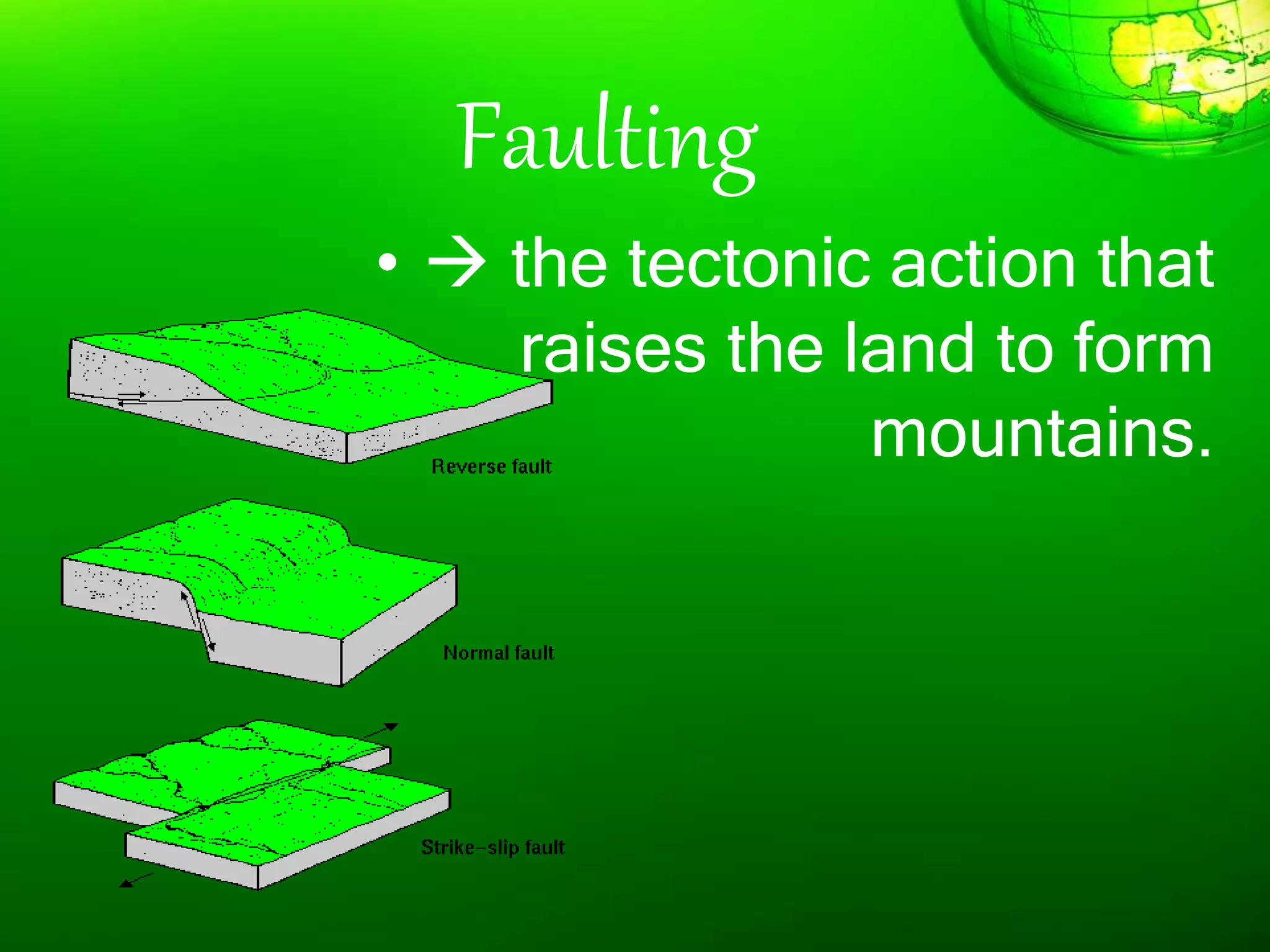
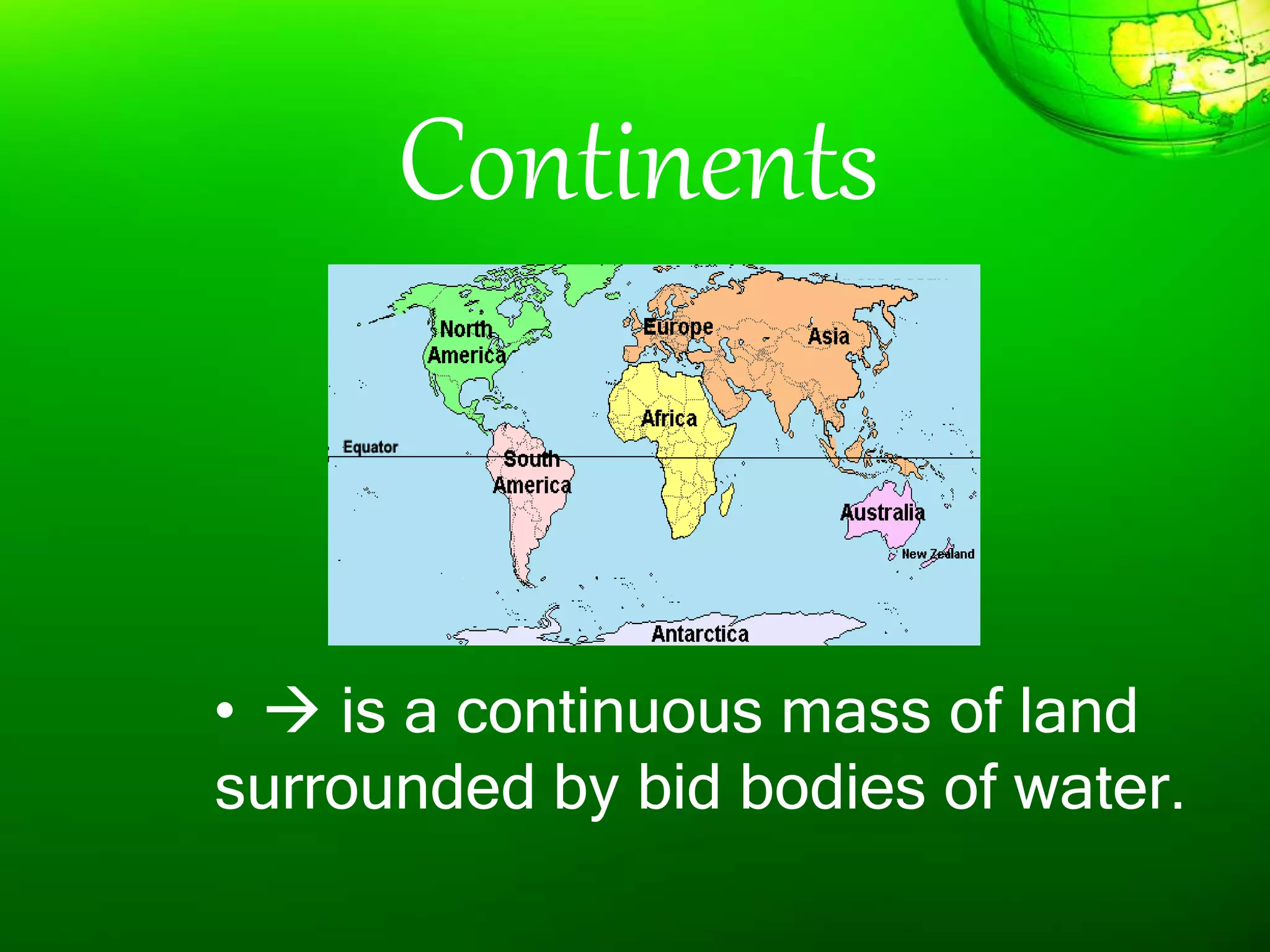
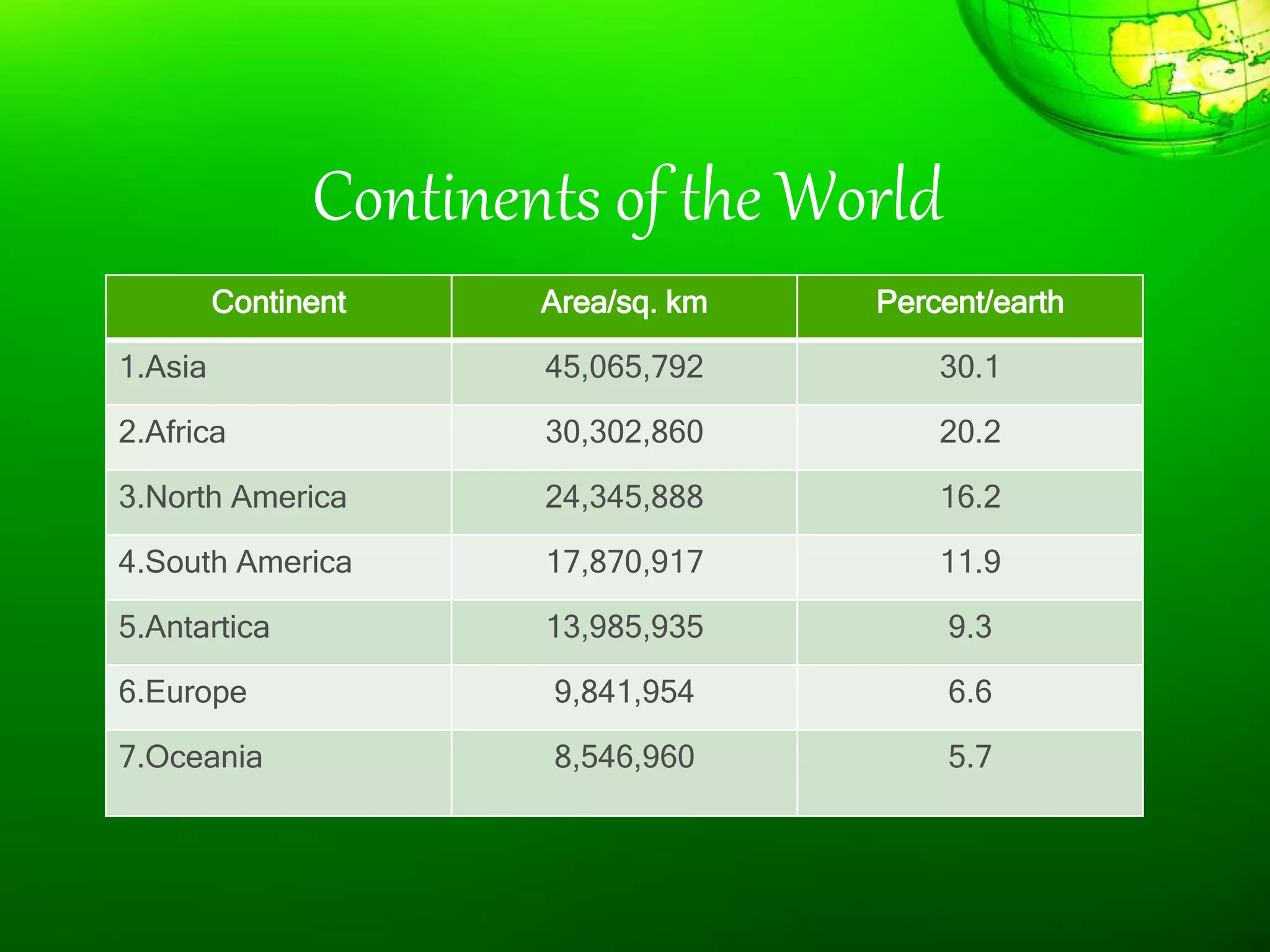
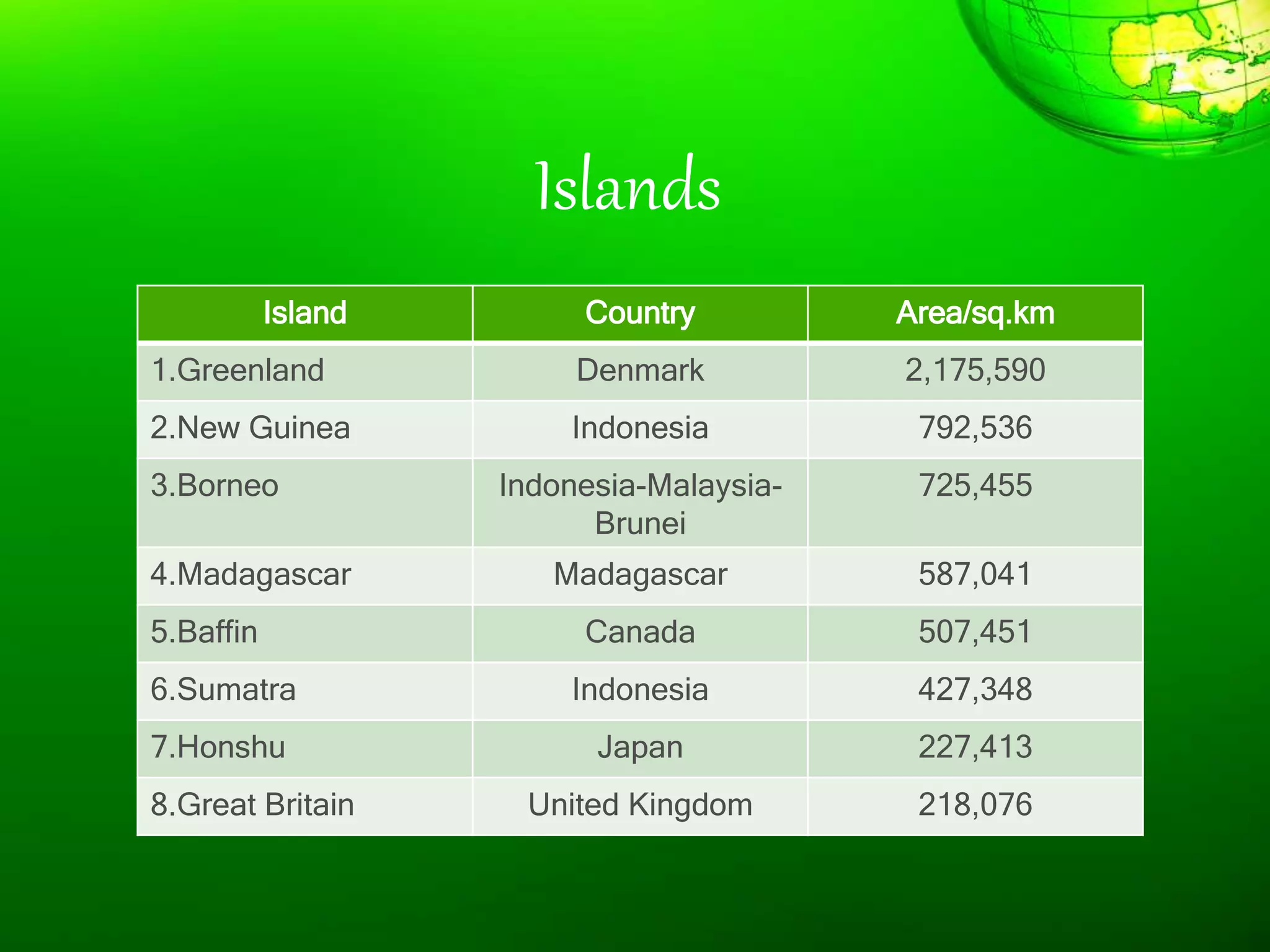
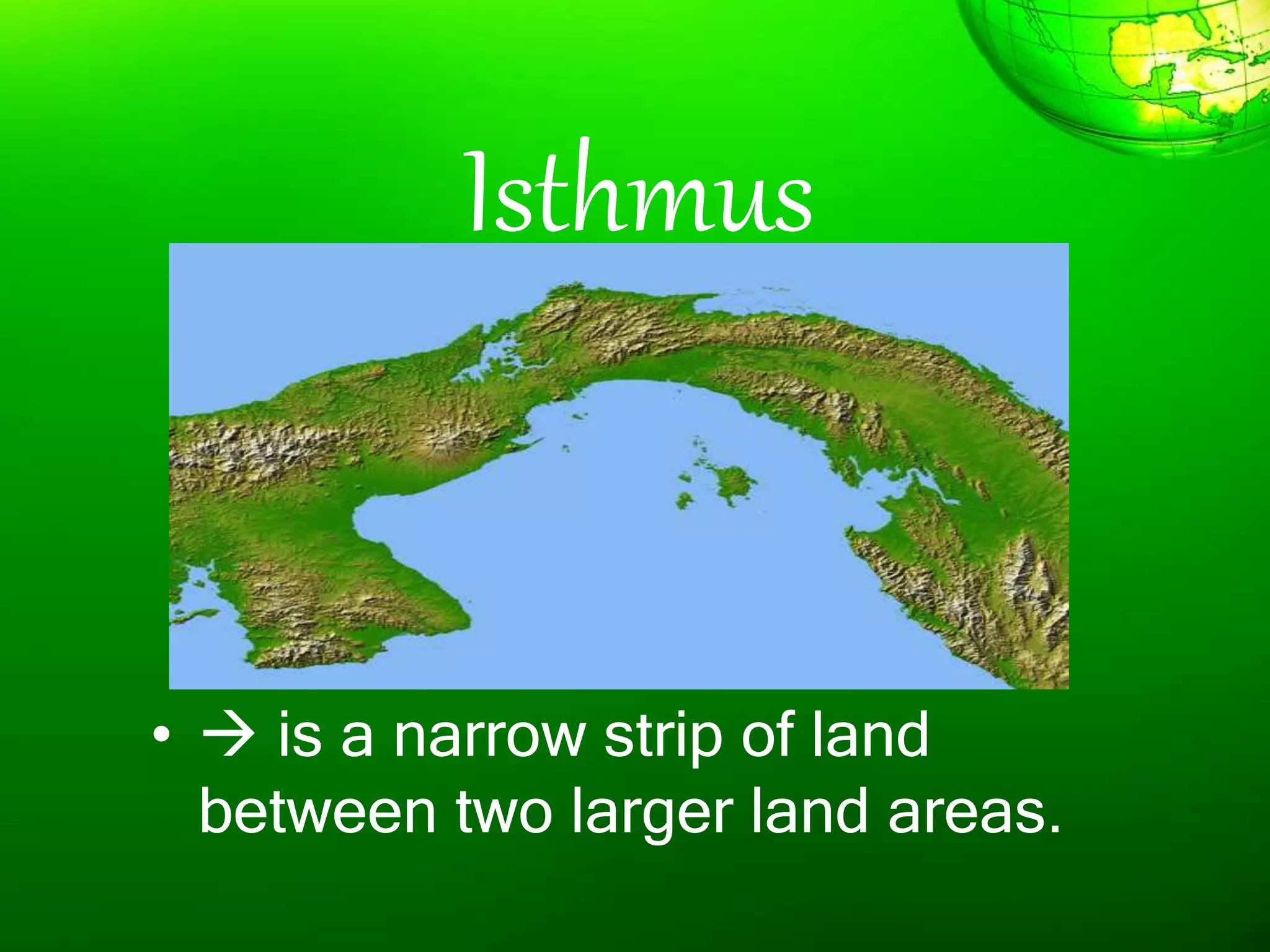
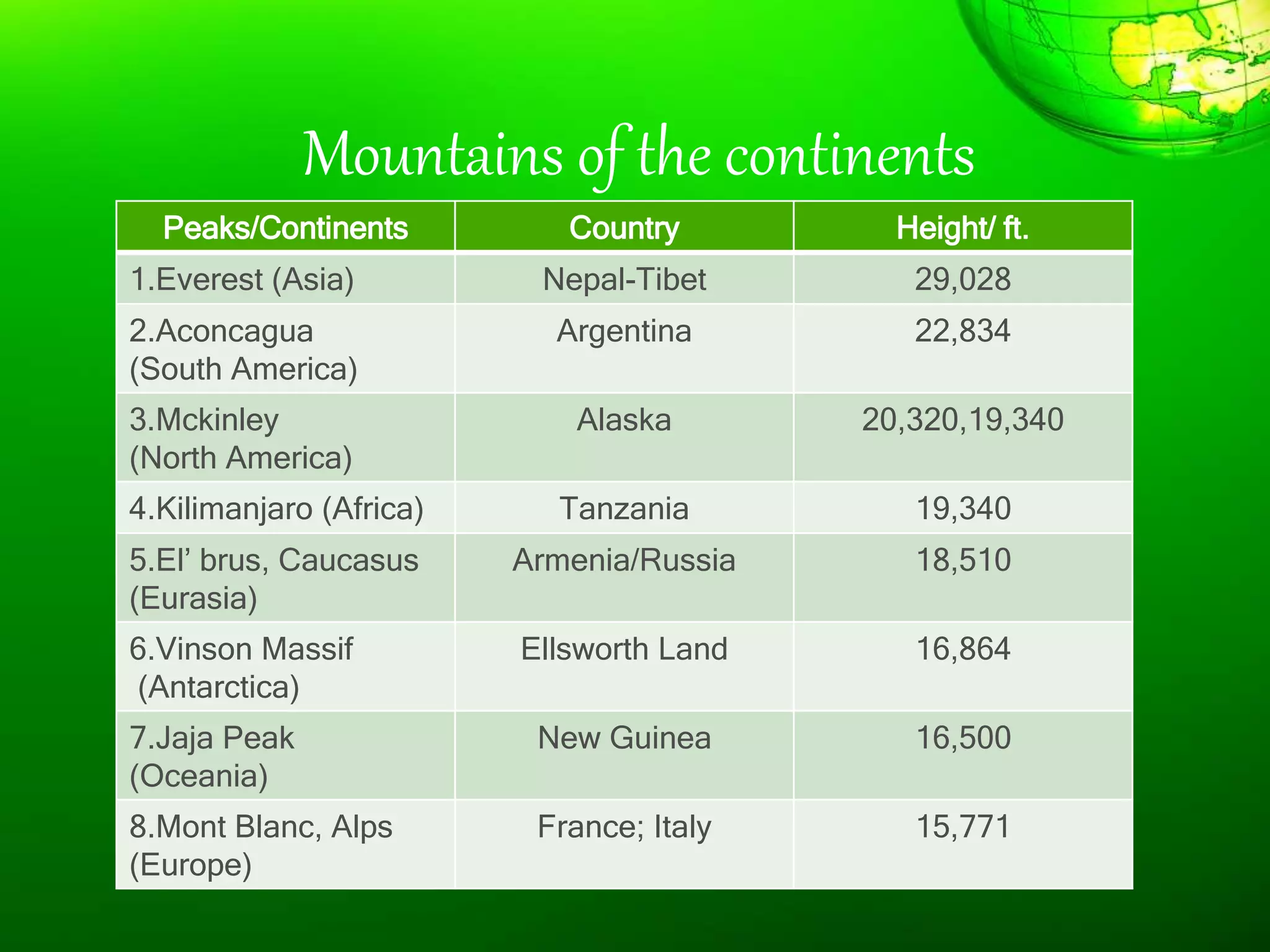
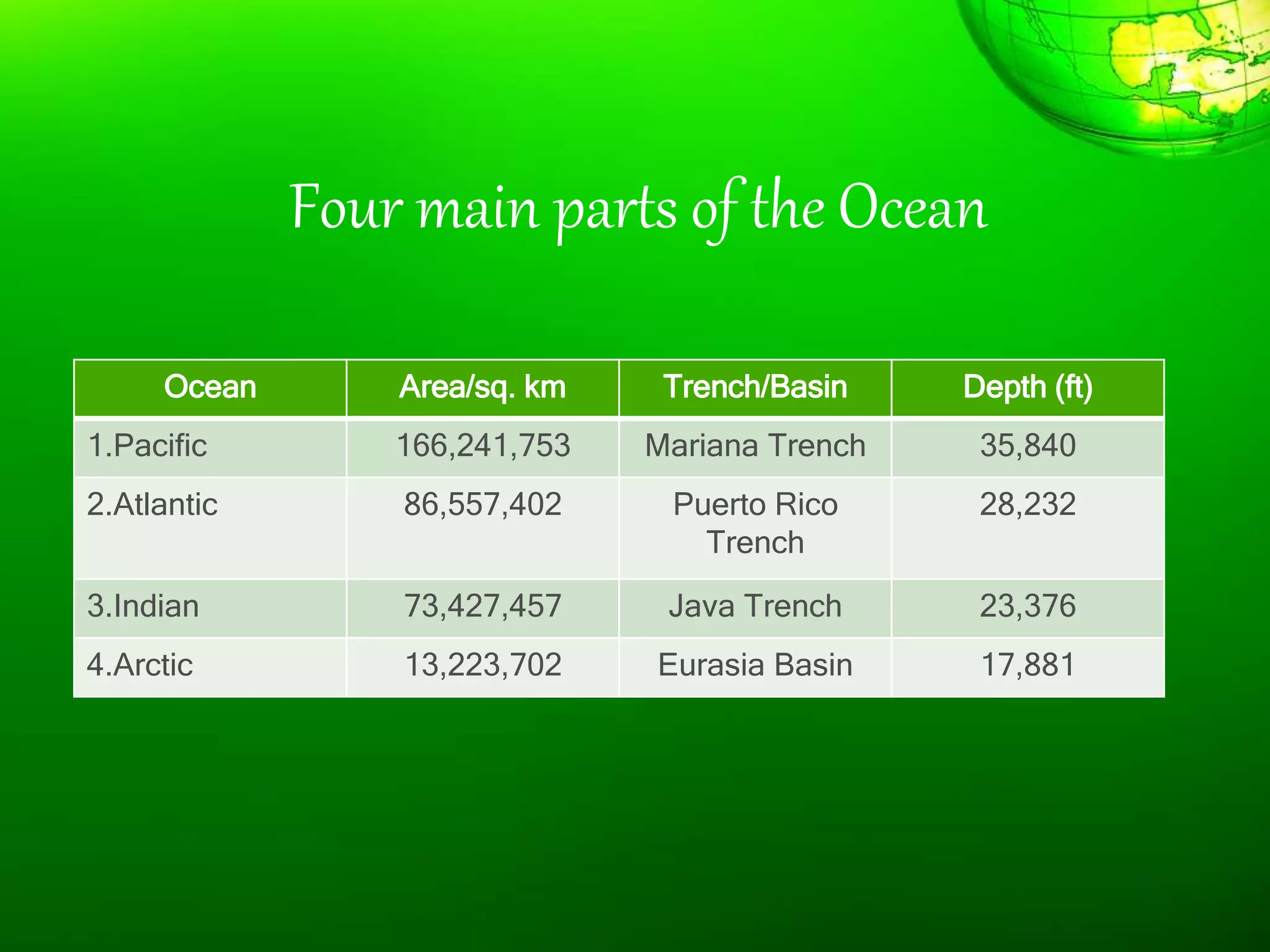
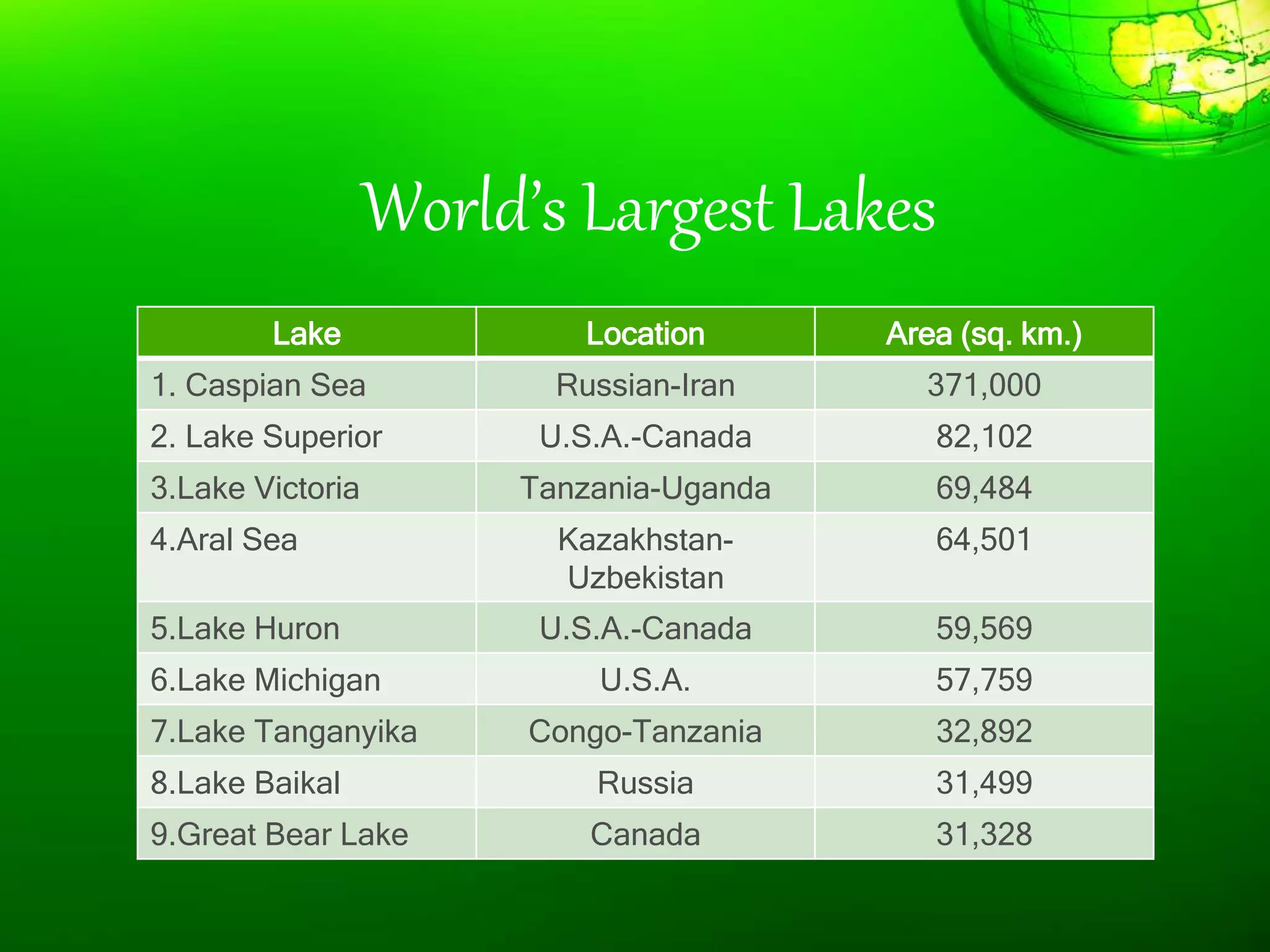
1. The document discusses different types of landforms and water bodies found on Earth including continents, islands, peninsulas, isthmus, capes, mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, lakes, seas, gulfs, bays, straits, canals, and glaciers.
2. It also describes the theory of plate tectonics which proposes that continents were once joined together and have since drifted apart.
3. Forces such as erosion, deposition, and plate tectonics shape the Earth's surface over millions of years and produce the variety of landforms and bodies of water present today.