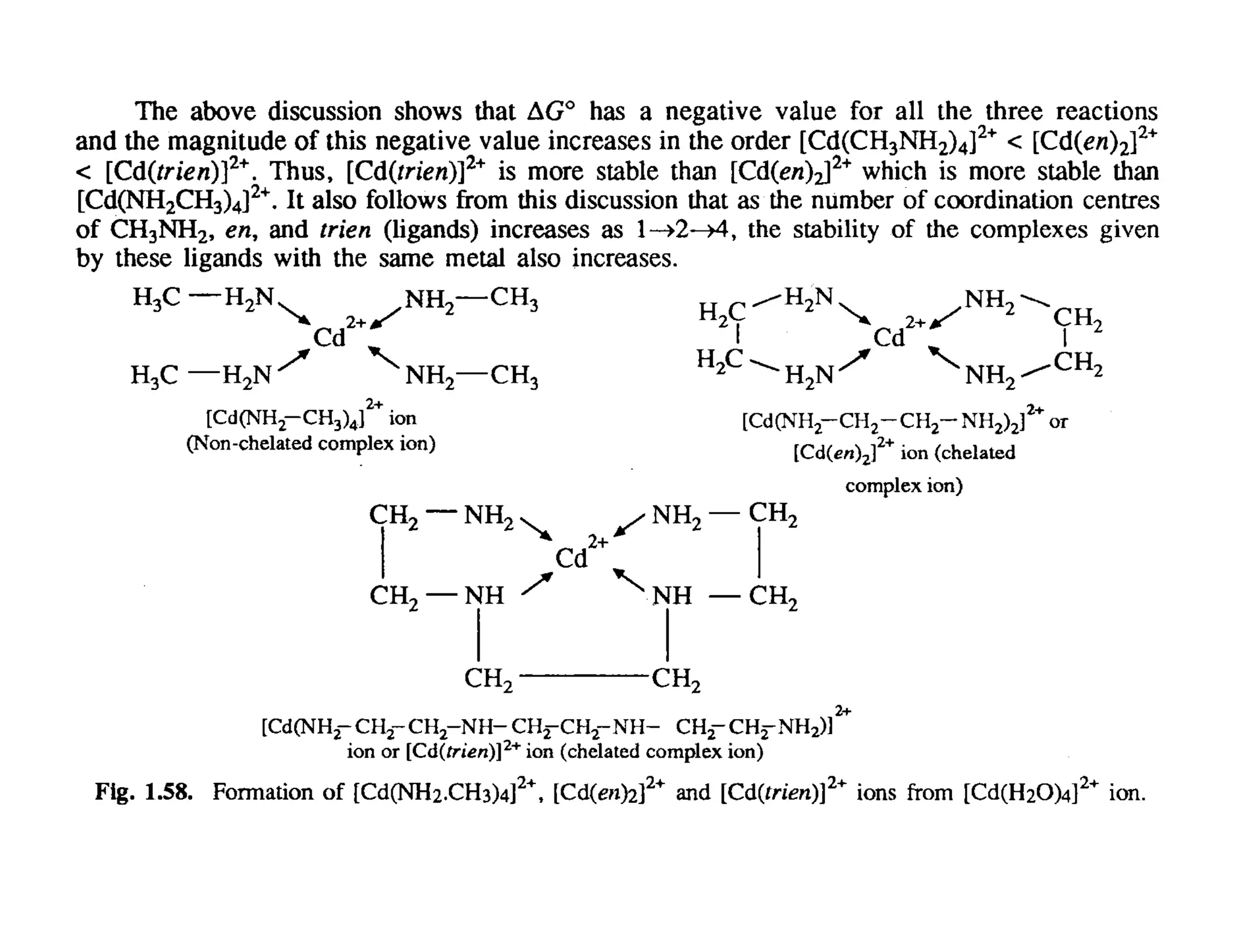
This document discusses chelates and the chelate effect. It defines chelates as coordination complexes containing ligands bonded to a central metal atom at two or more points, forming ring structures. The chelate effect refers to chelated complexes being more stable than similar non-chelated complexes due to an increase in entropy. Factors that influence the stability of chelated complexes include the number of donor atoms in the ligand, the size of the metal-ligand rings formed, and the presence of double bonds in the ligand.



![• For example, in the complex ion, [Fe(CN)6]3- the six (CN-) ions
are the ligands.
• In most of complexes a ligand acts as a donor partner, i.e., donates
one (or more) electron pair to the central metal.
• Note that in metallic carbonyls the ligand viz CO molecule acts
both as donor and acceptor (M CO).
Substrate
• A substrate may be defined as the reactant in which some bonds
are broken and some new ones are formed as a result of the attack
of a reagent.
Substrate Product
Attacking reagent Attacking reagent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-201213030949/75/Chelates-and-chelate-effect-4-2048.jpg)





![Chelate effect (Stability of chelates)
• Chelates are more stable than similar non-chelated complexes of the same
metal ion.
• Greater stability of chelated complex means that there will be smaller
dissociation of the chelated complex into its components in a particular
solvent.
• The enhanced stability conferred on a chelate is called chelate effect.
• The greater stability of a chelated complex as compared to that of a non-
chelated complex is due to the increase in entropy.
• Thus when we consider the formation of [Co(NH3)6]2+ (non-chelated
complex) and [Co(en)3]2+ (chelated complex) from [Co(H2O)6]2+ as
represented by reactions (a) and (b) given below:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-201213030949/75/Chelates-and-chelate-effect-13-2048.jpg)
![• We find that number of particles on the right hand side of reaction
(b) which represents the formation of chelated complex is greater
than that on the left hand side while the number of particles on both
sides of reaction (a) representing the formation of non-chelated
complex is the same.
• Consequently the chelated complex, [Co(en)3]2+ is more stable than
the non-chelated complex, [Co(NH3)6]2+.
• The stability of chelated complexes increases with the increase of
the number of donor atoms present in the chelating ligand.
• The stability of chelated complexes also depends on the size of the
ring formed in the complex.
• The chelated complexes containing 4-membered rings are not stable
while those containing 5- and 6-membered ring are quite stable.
• A chelated complex given by a polydentate ligand containing
double bonds is more stable than that given by a polydentate ligand
containing only single bonds.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-201213030949/75/Chelates-and-chelate-effect-14-2048.jpg)
![• For example an octahedral complex of acetylacetonato ligand,
is more stable than the octahedral complex of ethylenediamine with
the same metal ion, [M2+(NH2—CH2—CH2—NH2)3]2+.
• Note that both the complexes are chelated complexes.
• With the increase of the number of the rings present in the chelated
complex, the complex becomes more stable.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8-201213030949/75/Chelates-and-chelate-effect-15-2048.jpg)