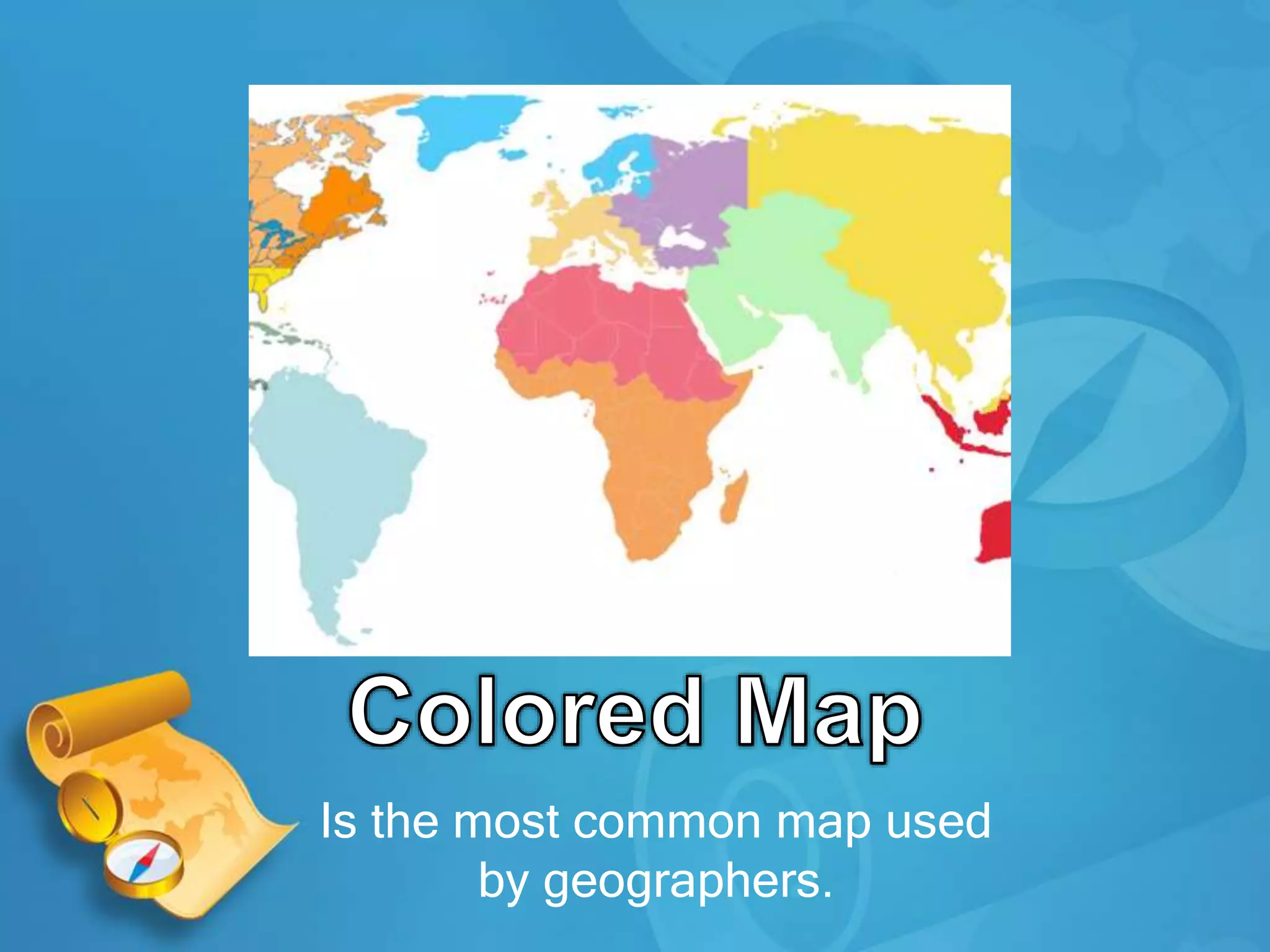
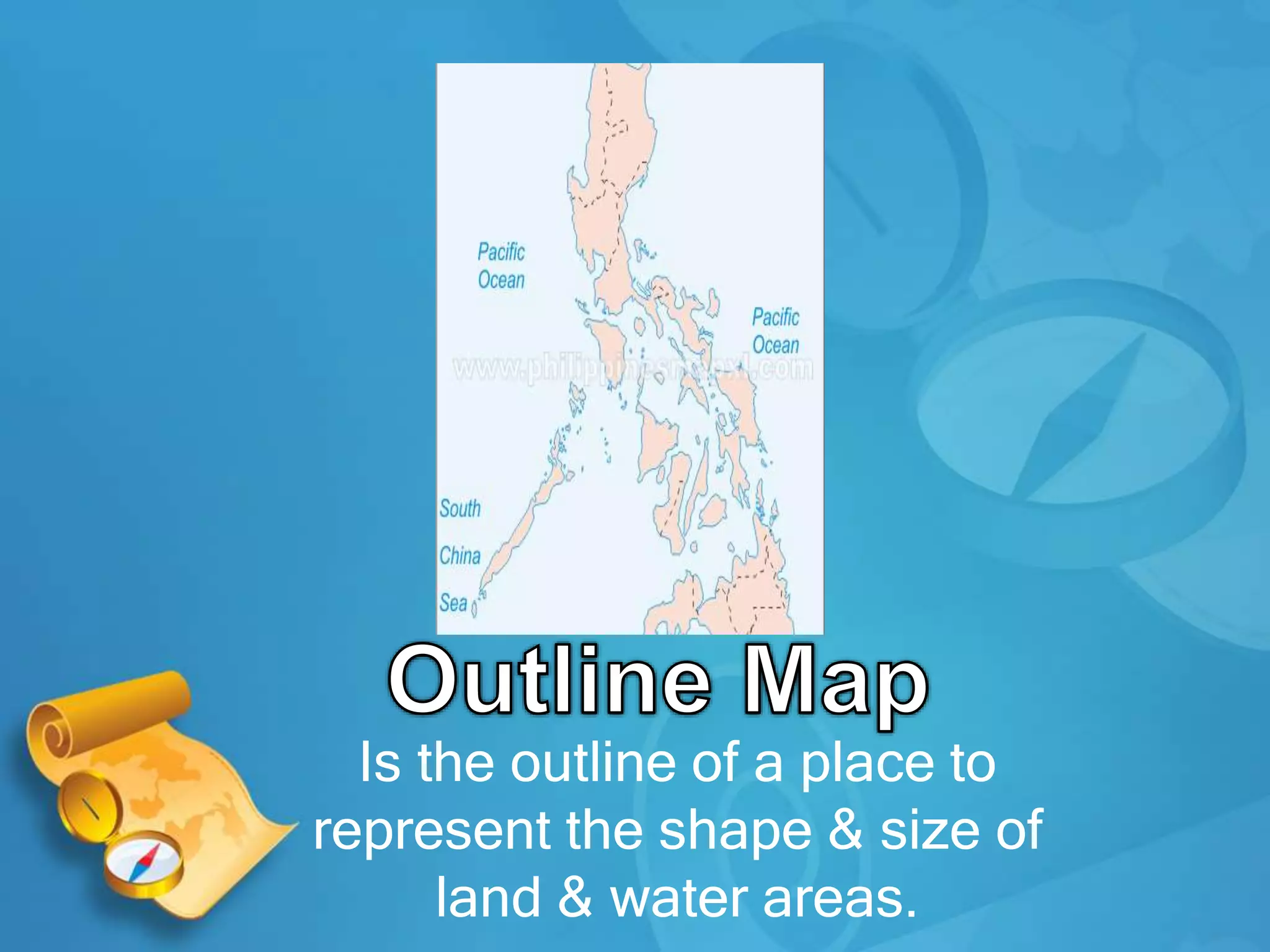
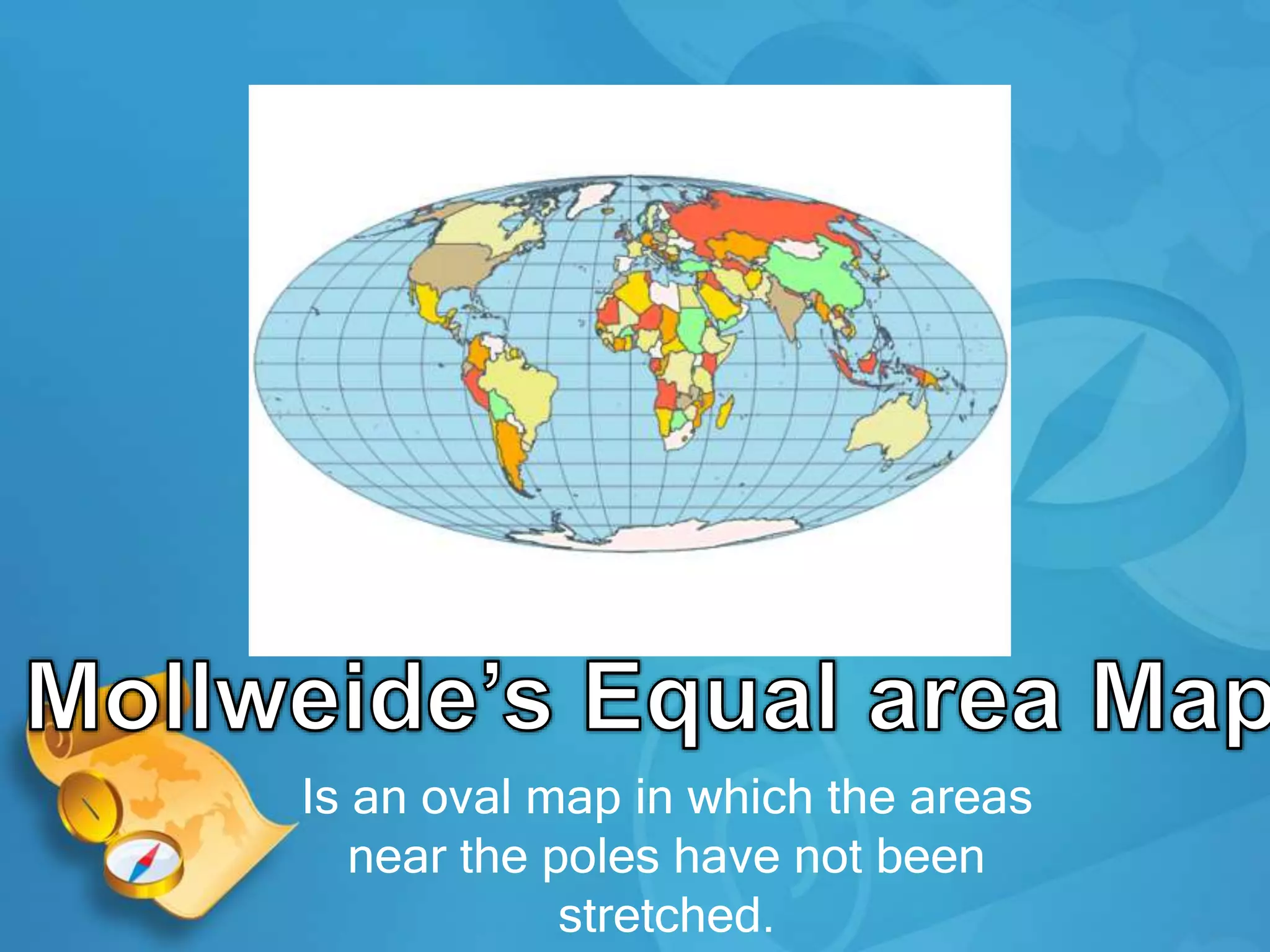
This document provides definitions and descriptions of key geographic concepts:
- Maps are representations of the Earth's surface and come in many forms, such as physical maps, globe maps, and political maps. The most common map used by geographers is the azimuthal equidistant projection map.
- Weather describes current atmospheric conditions in a place at a given time, while climate refers to long-term weather patterns over many years in an area. Key weather events include equinoxes and solstices.
- The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface, through processes like evaporation, transpiration, condensation, and precipitation.
- Major climate types include tropical