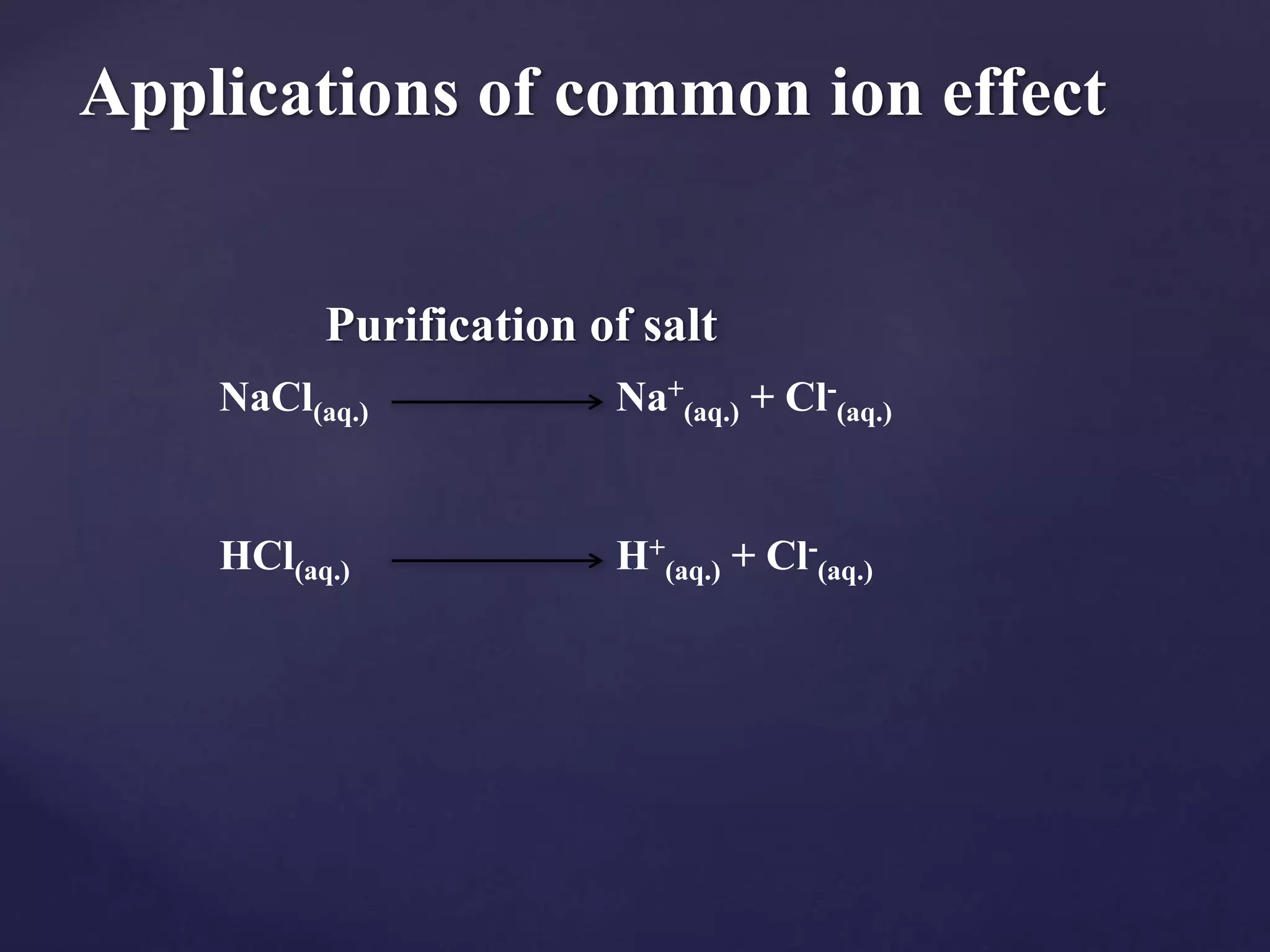
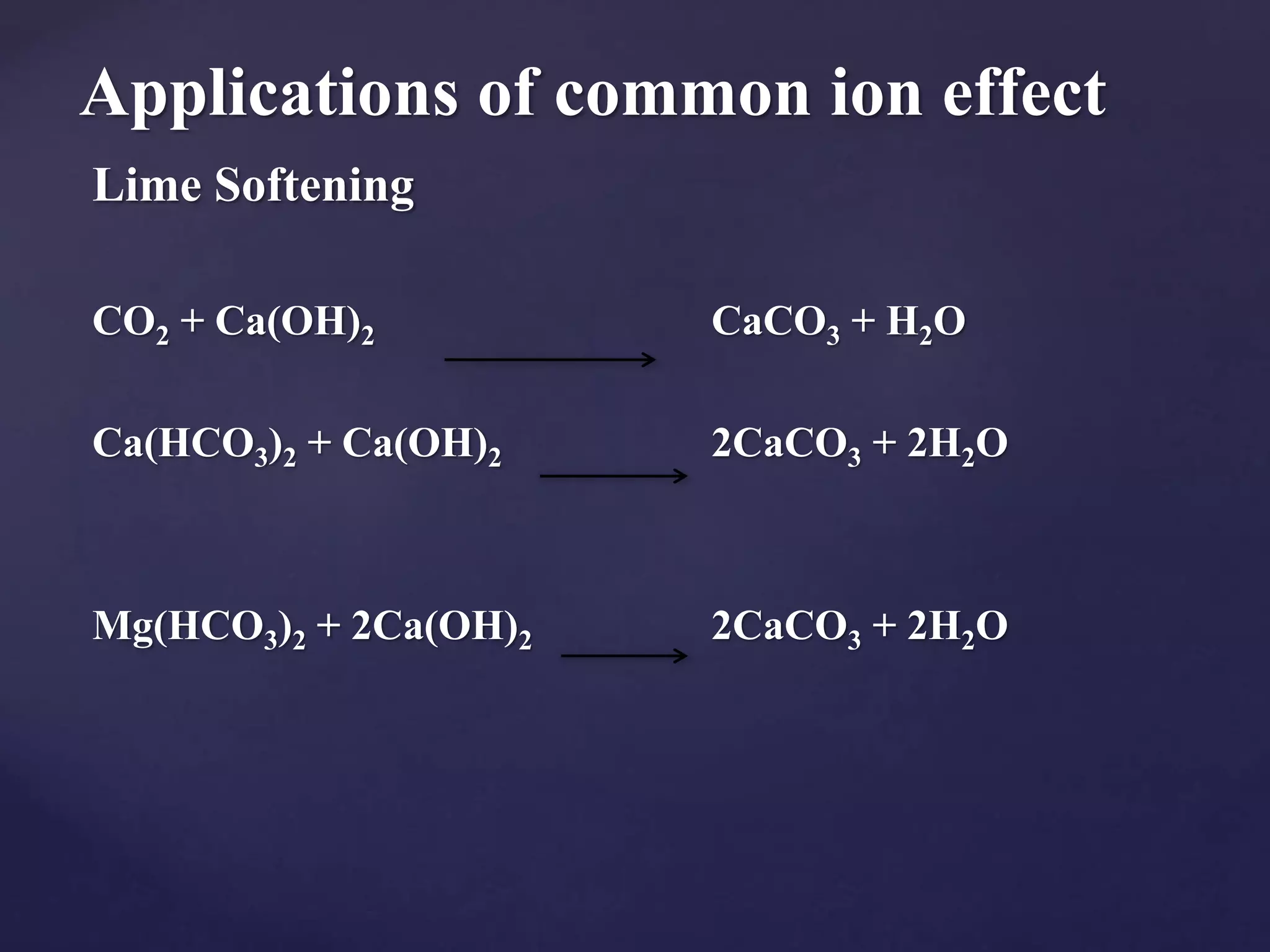
The document discusses the common ion effect, which is the reduction of salt dissociation due to the addition of a common ion, illustrated through examples such as silver chloride and barium iodate. It explains how solubility equilibria and the solubility product constant (Ksp) are affected by this phenomenon in various chemical contexts, including weak acids and bases. Additionally, it outlines practical applications of the common ion effect, such as in the purification of salts and the 'salting out' of soaps.




![Example
Dissociation of hydrogen sulphide in presence of
hydrochloric acid
H2S 2H+ + S2-
By applying the law of mass action, we have
Ka = [H+]2 [S2-]/ [H2S]
To the above solution of H2S , if we add hydrochloric acid,
then it ionizes completely as
HCl H+ + Cl-
common ion effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonioneffect-230811105858-83ffd6ac/75/COMMON-ION-EFFECT-5-2048.jpg)

![Solubility equilibria and solubility product
According to law of mass action
K= [Ag+] [Cl–] / [AgCl]
The amount of Ag Cl in contact
with saturated solution does
not change with time and the
factor [Ag Cl] remains the same.
common ion effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonioneffect-230811105858-83ffd6ac/75/COMMON-ION-EFFECT-7-2048.jpg)
![Solubility equilibria and solubility product
As [AgCl] is constant so
equilibrium expression is
Ksp= [Ag+] [Cl–]
where
[Ag+] and [Cl– ] are expressed in mol/L
The equilibrium constant in the new context is called the solubility
product constant (or simply the solubility product) and is denoted by
Ksp.
common ion effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonioneffect-230811105858-83ffd6ac/75/COMMON-ION-EFFECT-8-2048.jpg)
![Solubility of barium iodate in presence of barium
nitrate
Barium iodate, Ba(IO3)2, has a solubility product
Ksp = [Ba2+][IO3
-]2 = 1.57 x 10-9
Its solubility in pure water is 7.32 x 10-4 M.
common ion effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonioneffect-230811105858-83ffd6ac/75/COMMON-ION-EFFECT-9-2048.jpg)




![Common ion effect on solubility
Example
AgCl(s) Ag+ + Cl–
If S be the solubility of AgCl, we have
Ksp = [S mol/l Ag+] [S mol/l Cl–]
Suppose 0.25 mol/L excess of HCl is added to the solution.
Then ion product (Q) will be
Q = [S mol/l Ag+] [(S + 0.25) mol/l Cl– ]
If Q > Ksp Precipitation
If Q = Ksp Saturated solution
If Q < Ksp No precipitation
Applications of common ion effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/commonioneffect-230811105858-83ffd6ac/75/COMMON-ION-EFFECT-14-2048.jpg)